This document contains notes and materials for a Math 9 class covering quadratic functions for the 6th week of the 1st quarter. It includes:
1. A math prayer to work problems and trust in God's help.
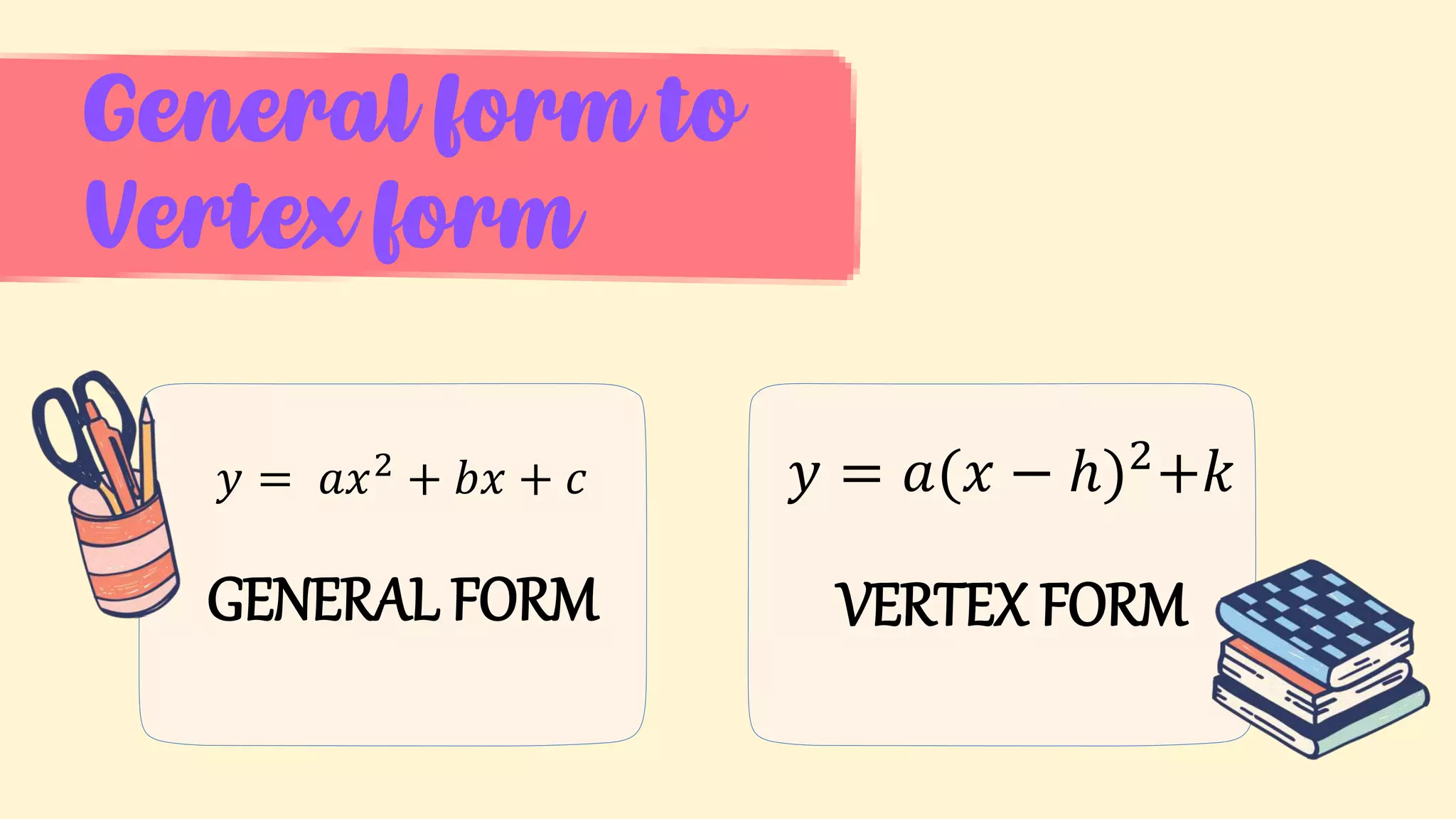
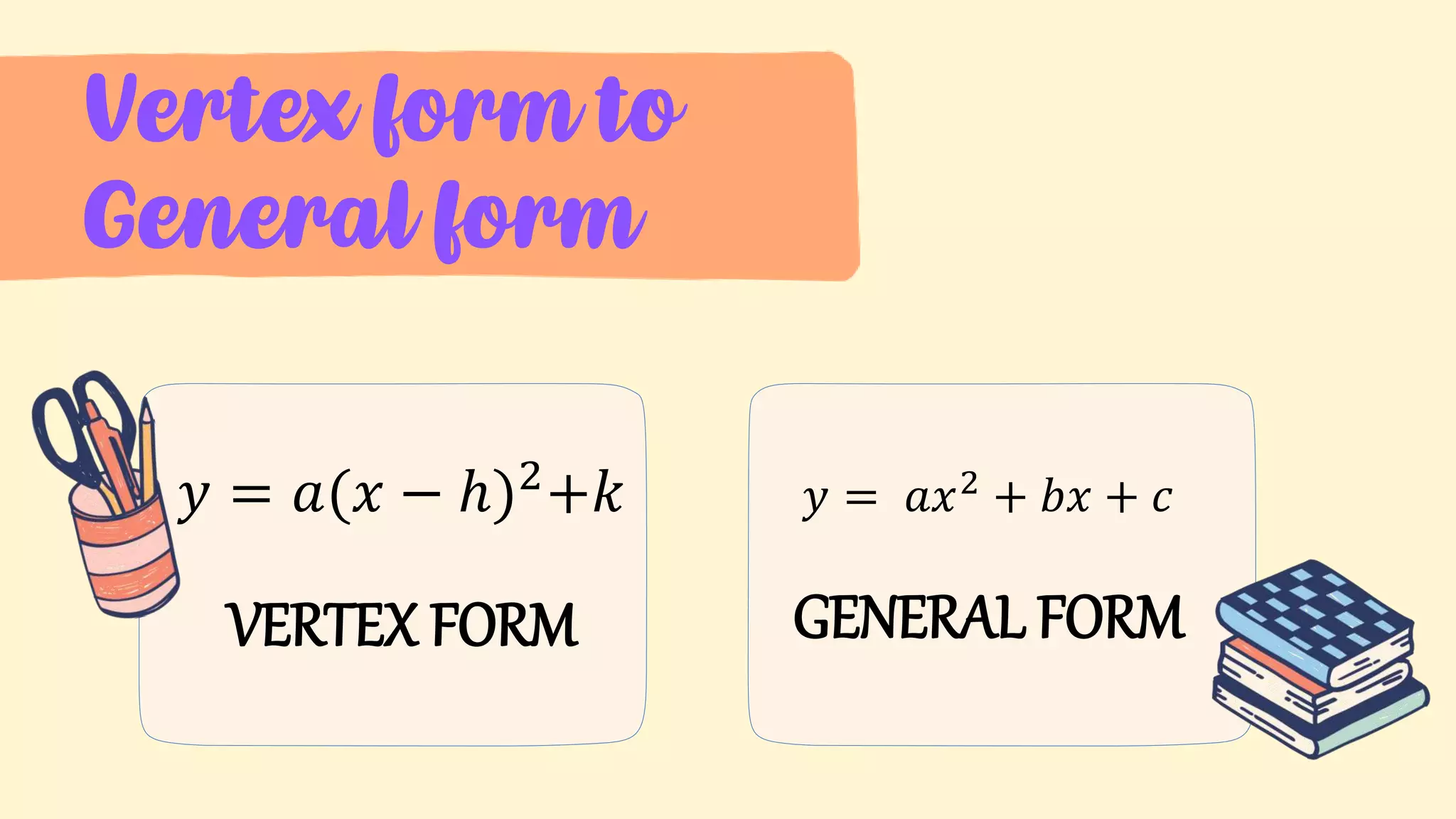
2. An overview of topics to be covered: illustrating quadratic functions, transforming between general and vertex forms, and determining parts of quadratic graphs.
3. A review question asking students to identify which situation represents a quadratic function.
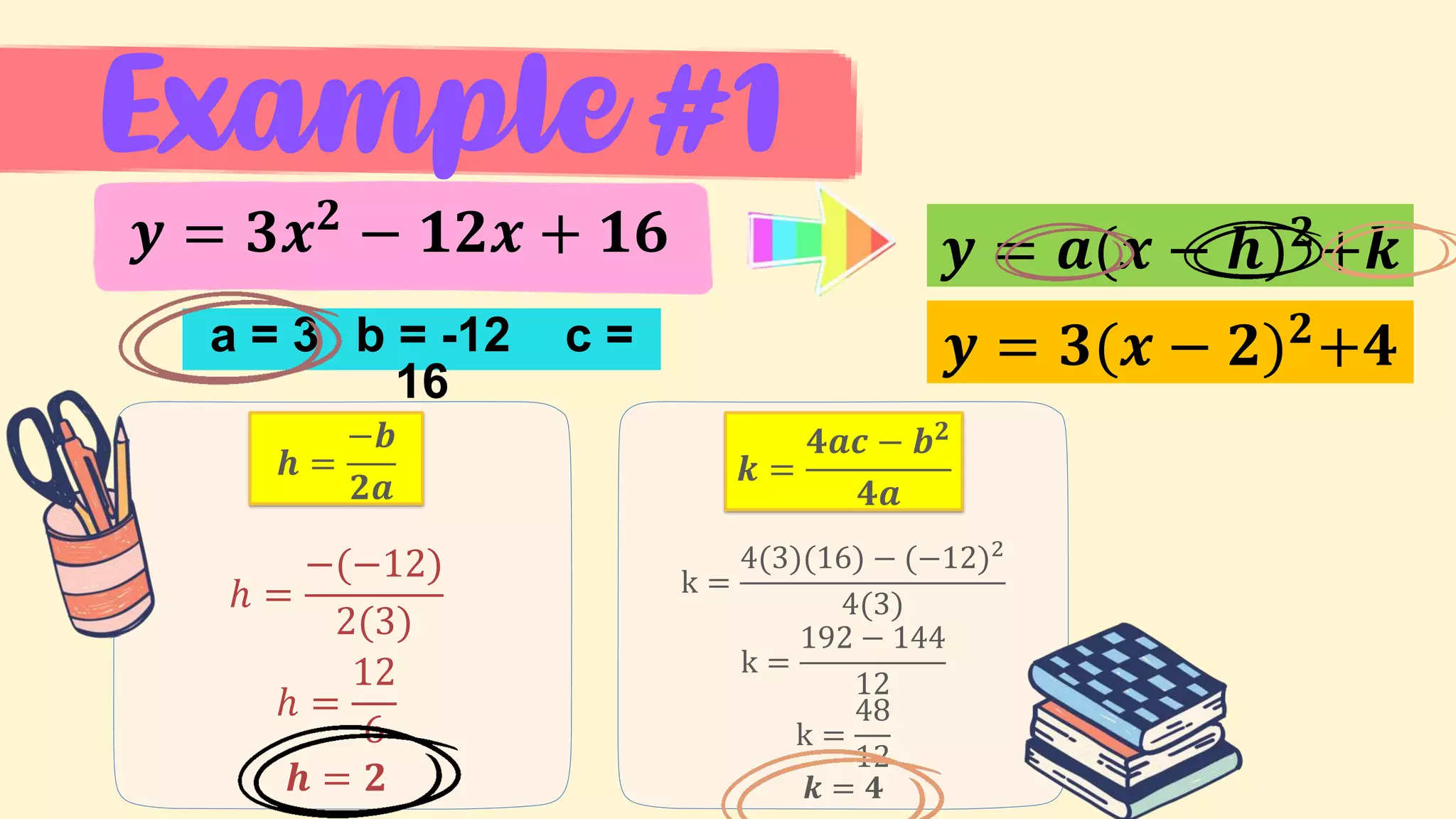
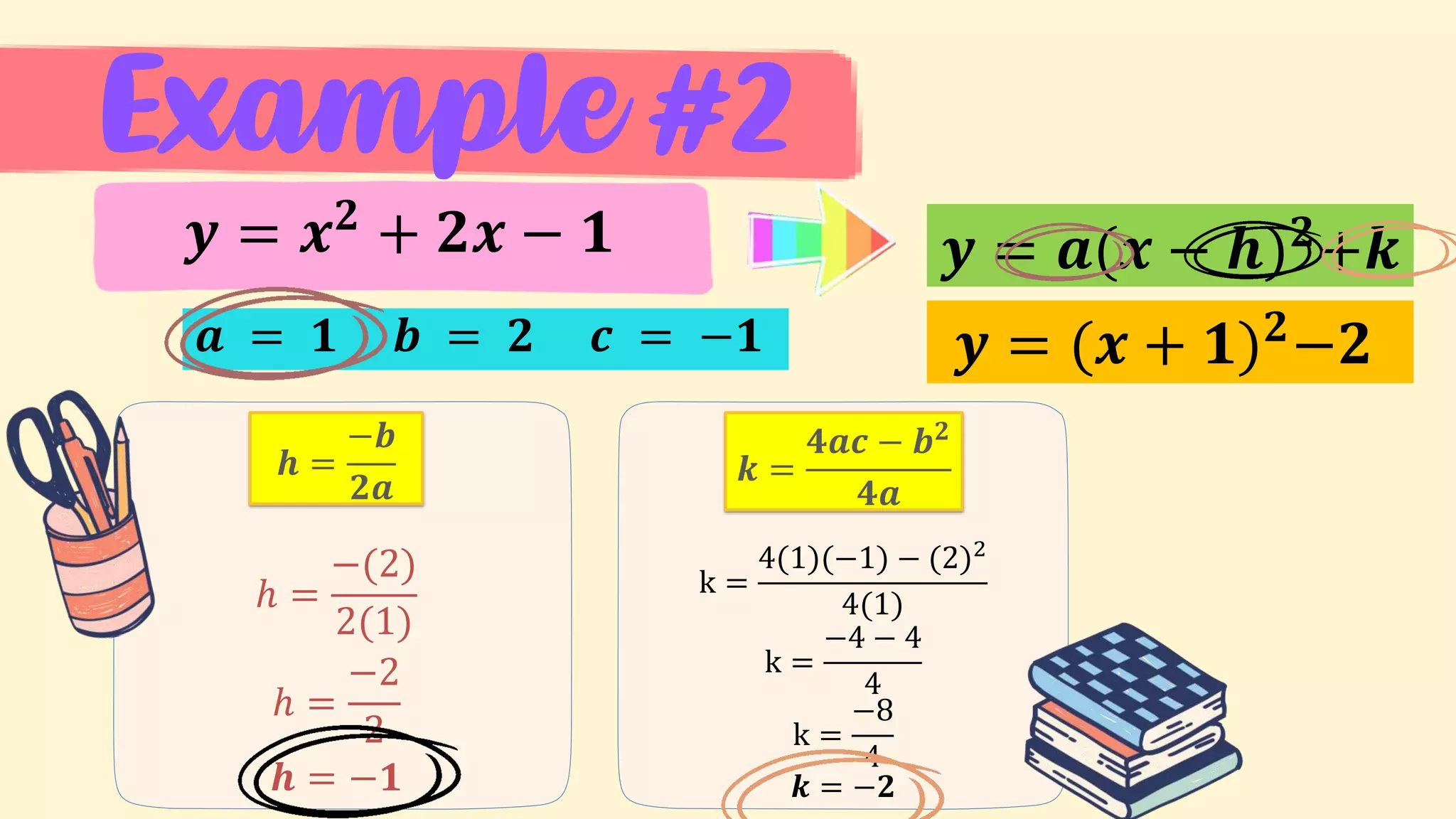
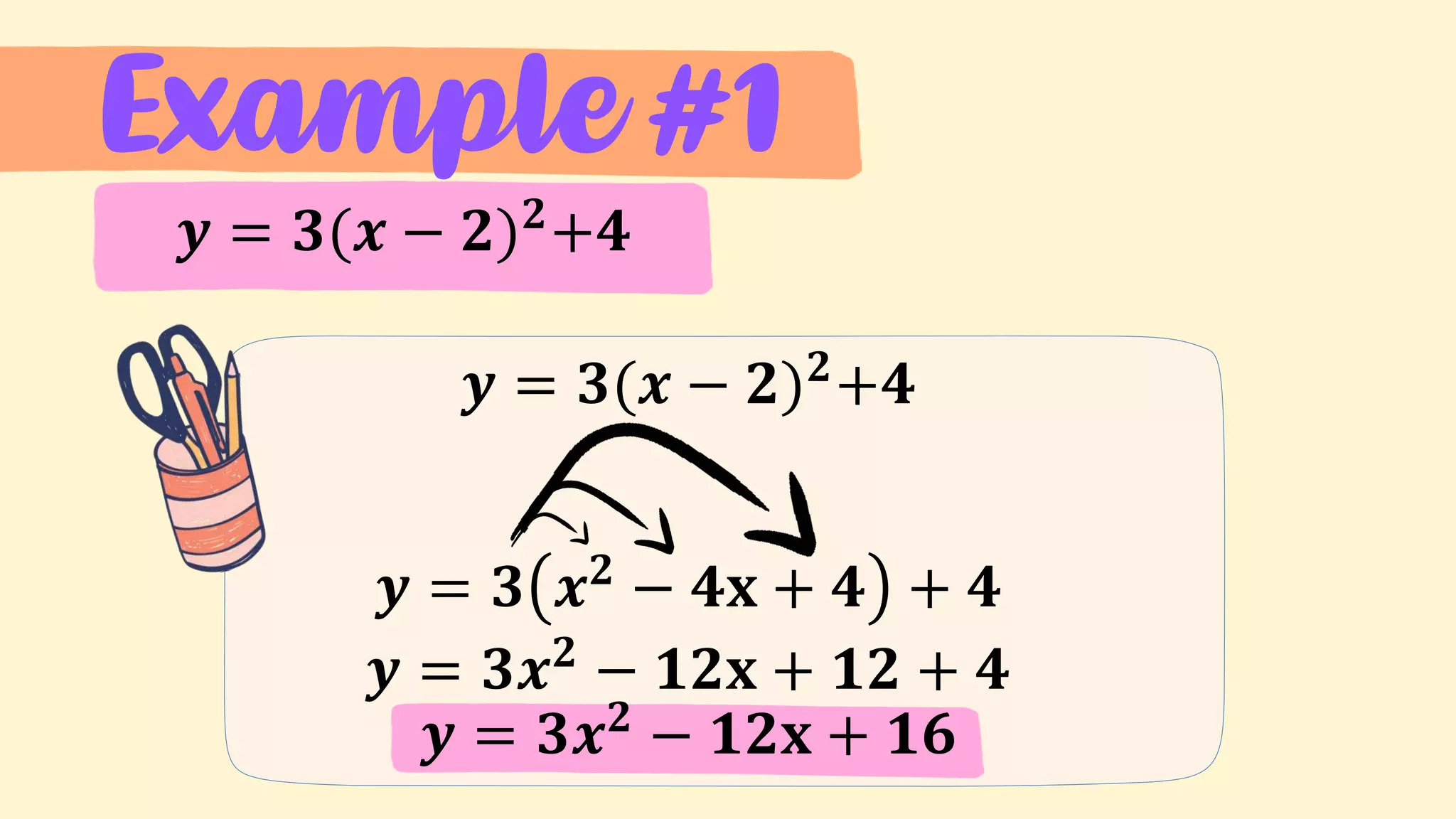
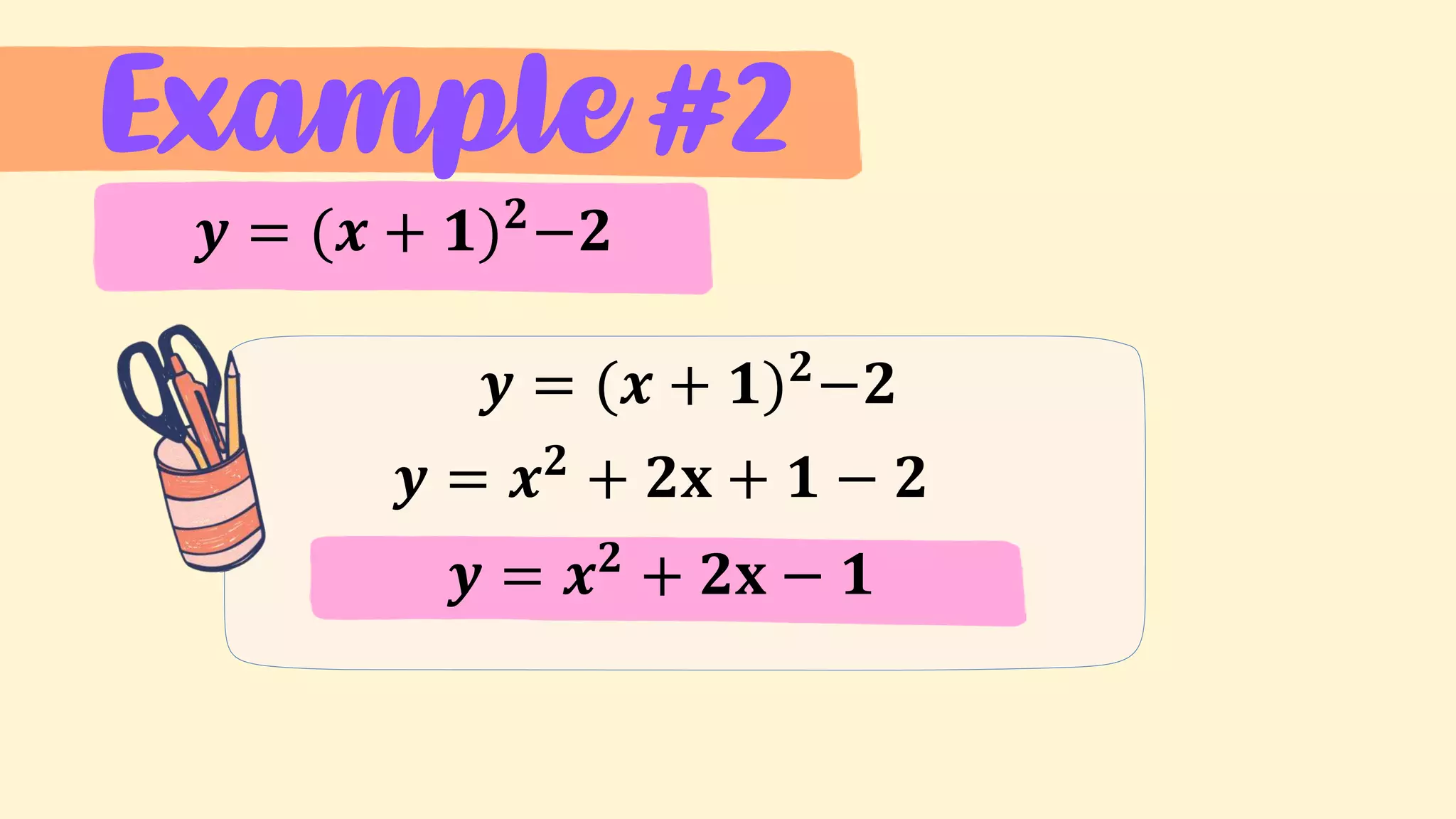
4. Examples of transforming between the general and vertex forms of quadratic functions.
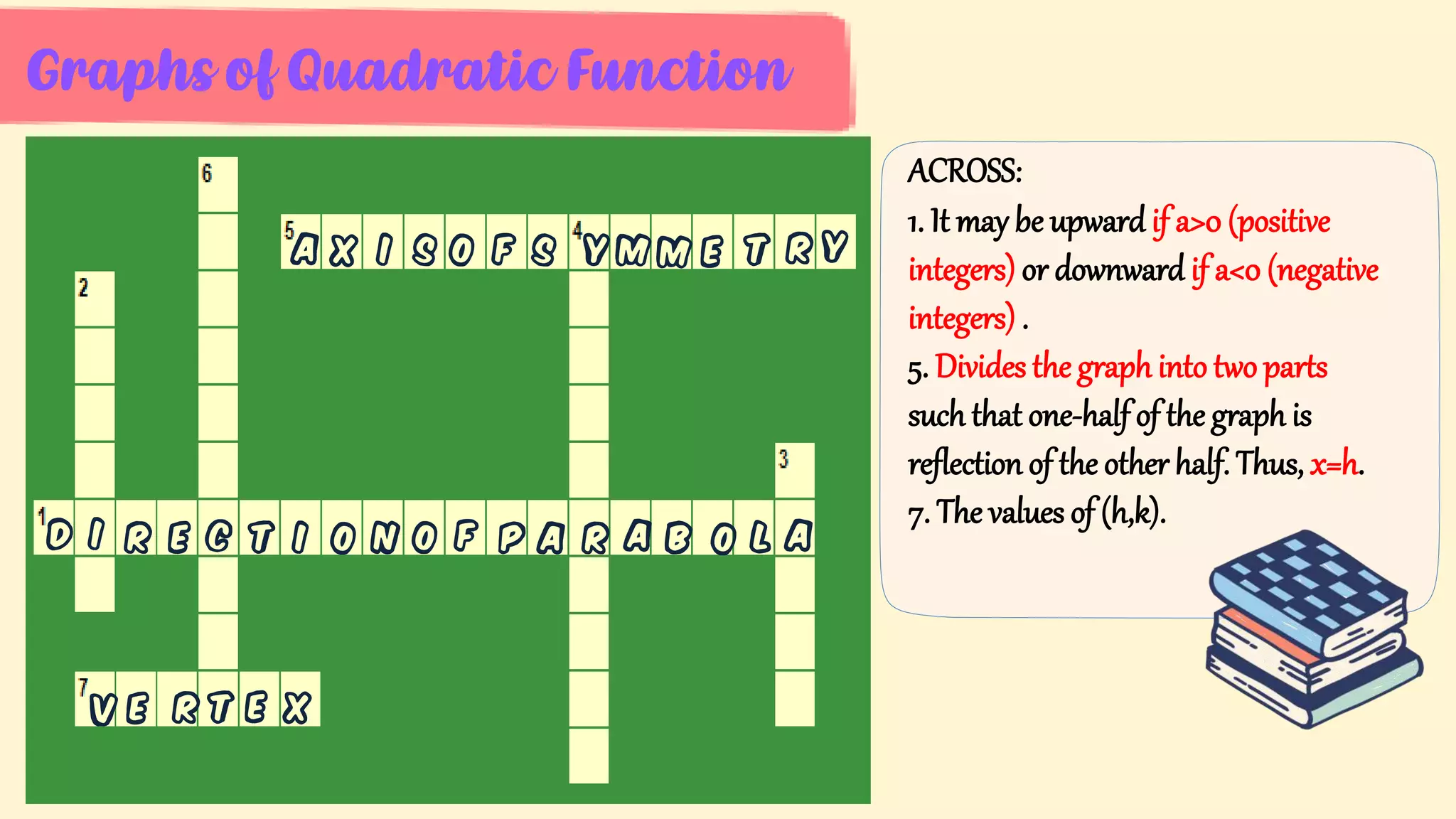
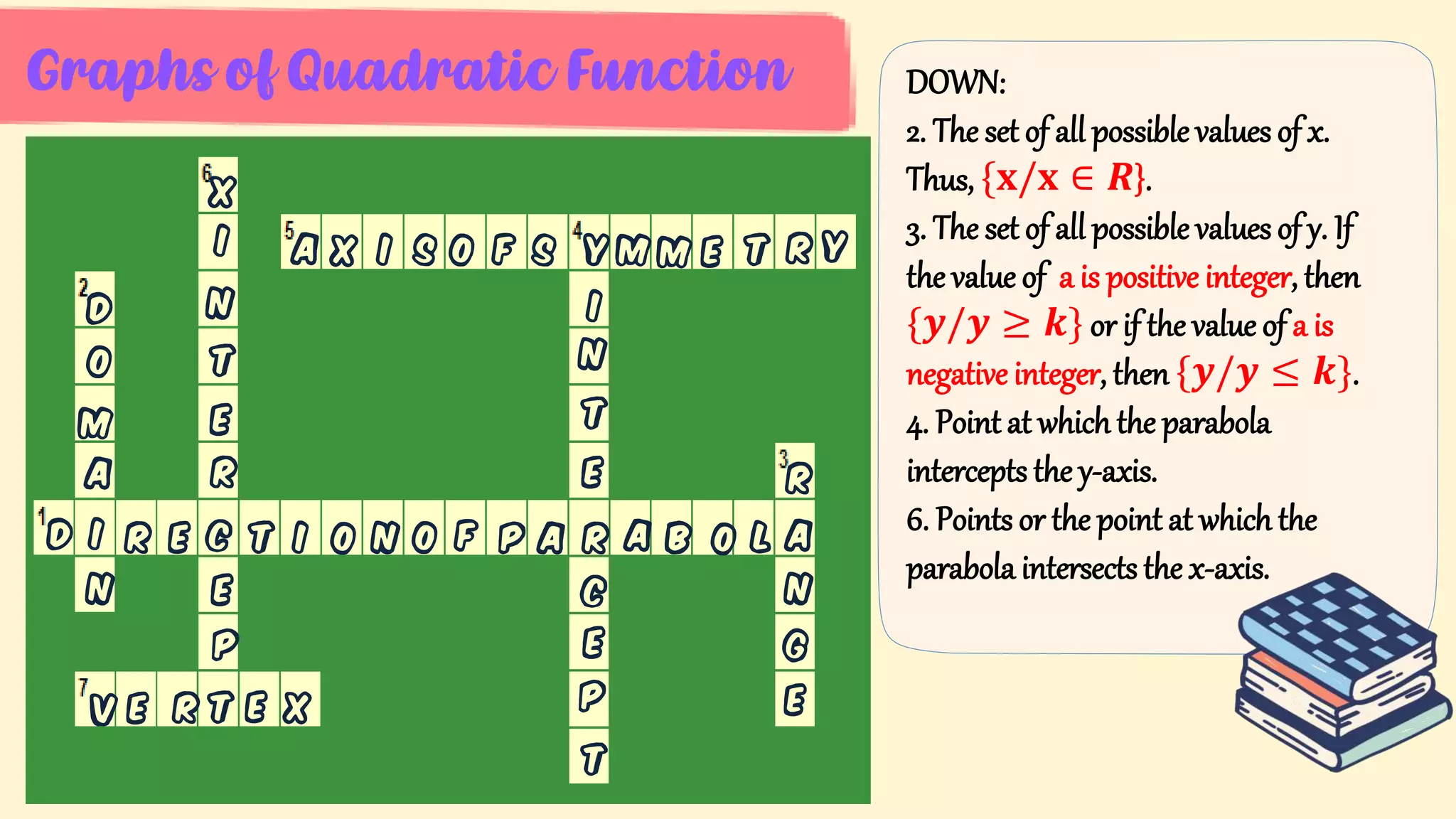
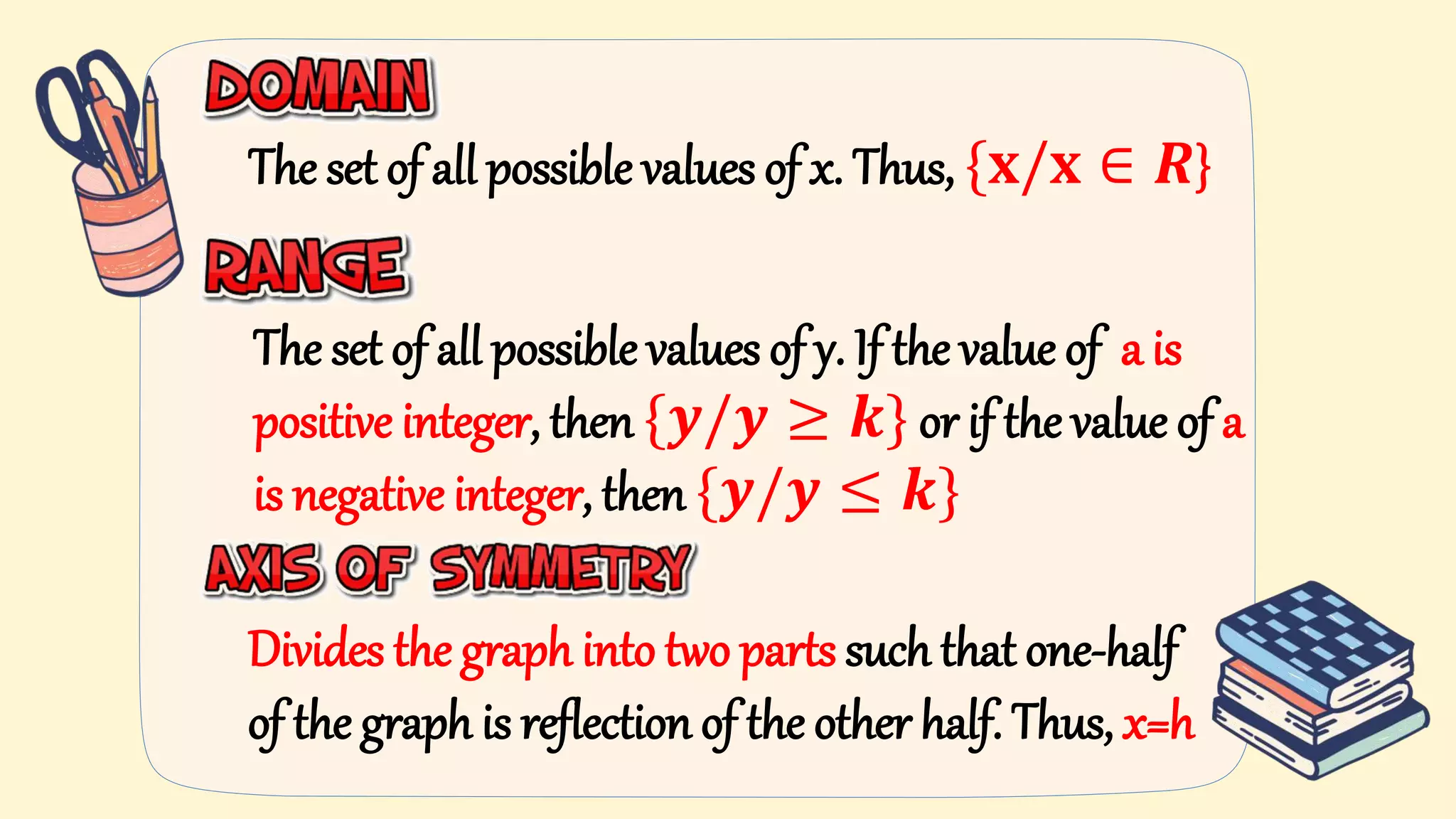
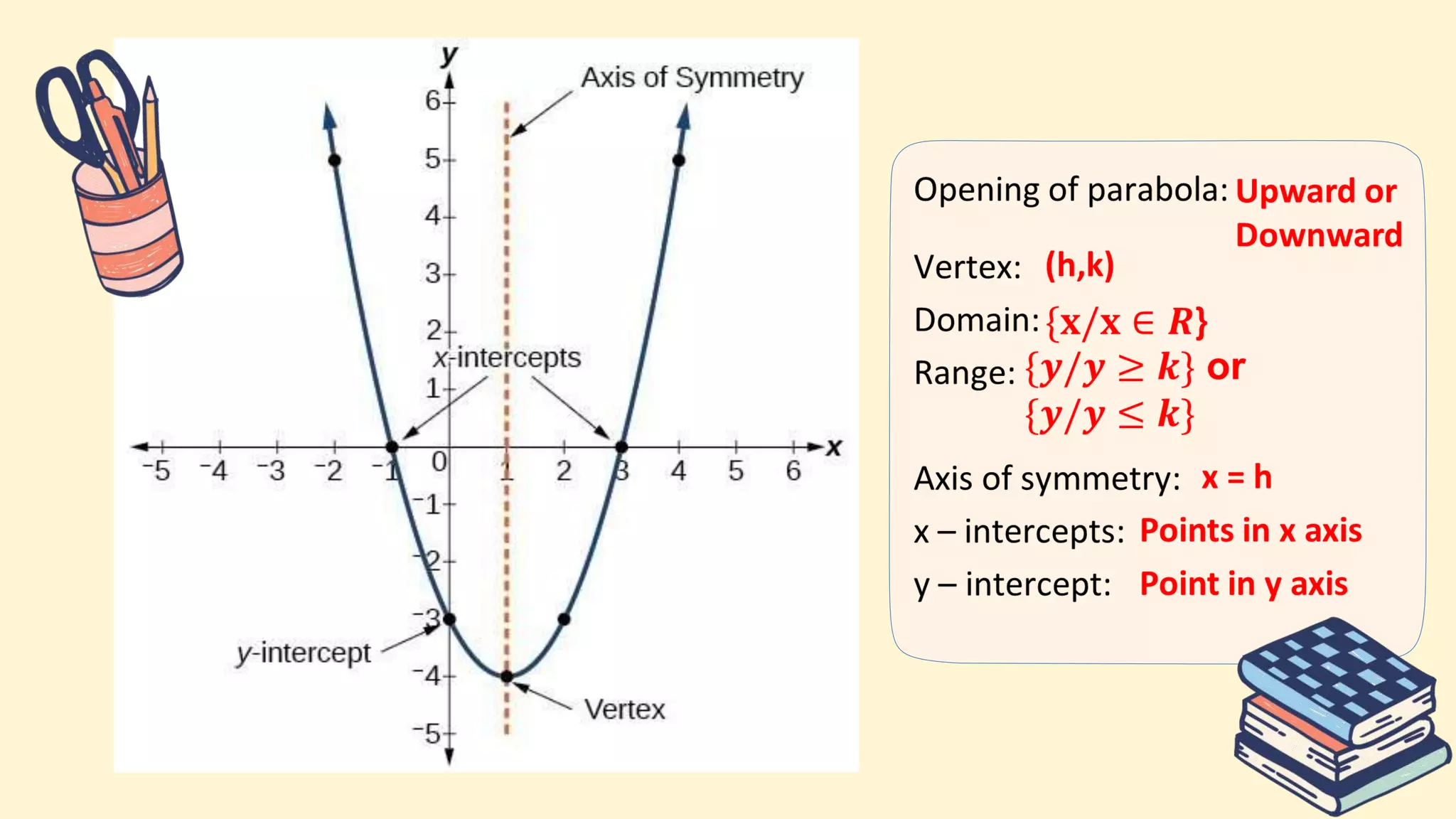
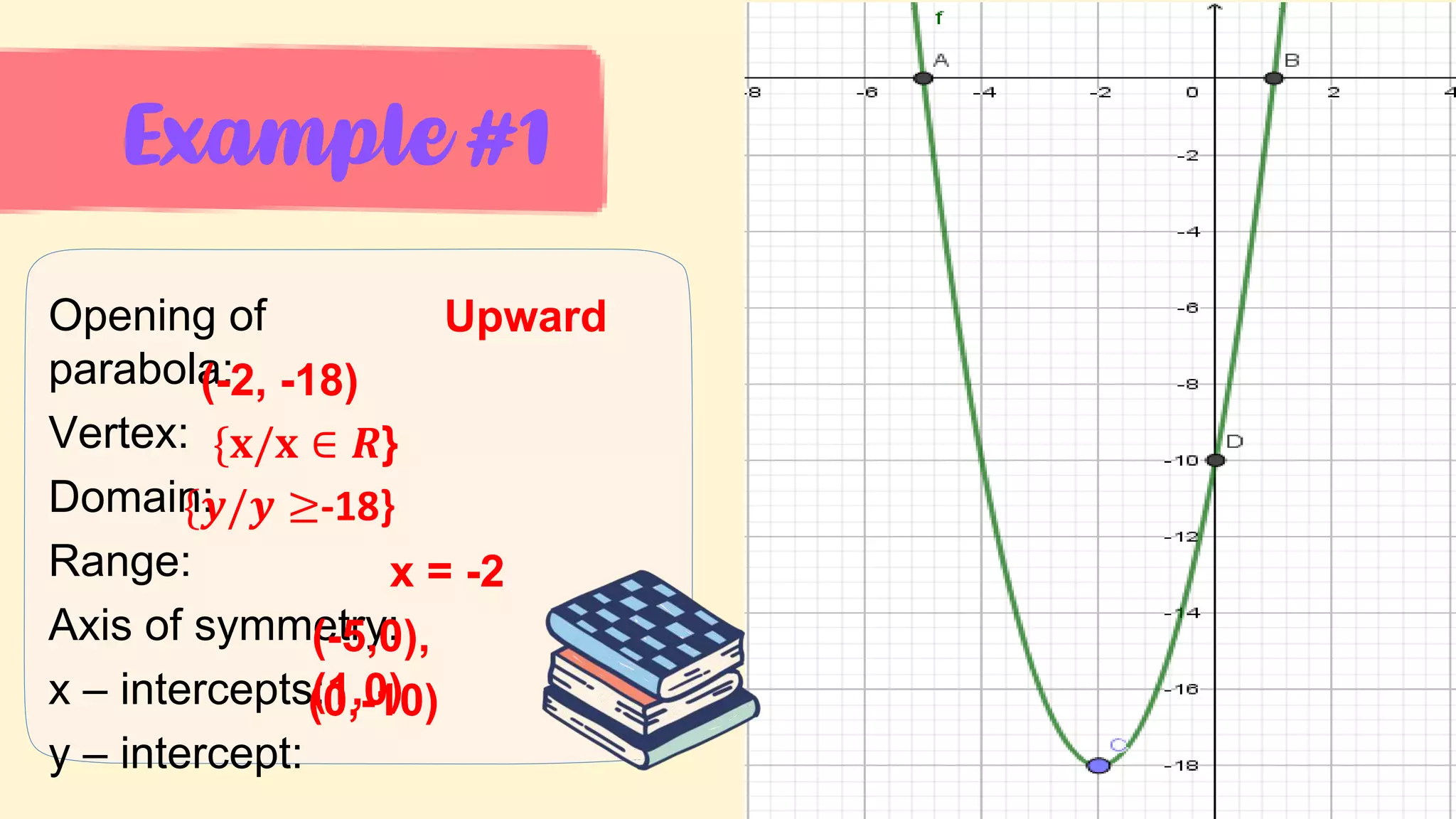
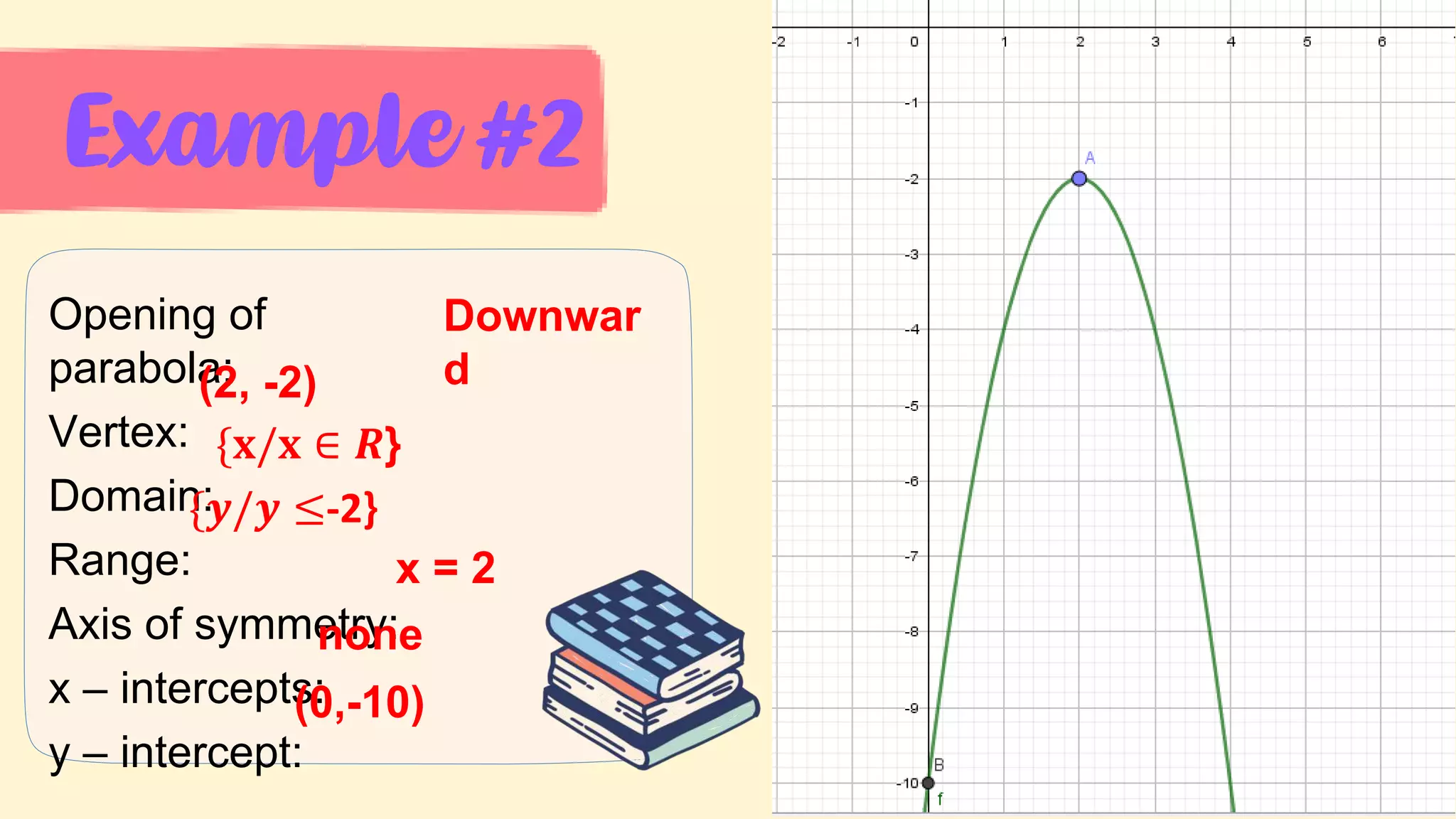
5. Key parts of graphs of quadratic functions including the vertex, axis of symmetry, x- and y-intercepts, and the effect of the leading coefficient on