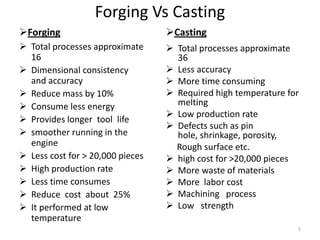
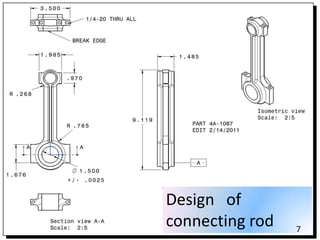
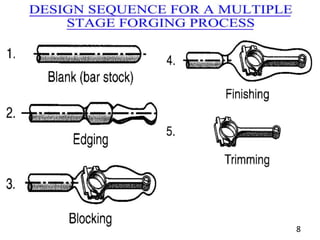
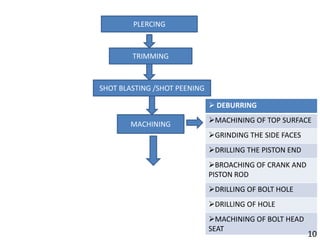
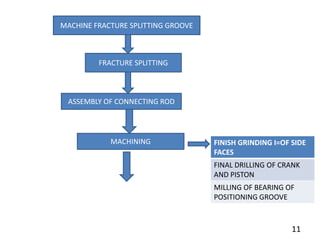
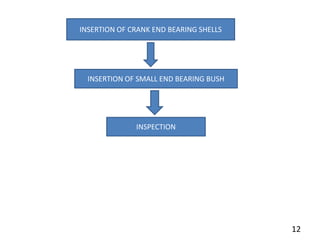
Group 3's presentation discusses the manufacturing of connecting rods. It compares the forging and casting processes, outlining the advantages of forging such as higher dimensional accuracy, lower costs for high production volumes, and smoother engine running. The presentation then details the specific forging and machining steps used to manufacture connecting rods, including heating, piercing, trimming, shot peening, fracturing, assembly, and inspection. Limitations discussed include the need for an environmentally friendly process and cost-effective finished product with limited mass deviation. Forging is considered more economical than casting for production volumes above 20,000 pieces.