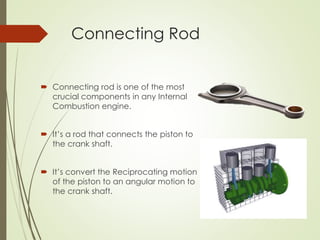
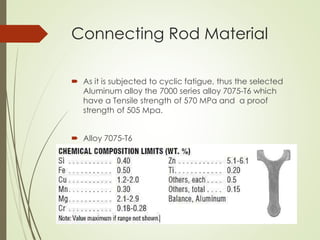
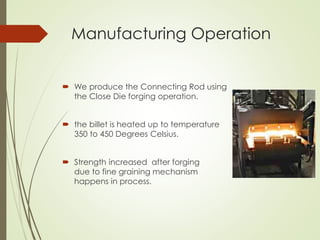
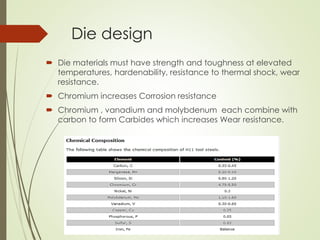
The document discusses the significance of aluminum, particularly the 7000 series alloy 7075-T6, in forging operations for producing durable components like connecting rods used in internal combustion engines. It highlights the advantages of forging over casting and machining, emphasizing the stresses on connecting rods and the importance of selecting appropriate die materials for manufacturing. The text concludes with a summary of aluminum's applications and the critical factors influencing the forging process.