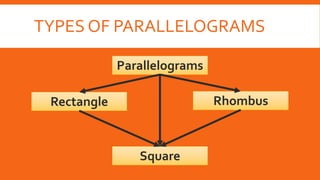
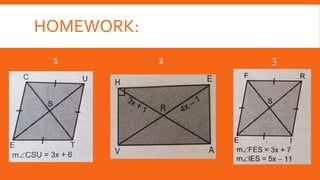
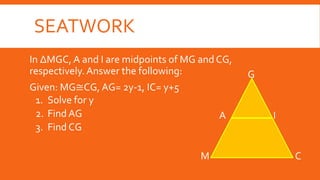
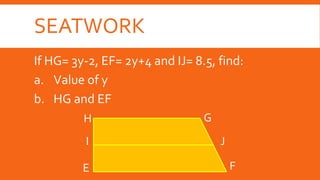
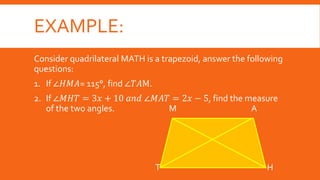
This document defines and describes types of quadrilaterals including parallelograms, trapezoids, kites, rectangles, rhombuses, and squares. It provides properties and theorems for each shape and examples to solve problems involving midlines, midsegments, isosceles trapezoids, and kites. Seatwork and homework problems are also presented.