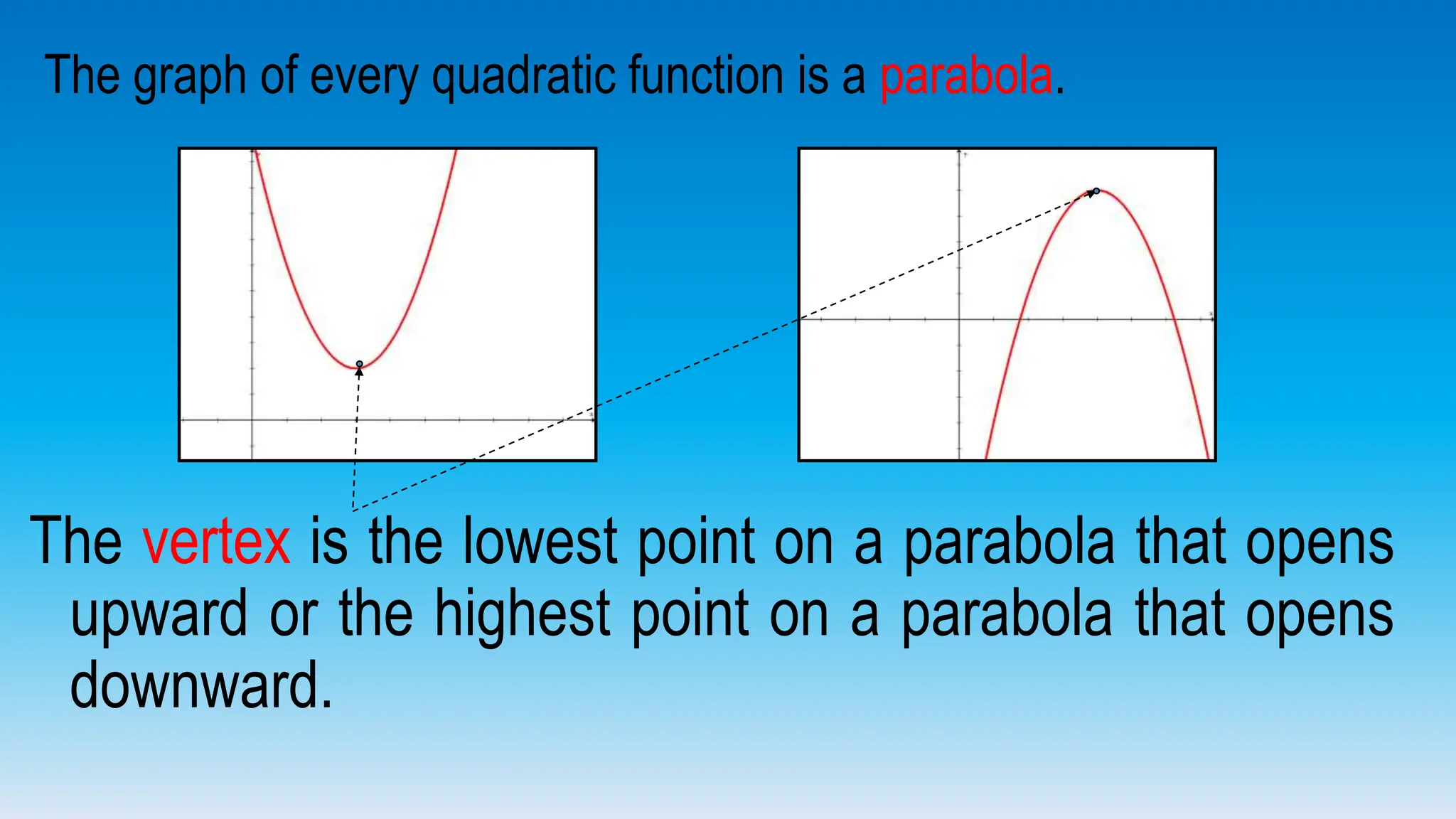
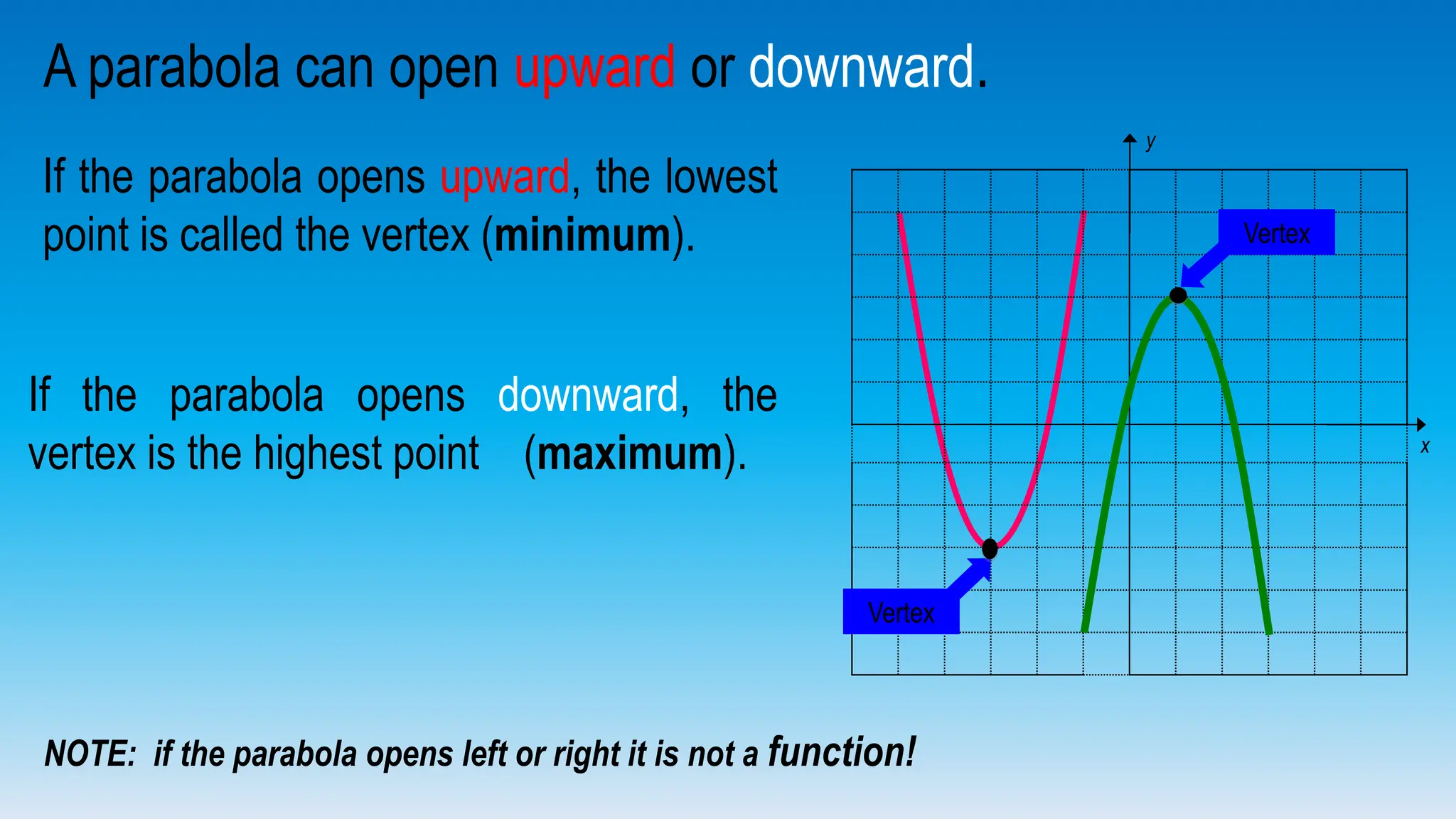
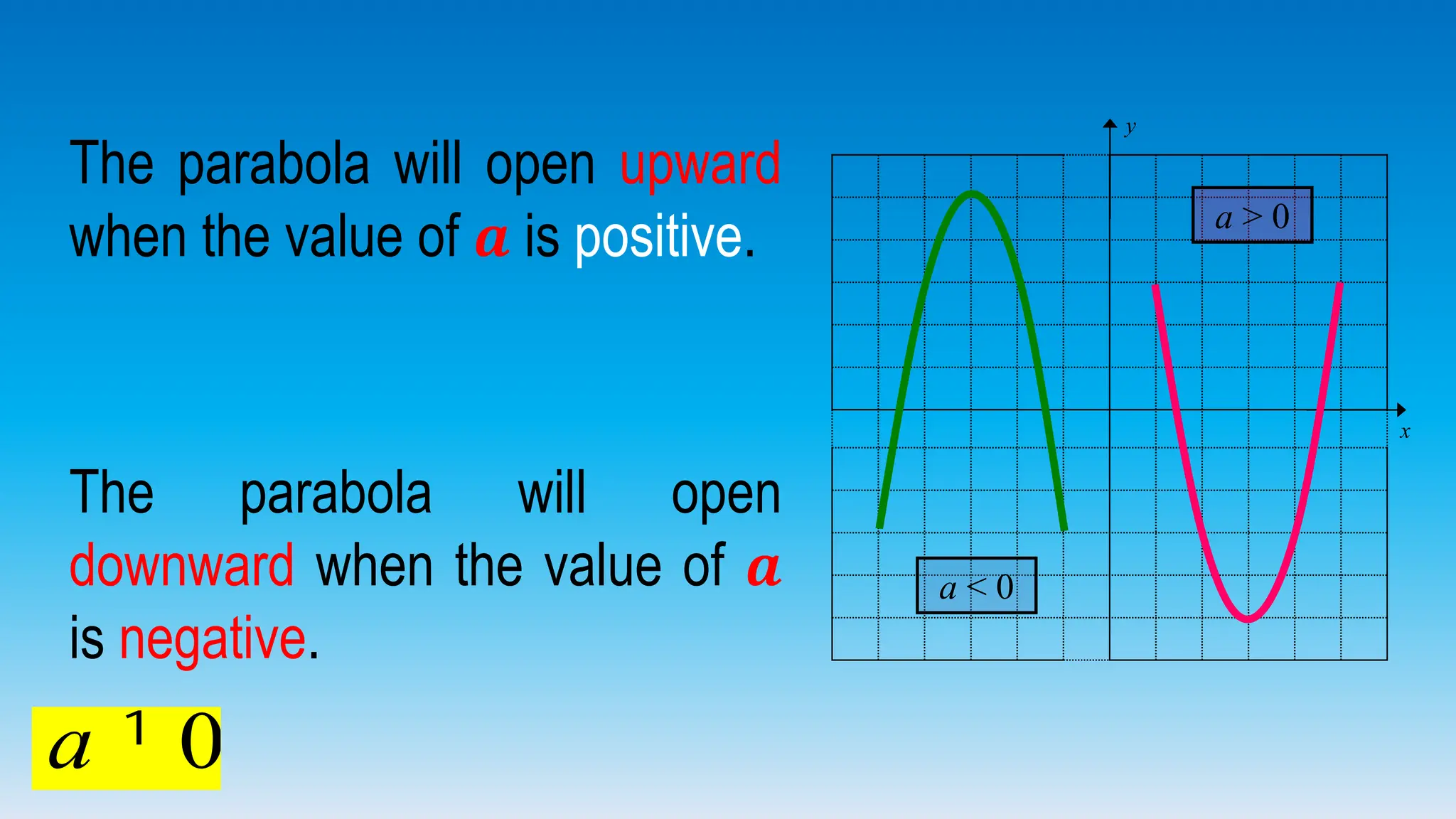
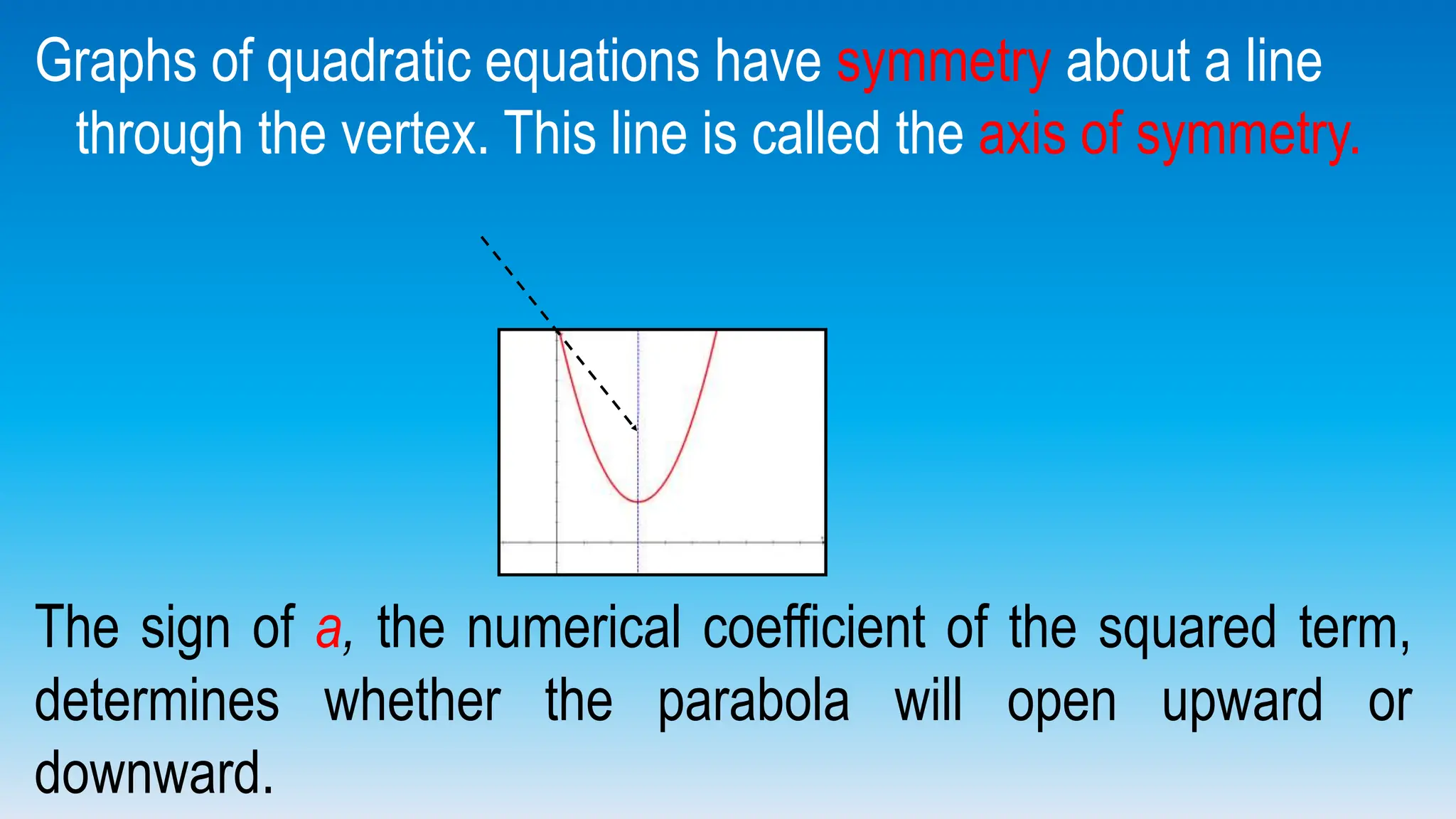
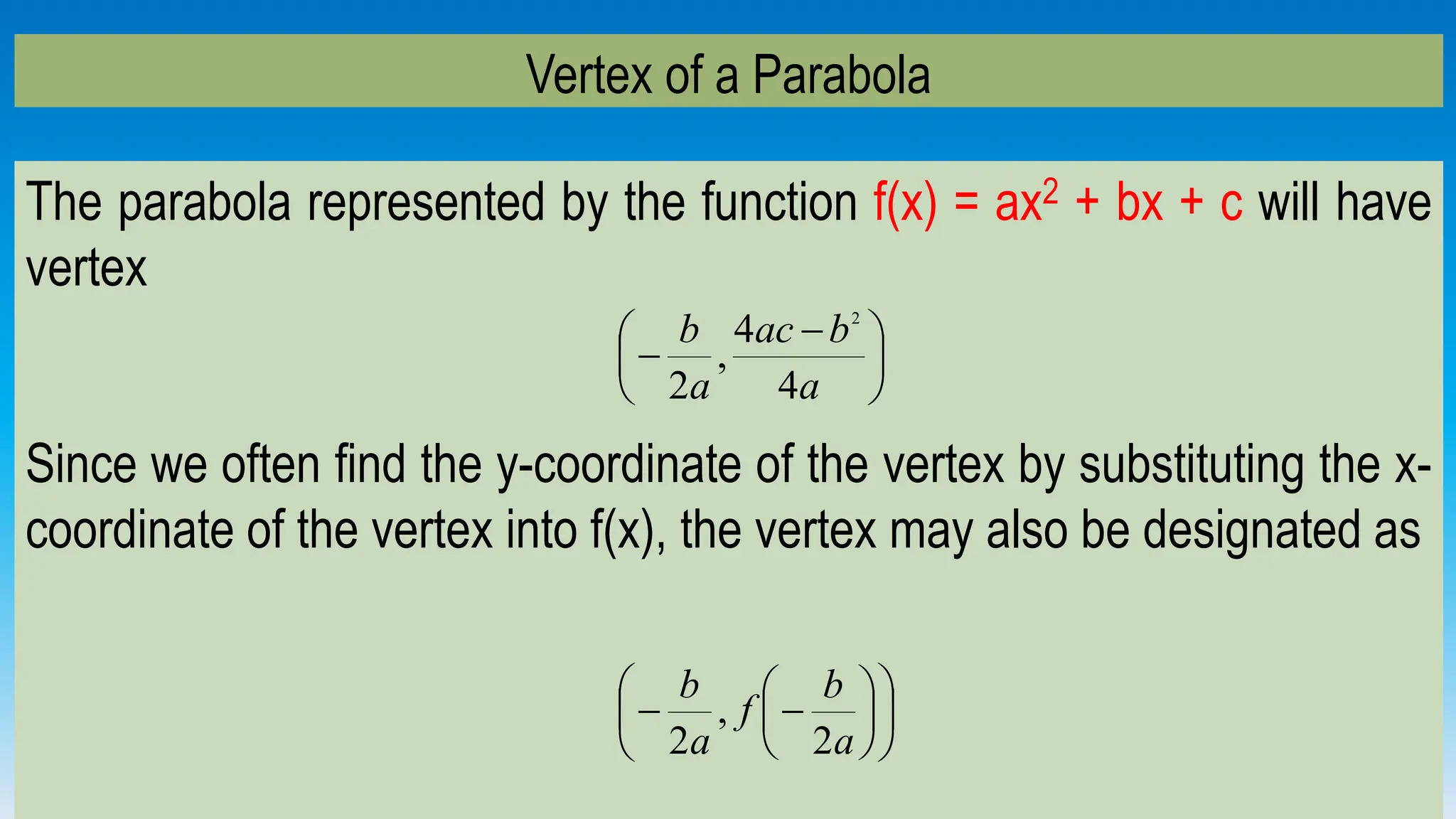
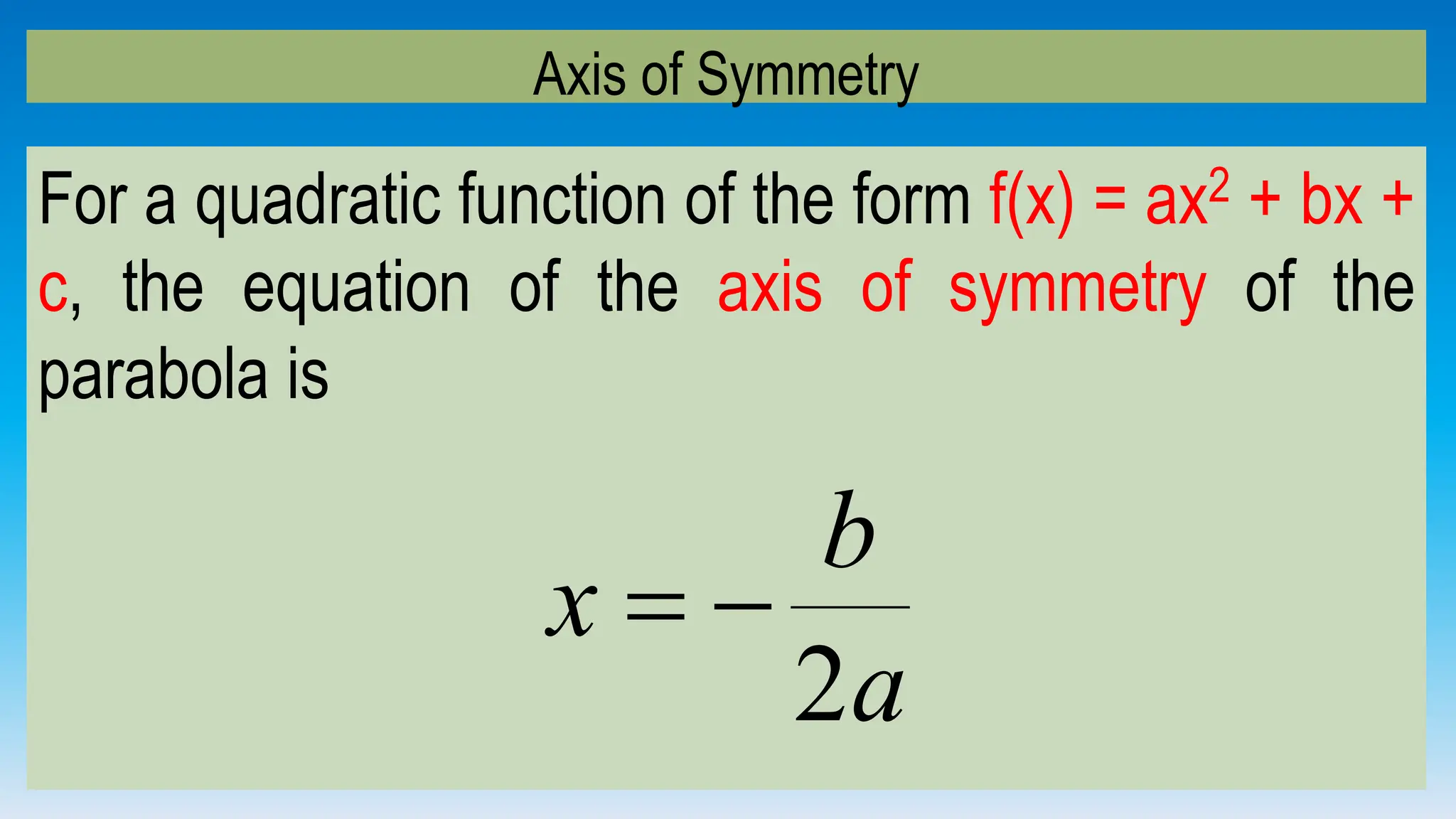
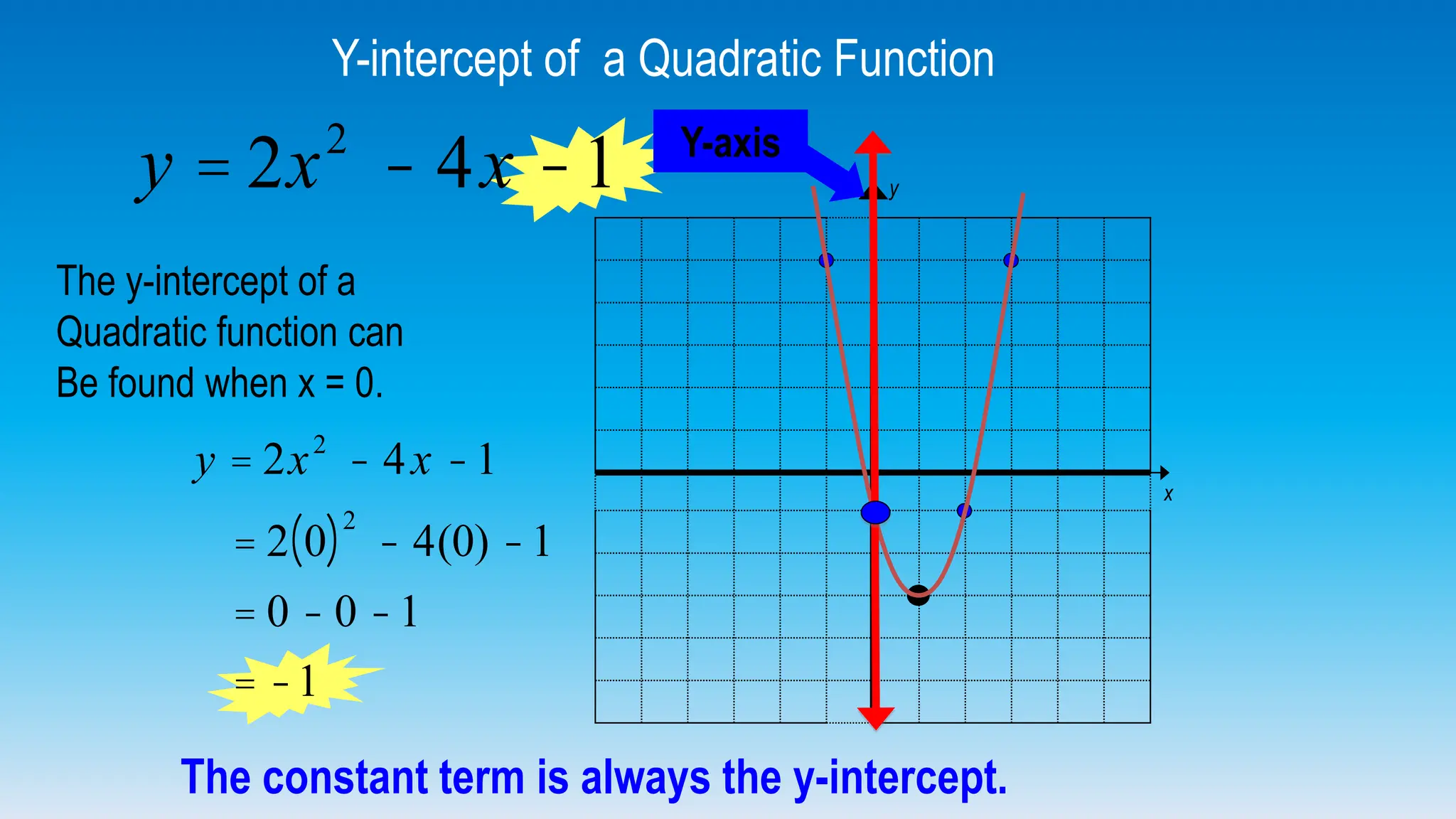
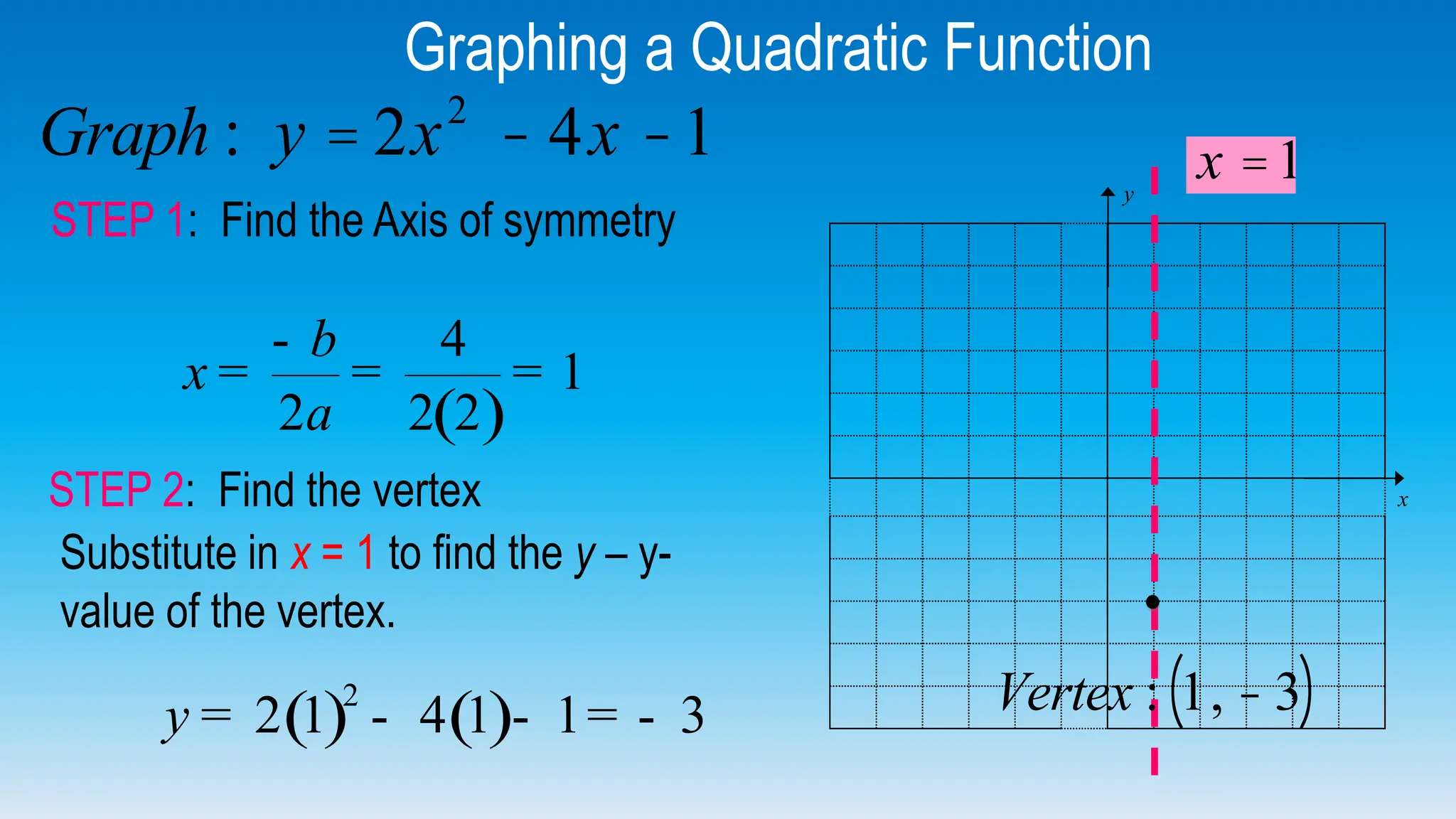
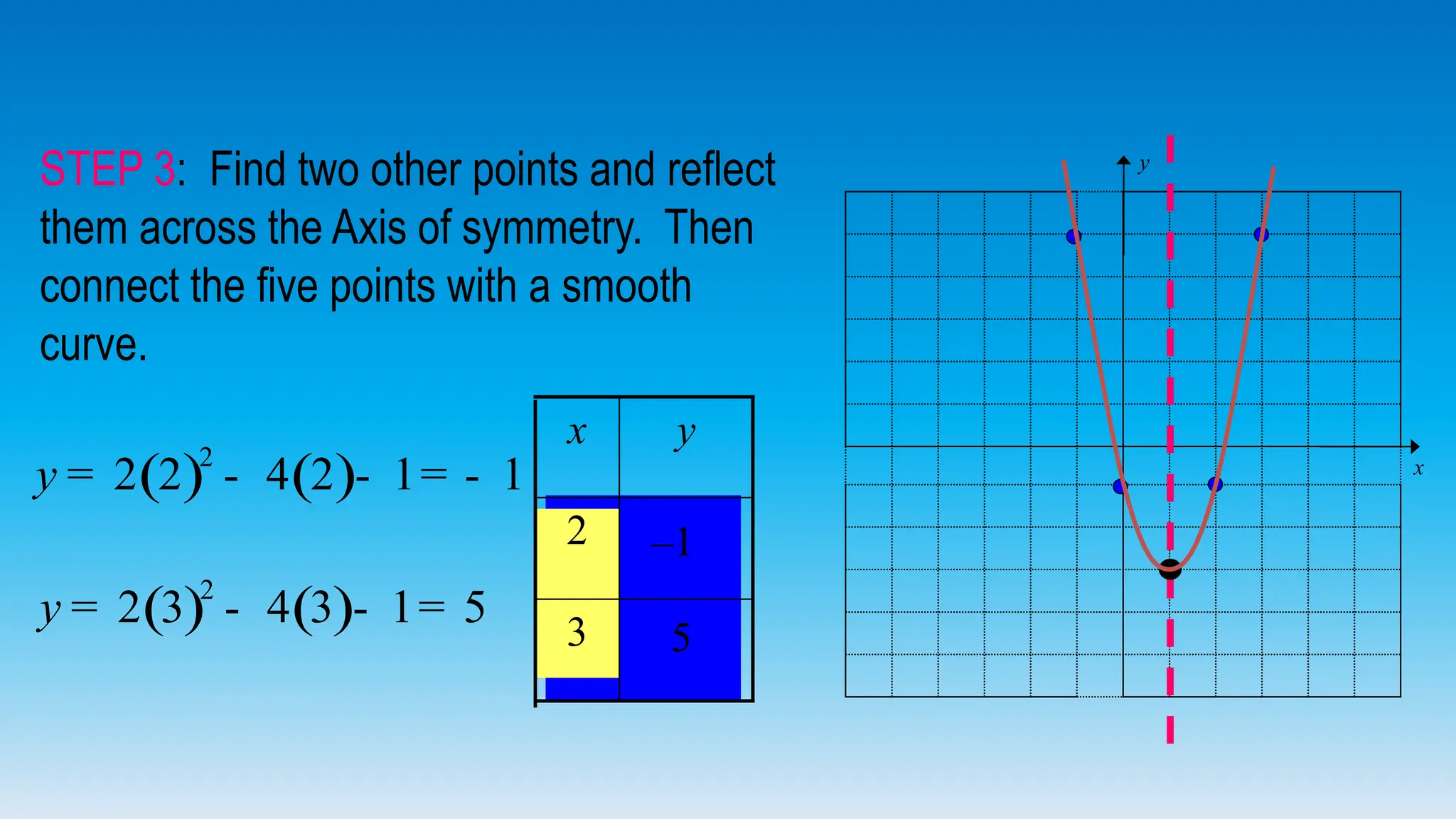
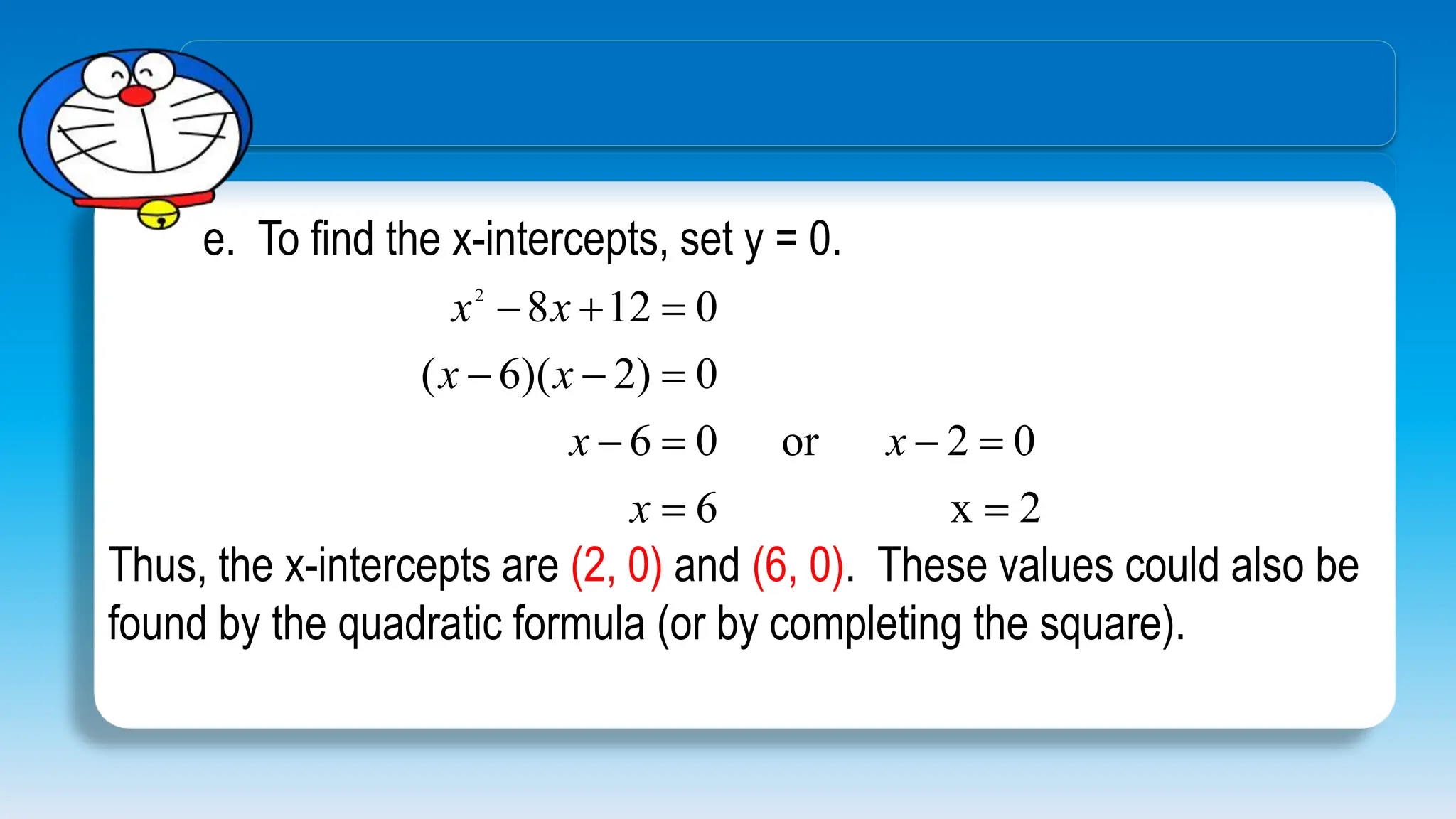
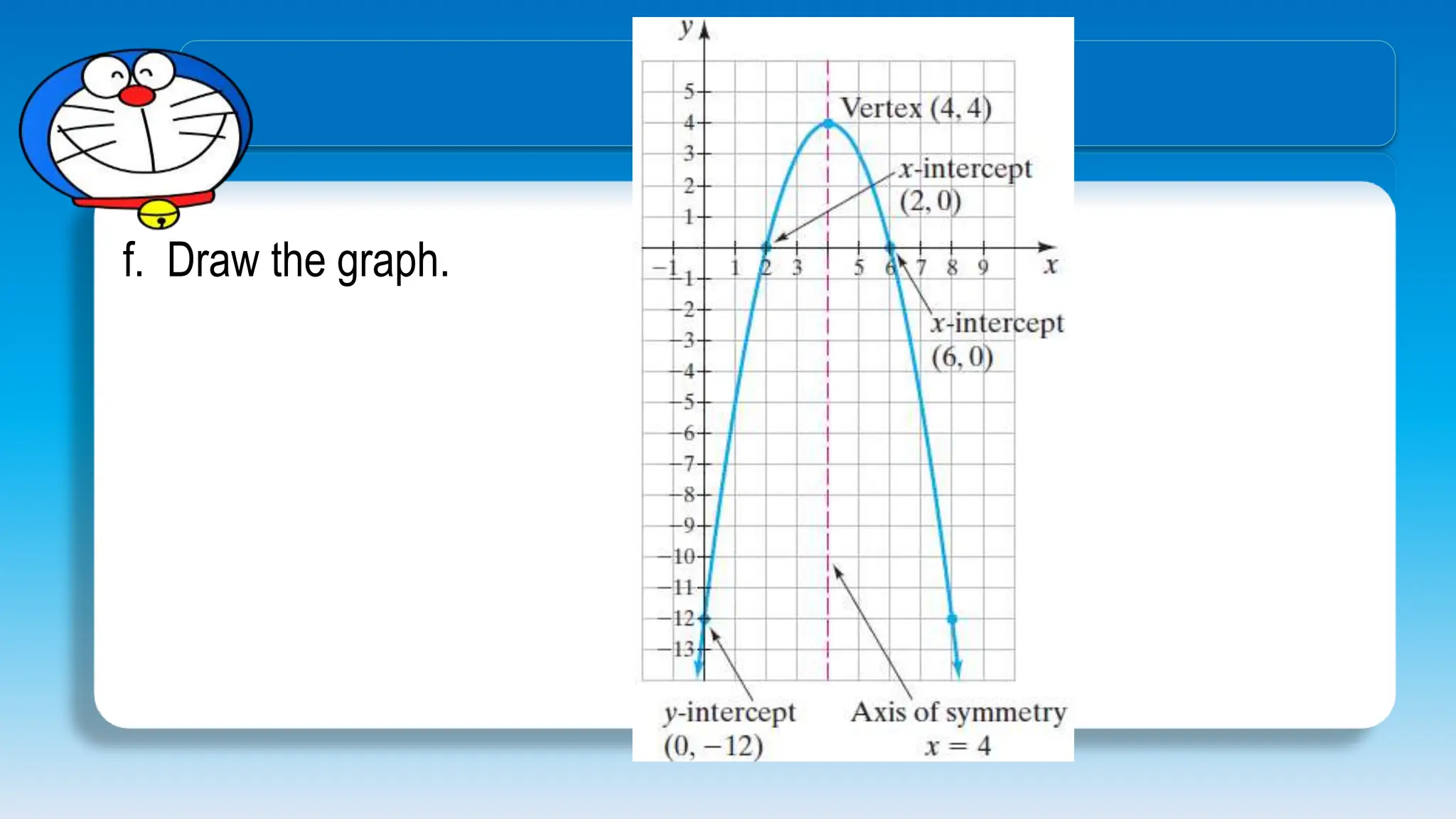
The document explains how to graph quadratic functions, including determining the domain, range, intercepts, axis of symmetry, and vertex. It defines a quadratic function in the form f(x) = ax² + bx + c, discusses the characteristics of parabolas, and provides step-by-step examples of graphing techniques. The document emphasizes the role of the coefficient 'a' in determining the direction in which the parabola opens and how to find critical points on the graph.