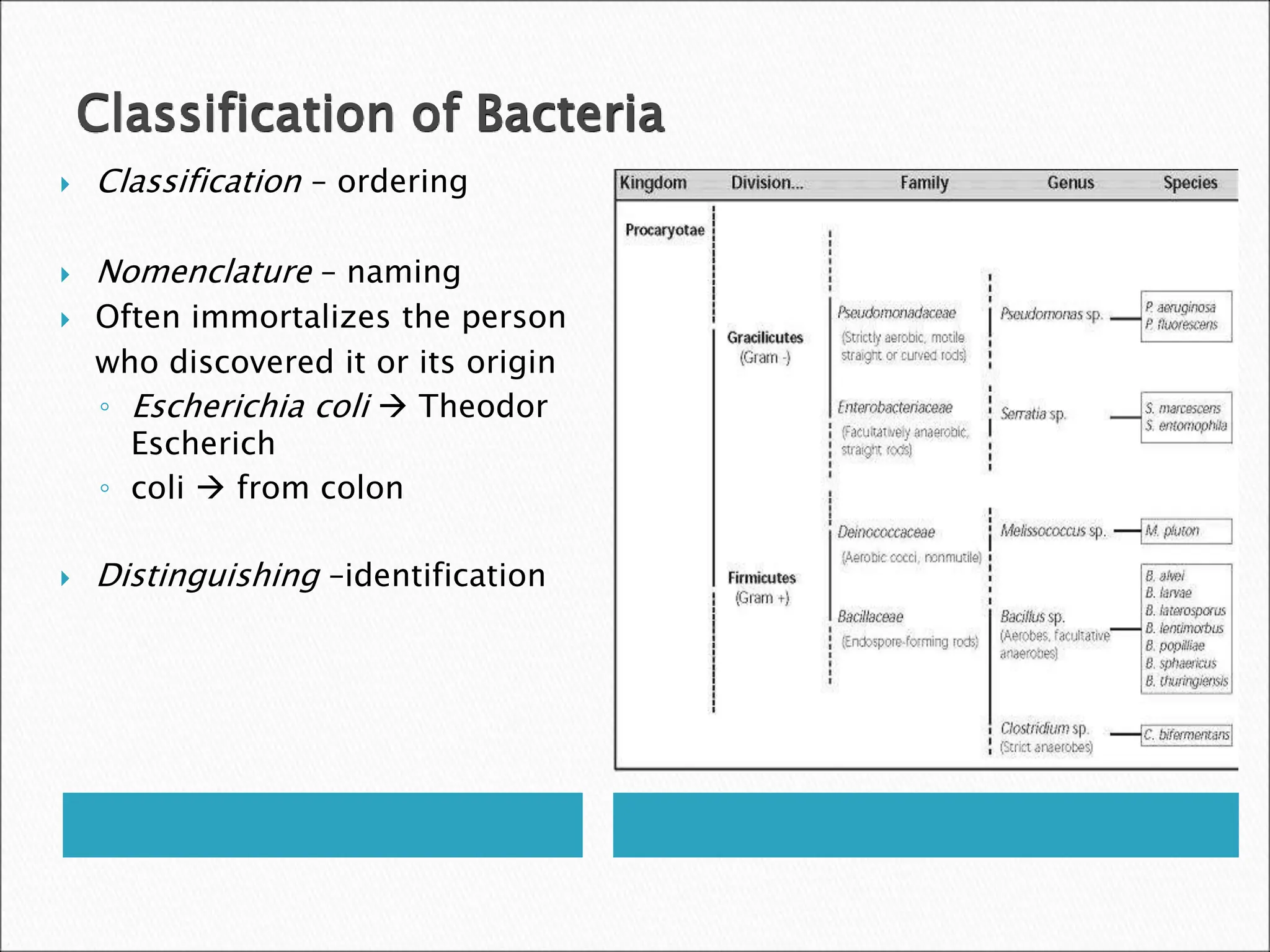
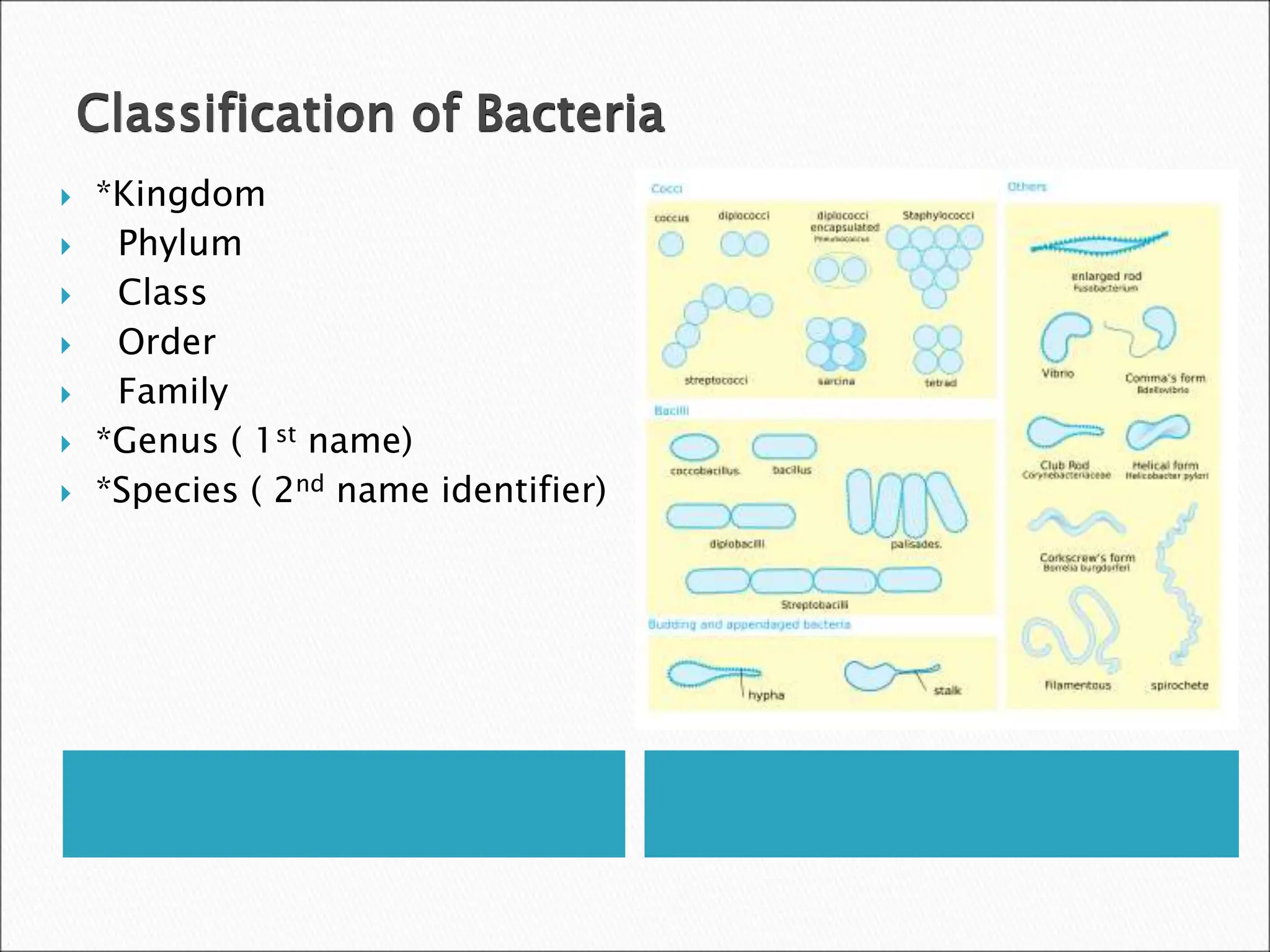
This document discusses the classification and types of bacteria. It explains that bacteria are classified based on their physical characteristics and placed in a taxonomic hierarchy of kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Some key points:
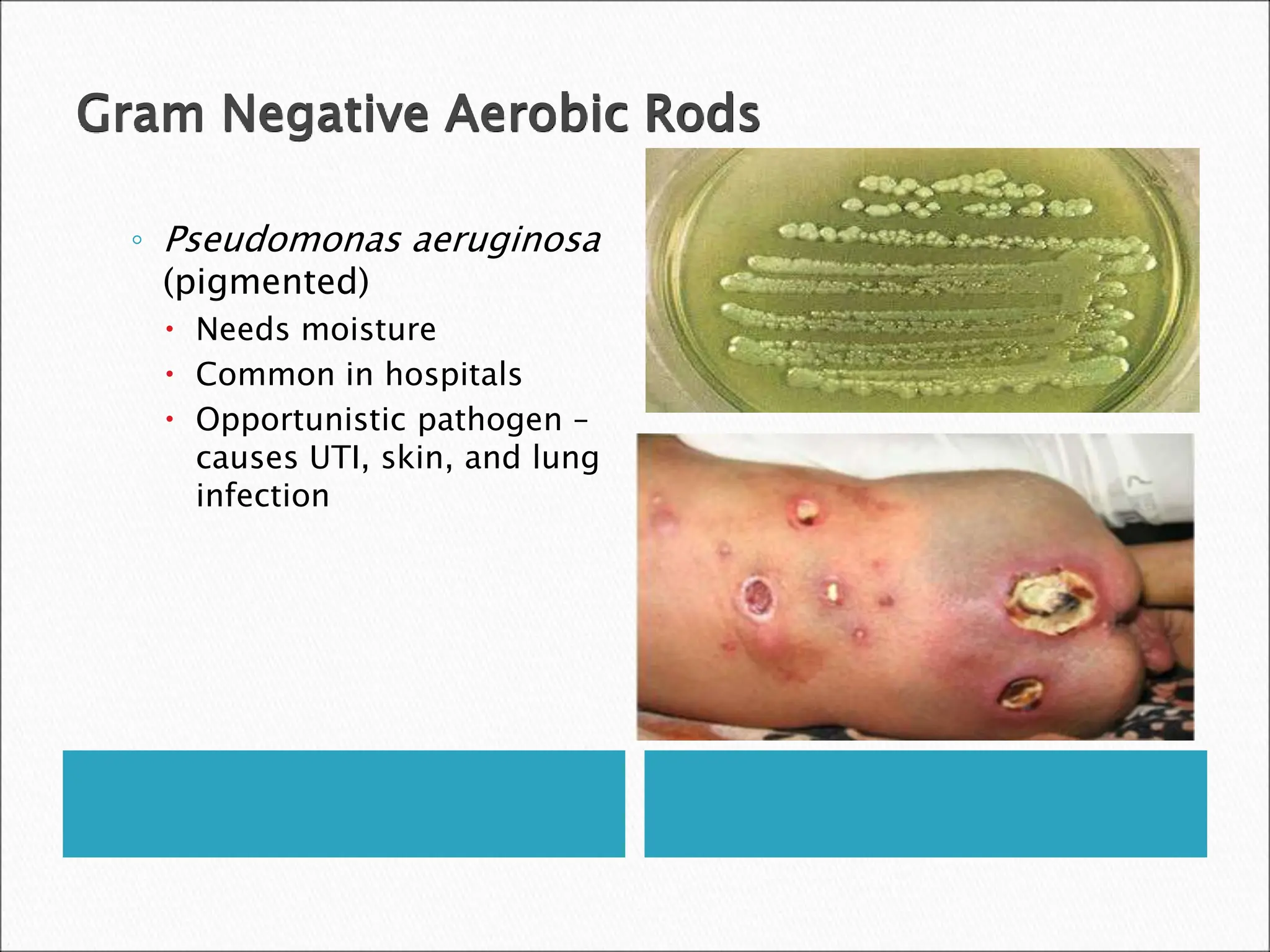
- Gram negative bacteria include spiral bacteria like Campylobacter jejuni, aerobic rods like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Legionella pneumophila, facultative rods like Salmonella and Shigella, and anaerobic rods like Fusobacterium.
- Gram positive bacteria include cocci like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, and endospore forming rods like Clostridium tetani and Clostridium diffic