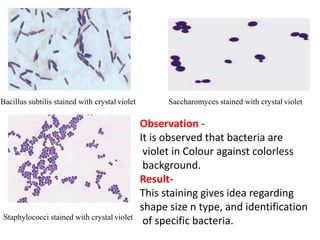
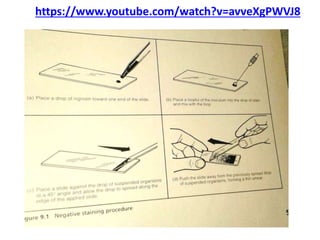
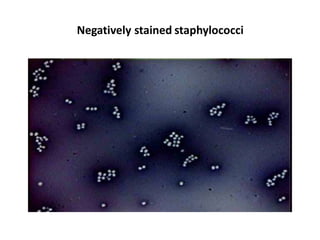
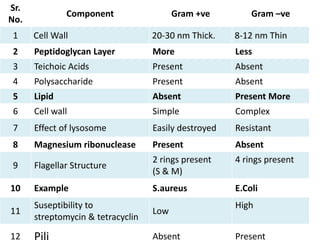
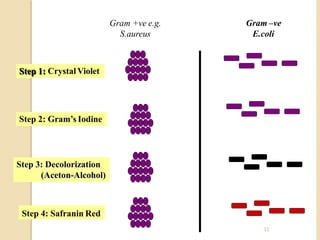
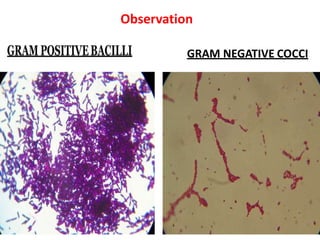
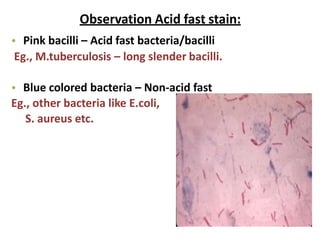
Dyes are used to stain microbes to make them visible under a microscope. There are two main types of dyes - basic dyes that stain negatively charged cell components and acidic dyes that stain positively charged ones. Simple staining uses a single dye while differential staining compares staining patterns to distinguish cell types. Gram staining differentiates between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on differences in cell wall structure and acid-fast staining identifies Mycobacteria by their waxy cell walls that retain dye after acid treatment. Proper staining techniques and use of different dyes provides important information about microbial morphology and classification.