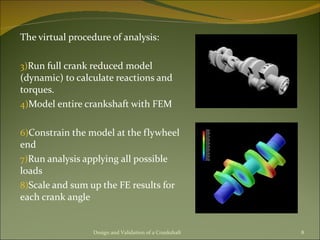
The document discusses the design and validation process for a crankshaft. It begins with an overview of crankshafts and their function in converting linear piston motion to rotational motion in engines. It then outlines the 5 main steps in the design and validation process: 1) conceptual design, 2) process analysis and selection, 3) testing, 4) production, and 5) quality improvement. Key aspects of each step like dimensions, stresses, fatigue testing, and hardening processes are covered. The goal is to take an initial design concept and improve it using analysis, testing, manufacturing, and standards to validate the design.