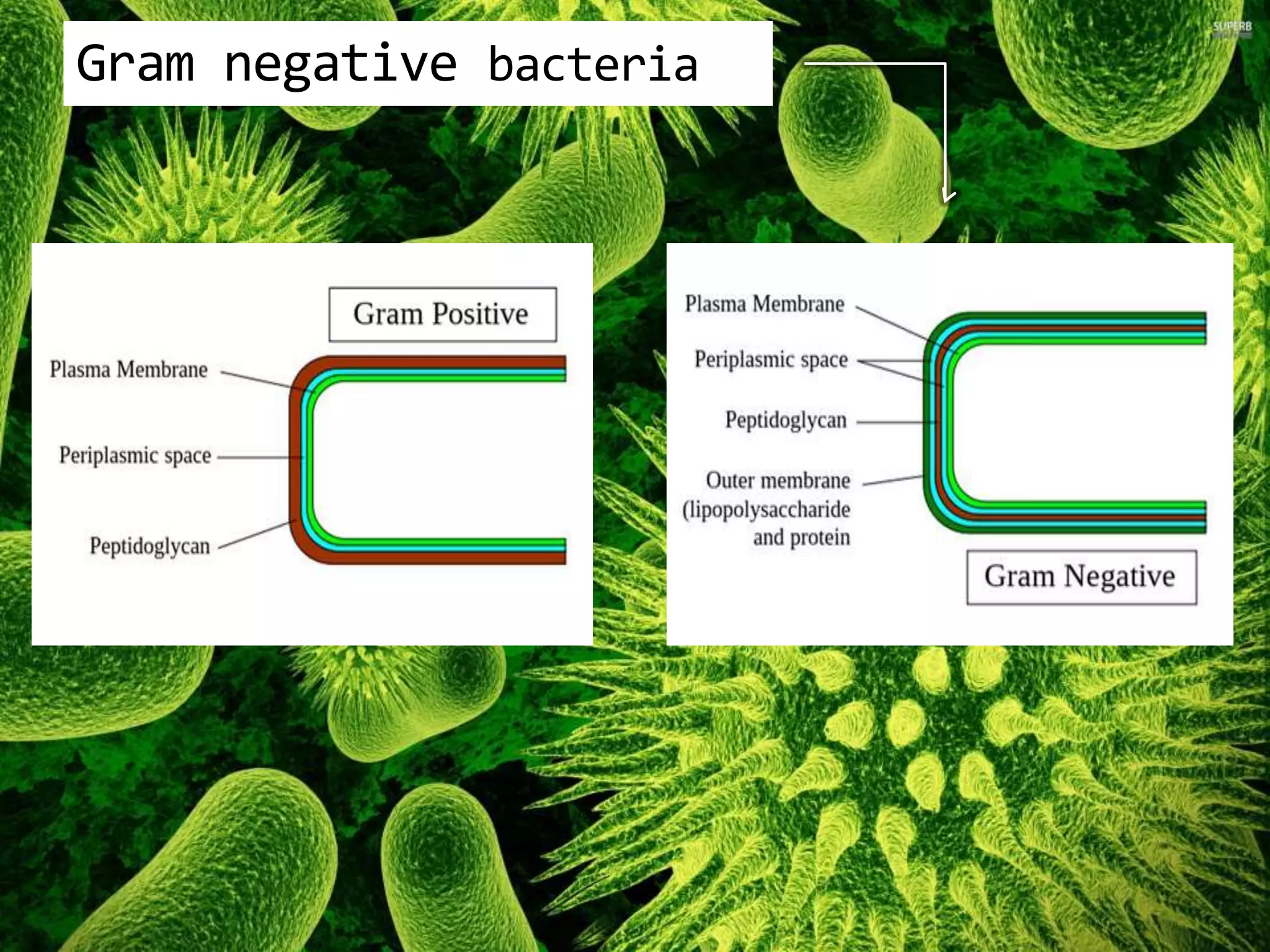
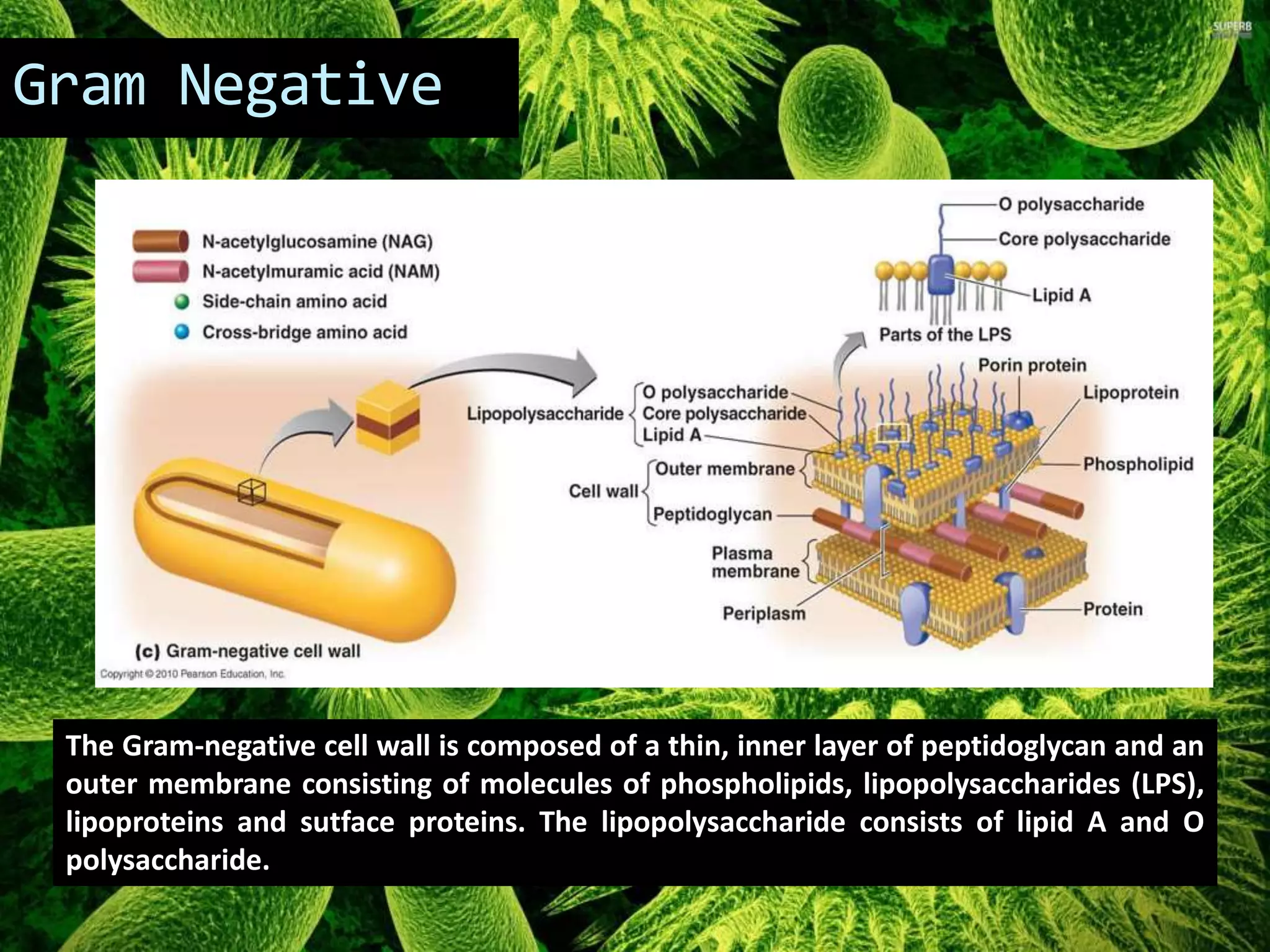
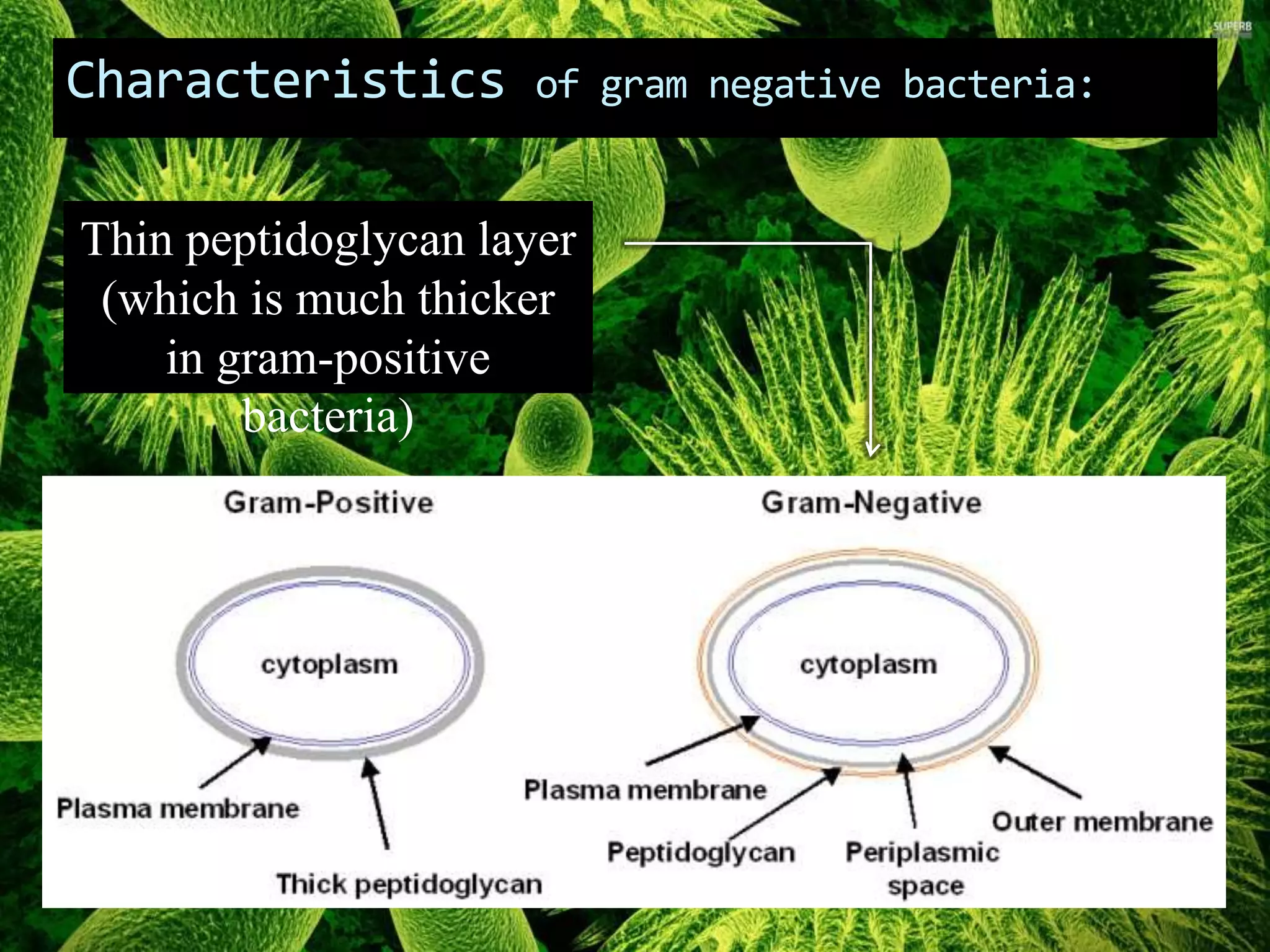
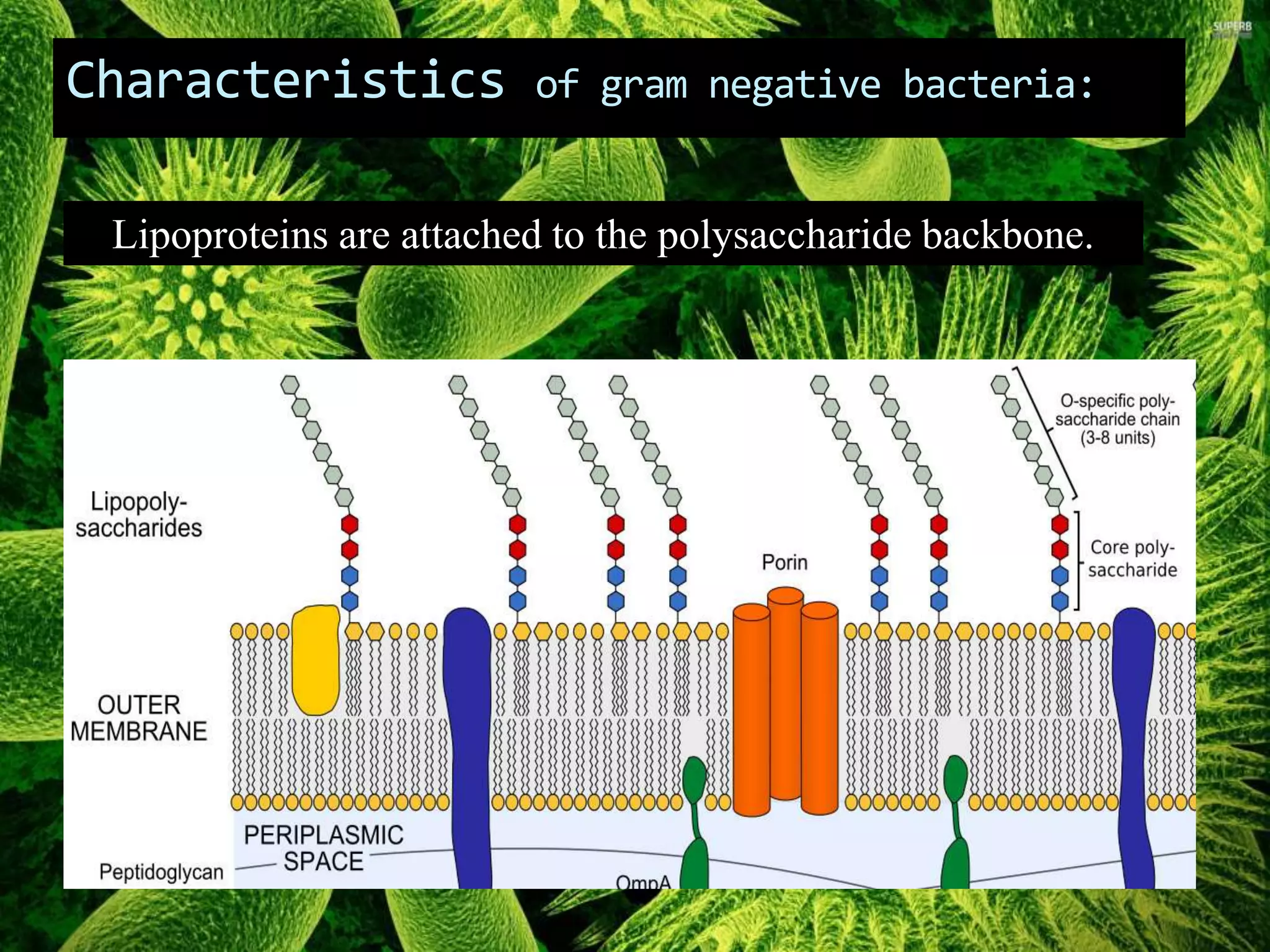
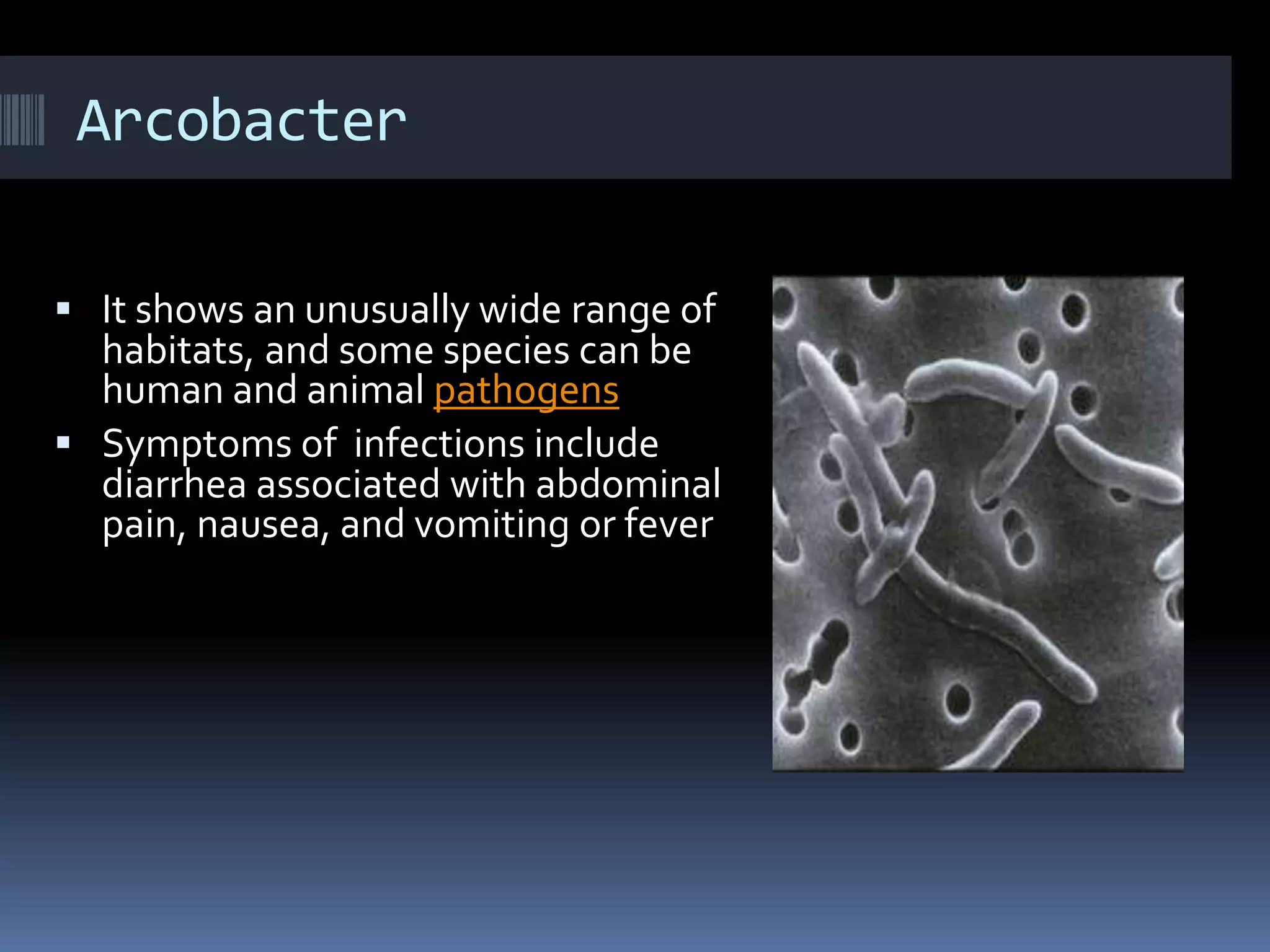
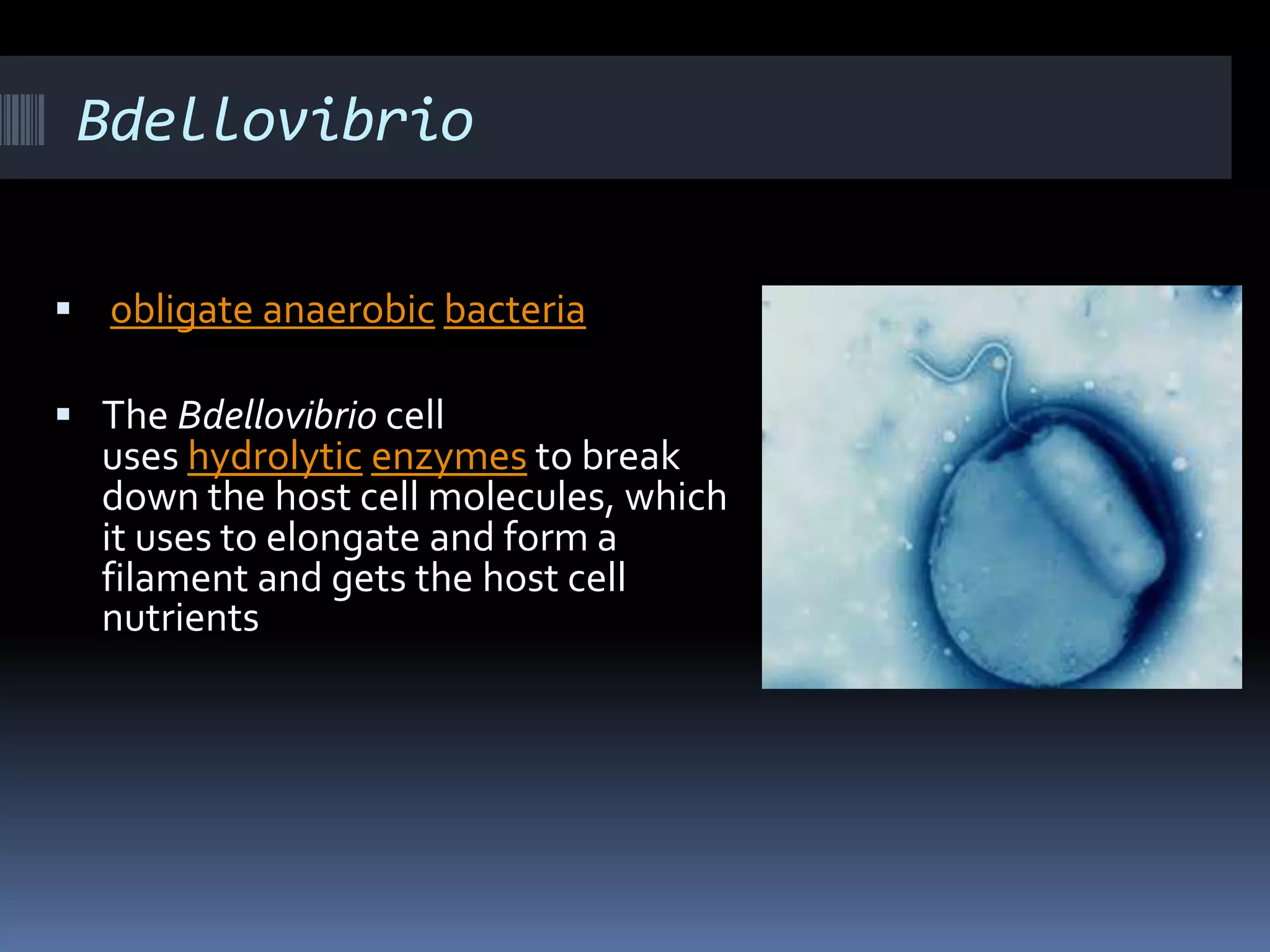
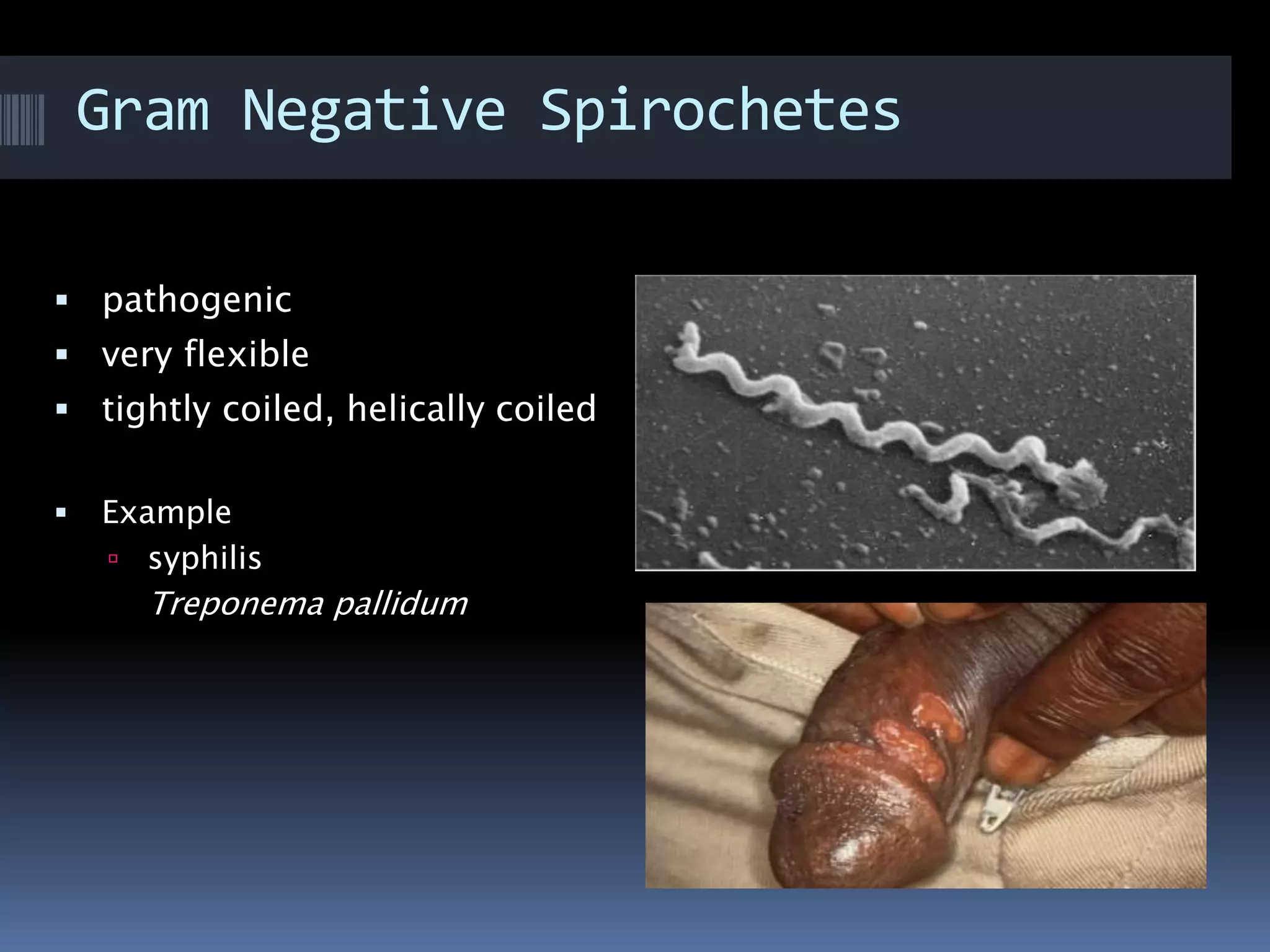
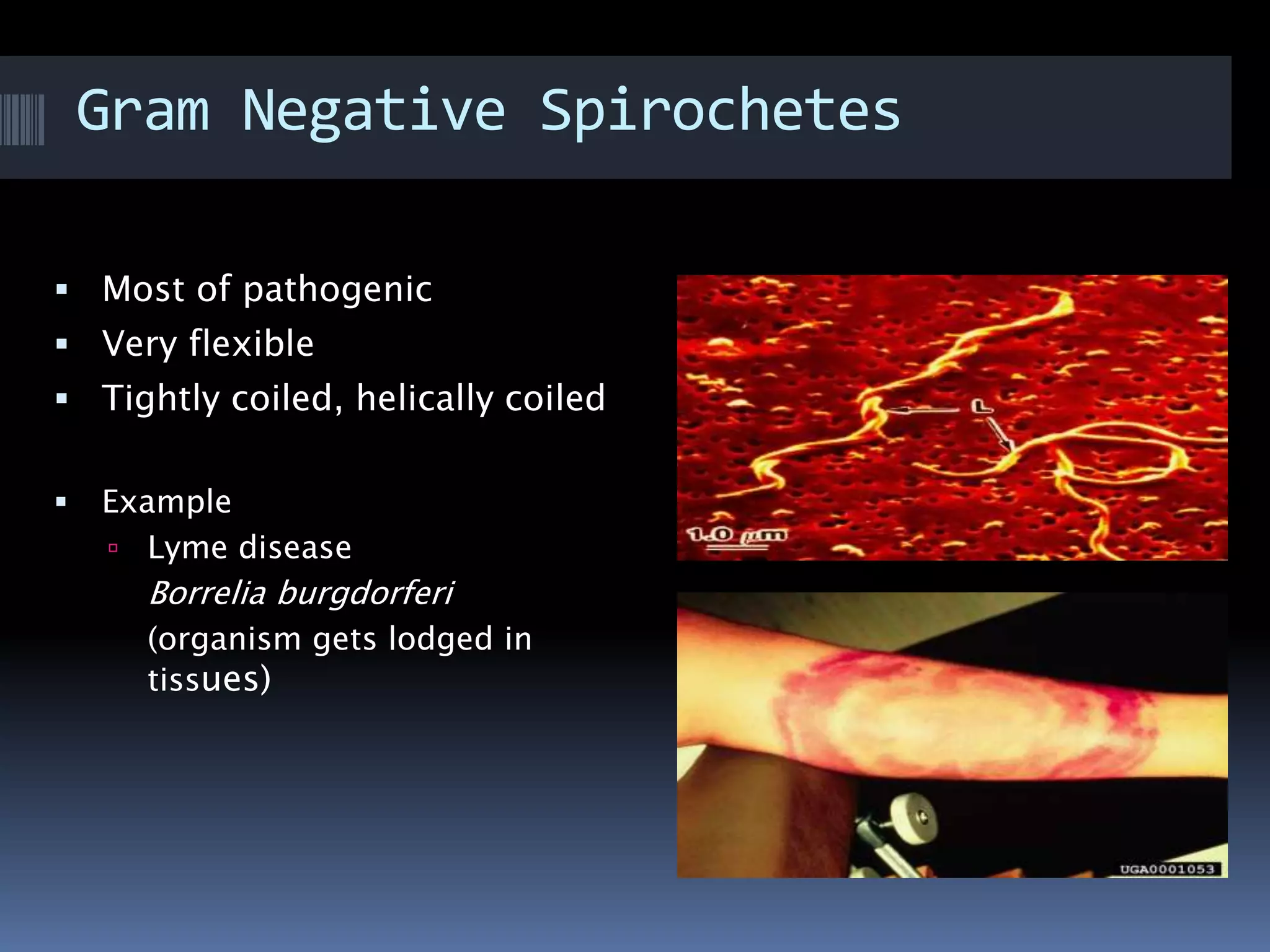
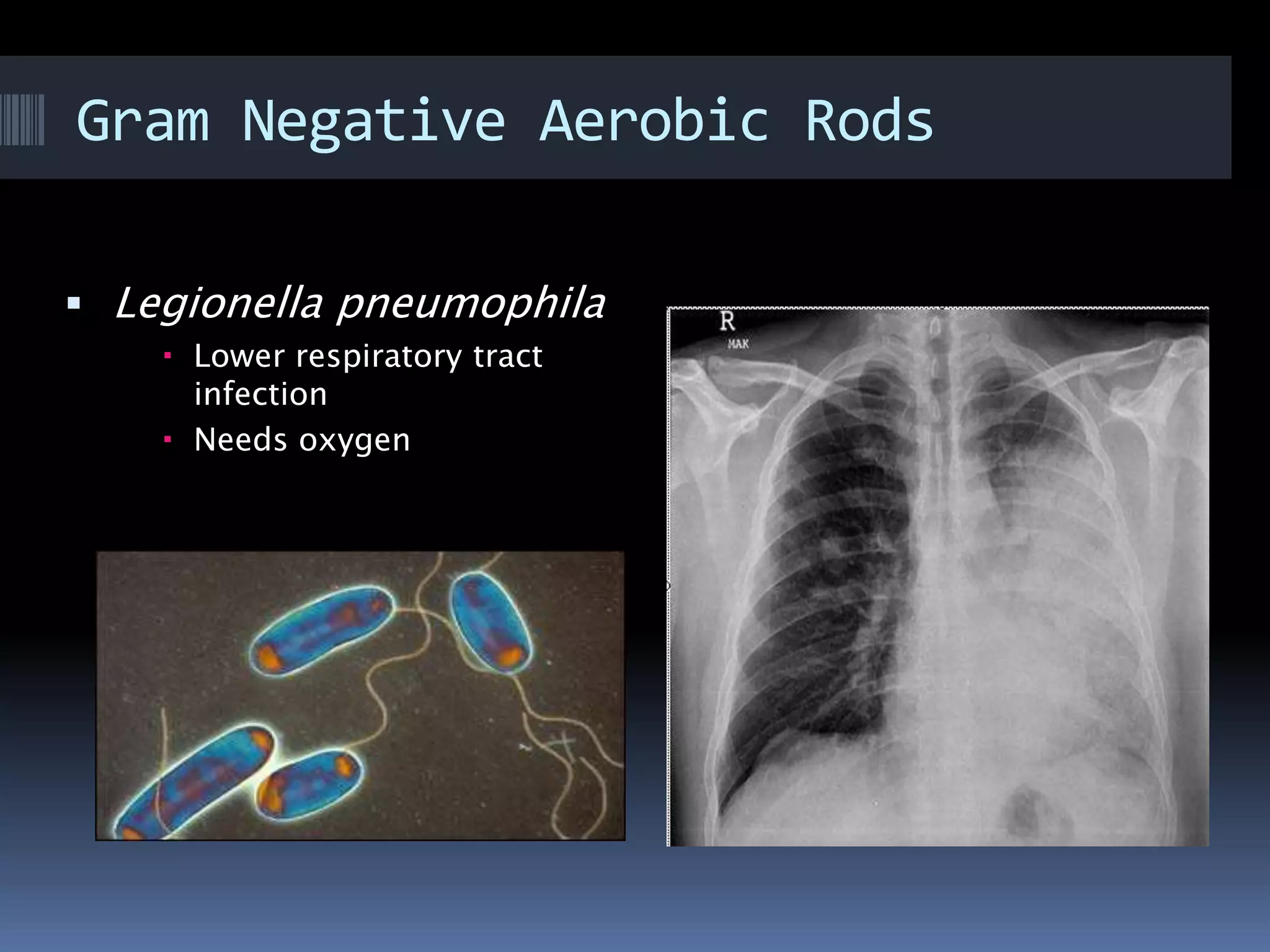
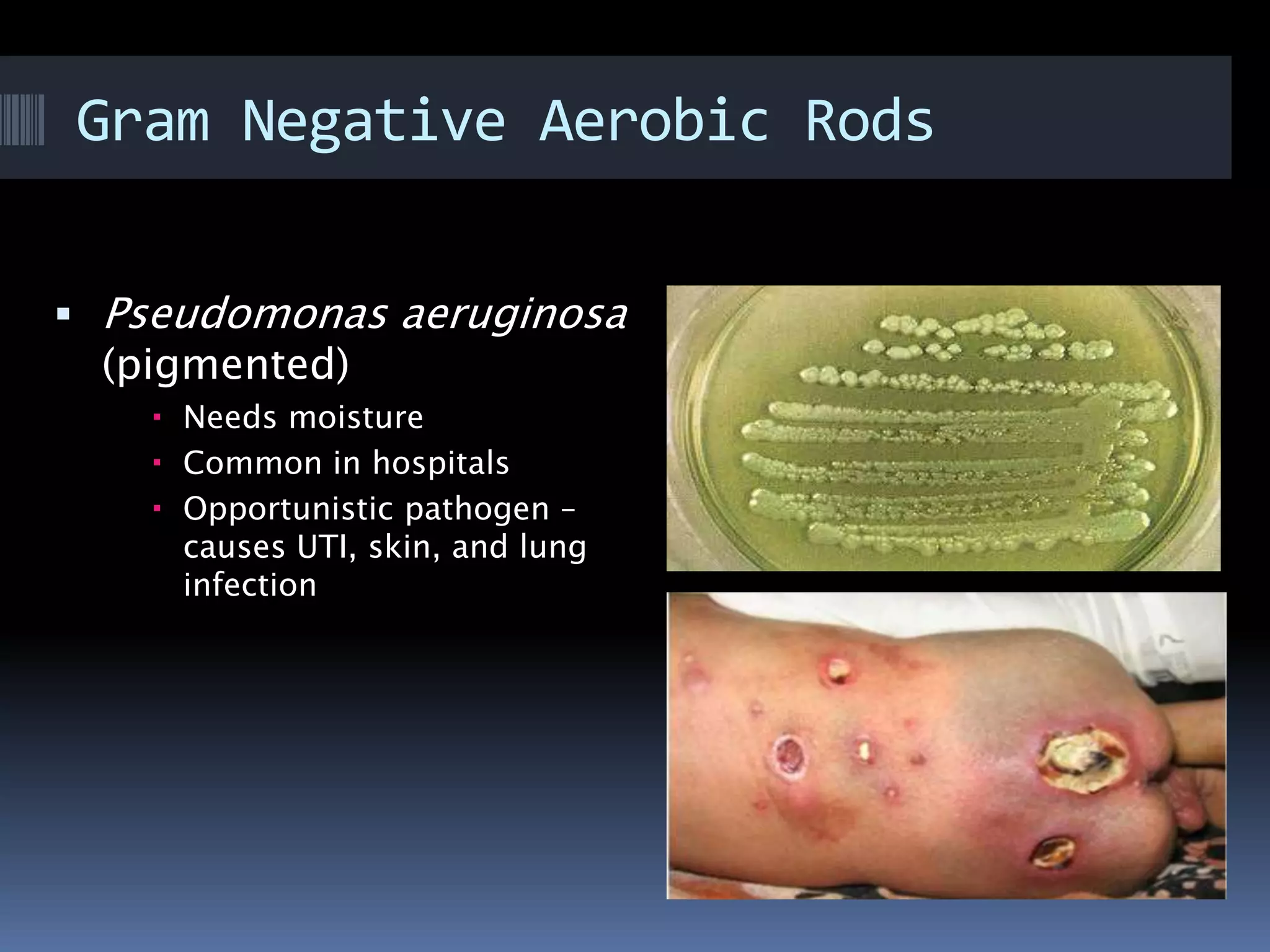
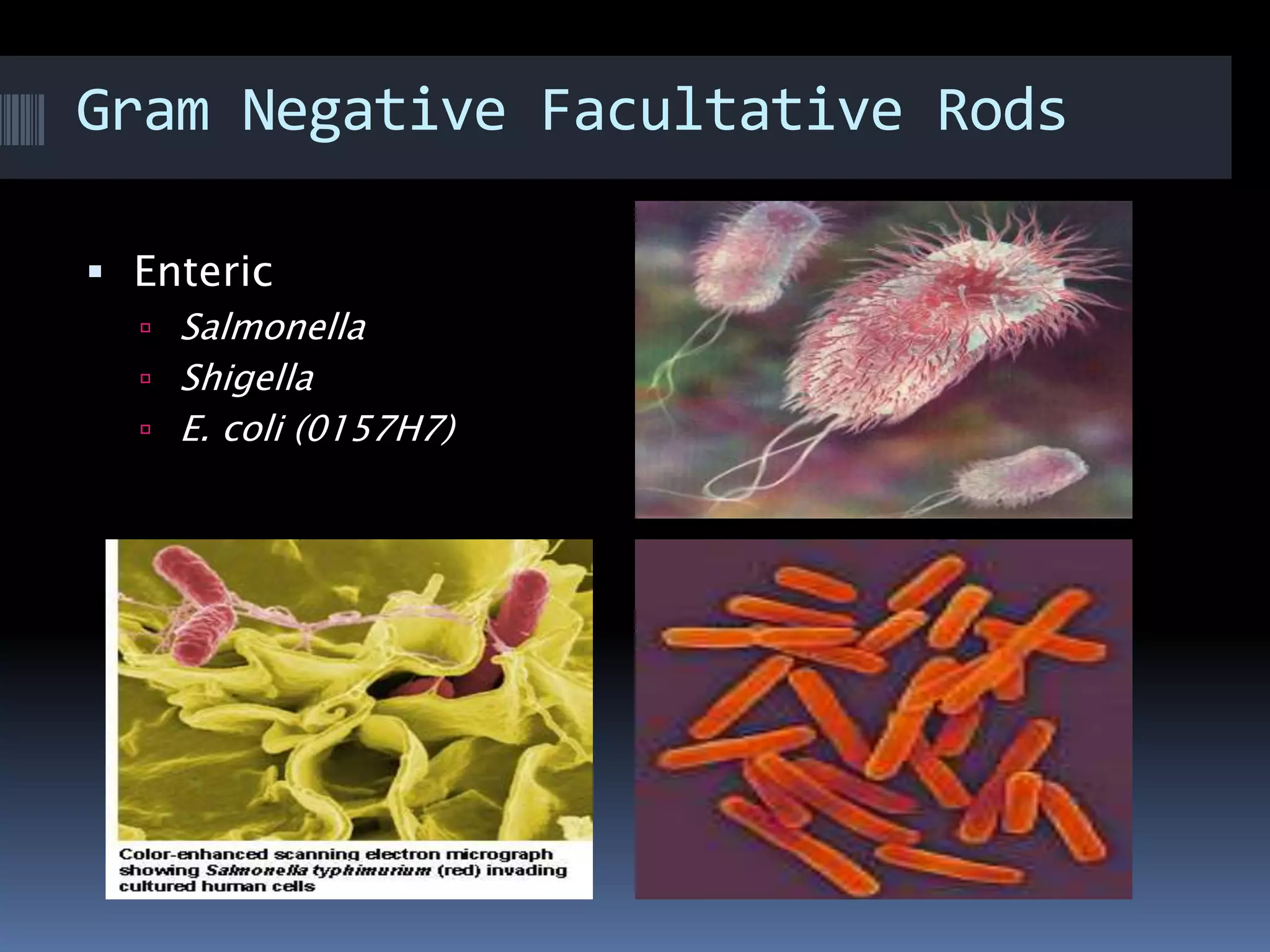
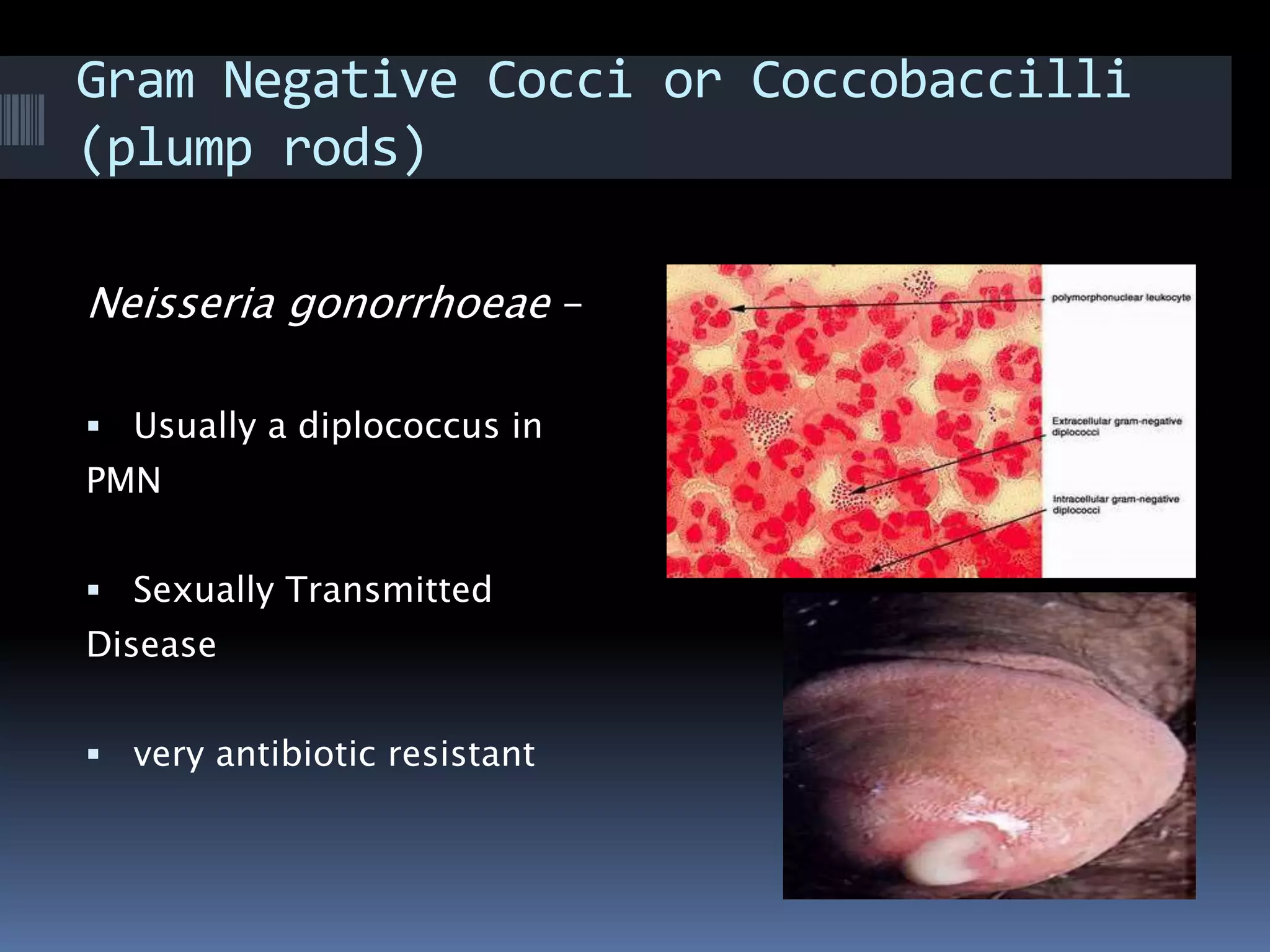
Gram negative bacteria are identified by their inability to retain crystal violet stain using the Gram staining method. They appear pink under microscopy due to the counterstain. Gram negative bacteria have an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides and a thin peptidoglycan layer, distinguishing them from Gram positive bacteria which have a thick peptidoglycan layer but lack an outer membrane. Common Gram negative bacteria that can cause human diseases include Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Legionella pneumophila, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are associated with infections like food poisoning, sexually transmitted diseases, pneumonia, and others.