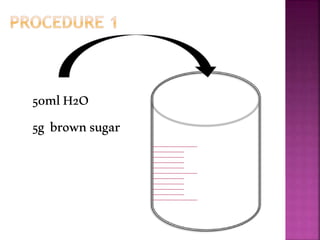
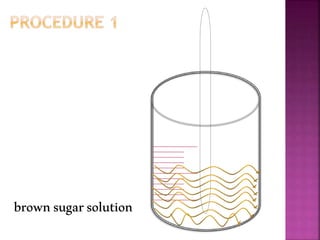
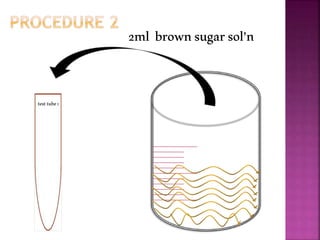
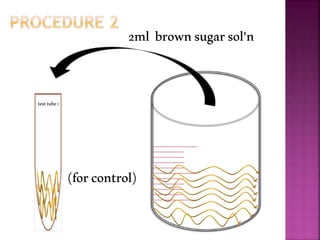
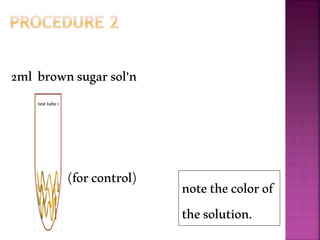
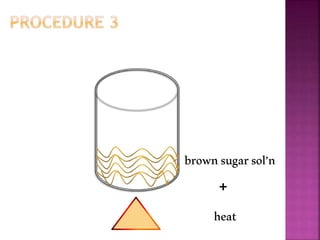
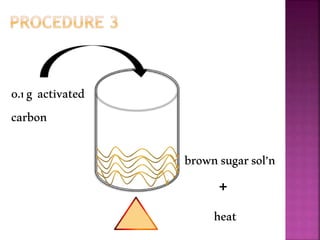
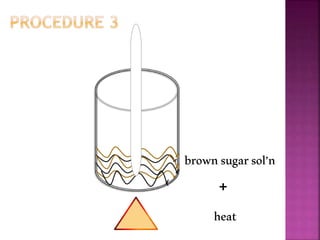
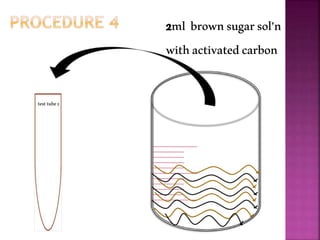
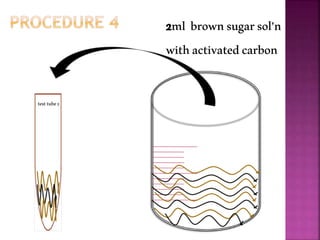
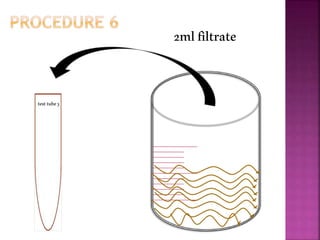
This document outlines an experiment to purify brown sugar using heat and activated carbon. Students will create a brown sugar solution, then test the solution in three test tubes: one with no treatment, one heated, and one filtered after adding activated carbon. Activated carbon is effective at decolorizing the solution because its high surface area and non-polar nature allow it to absorb non-polar impurities like those found in brown sugar. Key factors that affect the process include contact time between the solution and activated carbon, temperature, and the amount of activated carbon used.