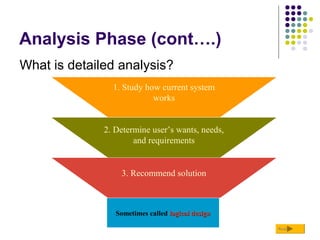
The document discusses the systems development life cycle (SDLC), which is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. It describes the key phases of the SDLC as planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. In the planning phase, a project request is submitted and feasibility is determined. In the analysis phase, preliminary investigation and detailed analysis of requirements are conducted. The design phase develops the user interface and application architecture. In implementation, programs are written, tested, installed, and users are trained. Maintenance ongoing includes corrections, adaptations to changes, and security controls.