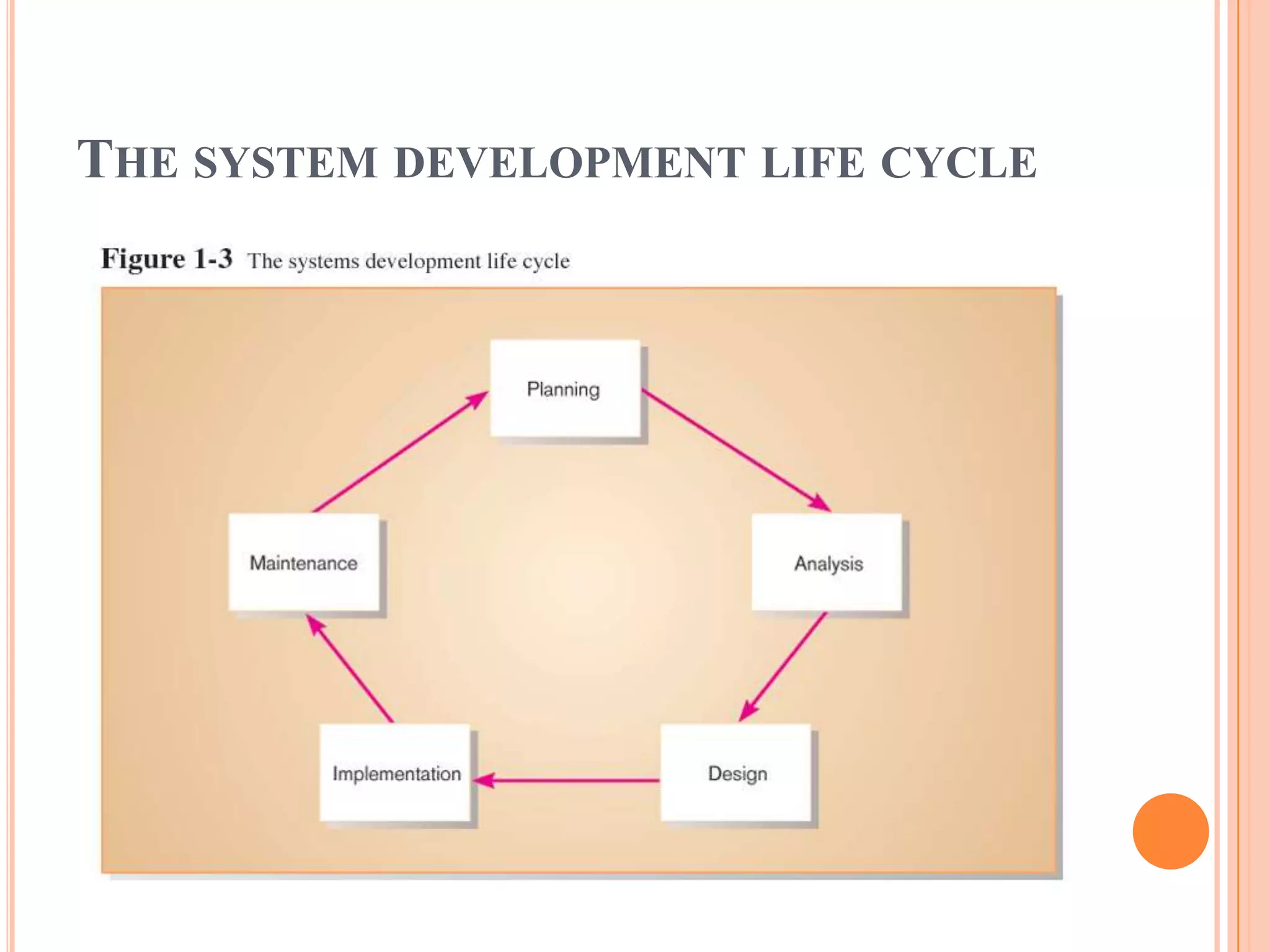
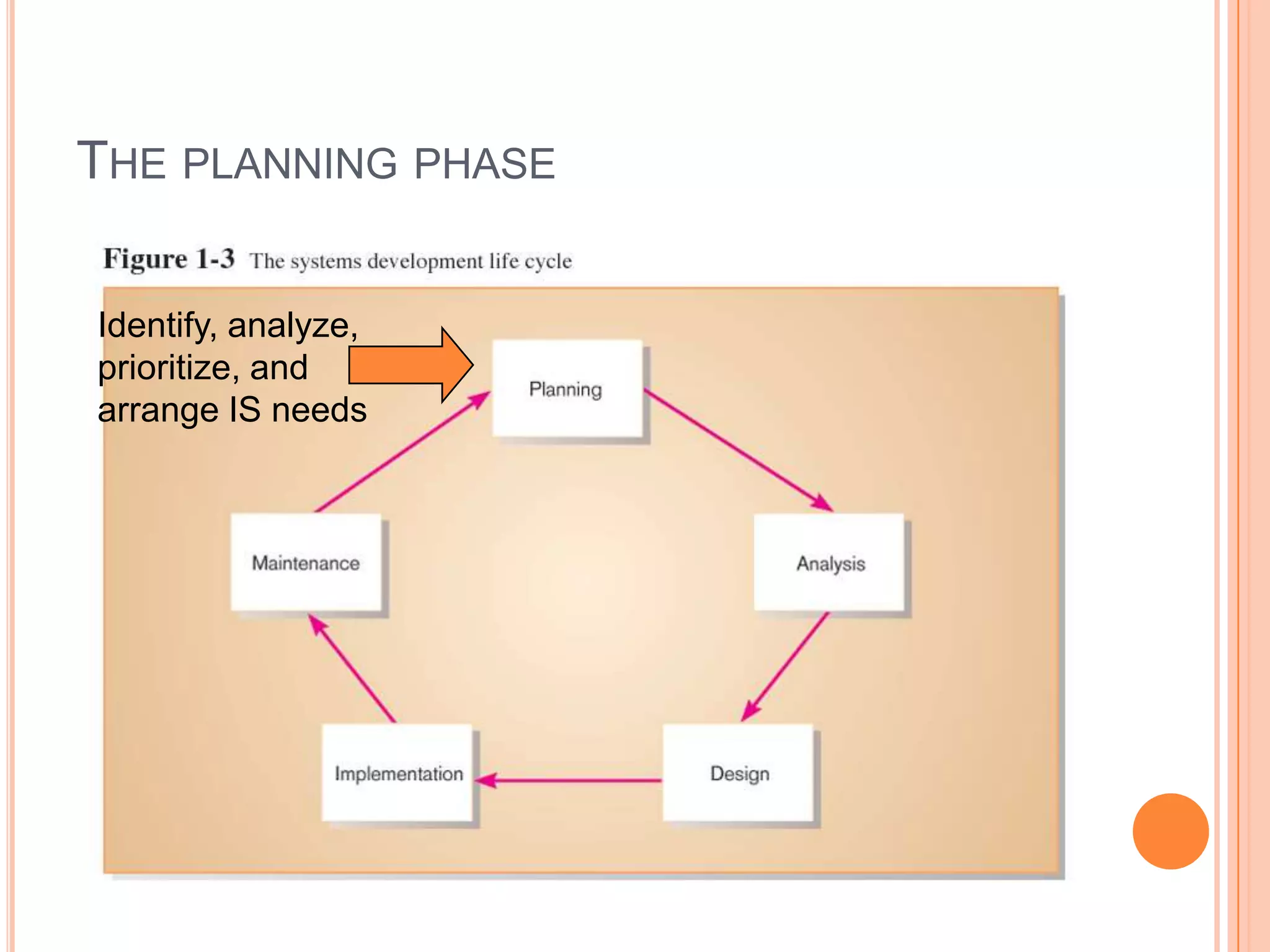
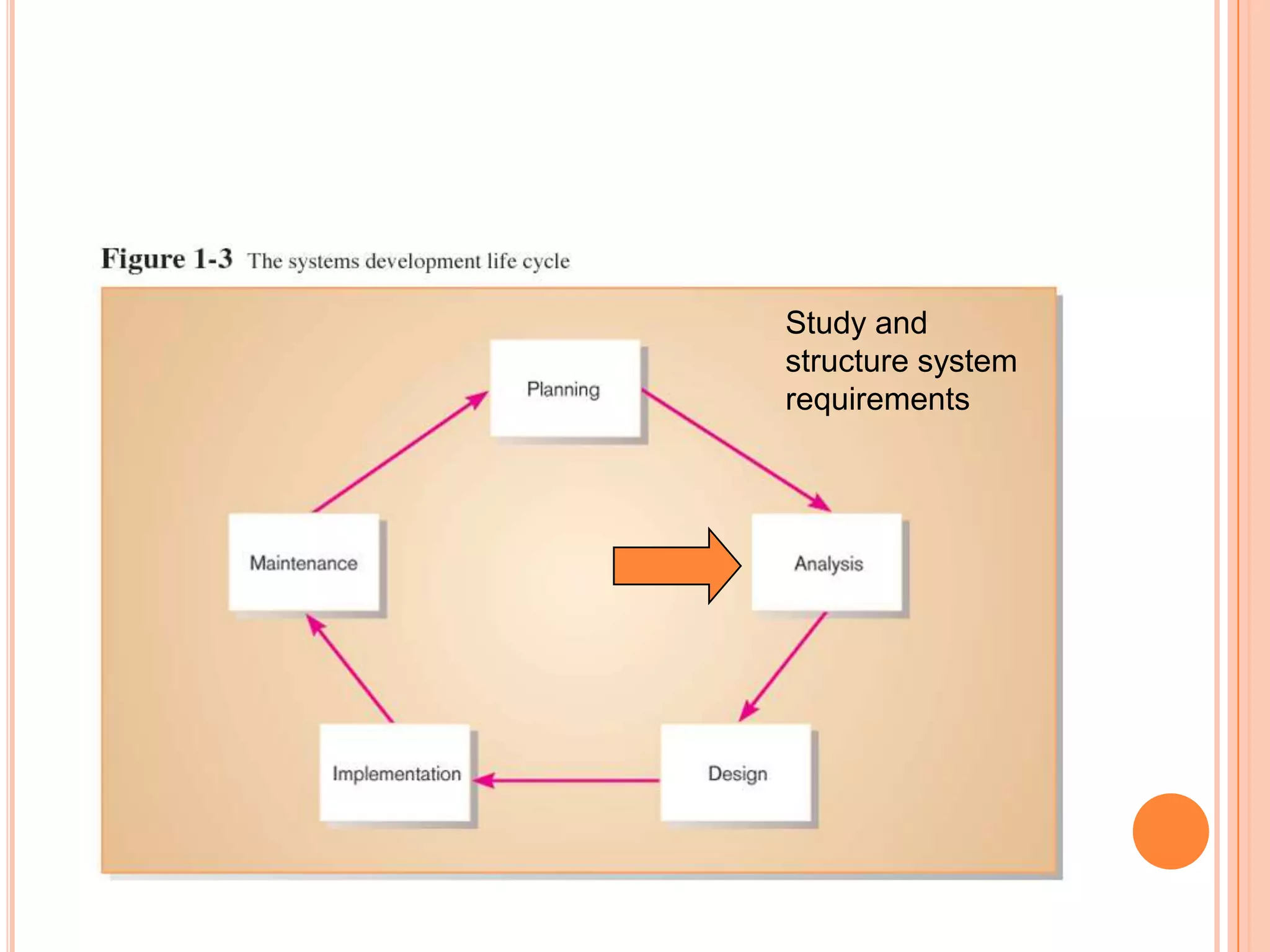
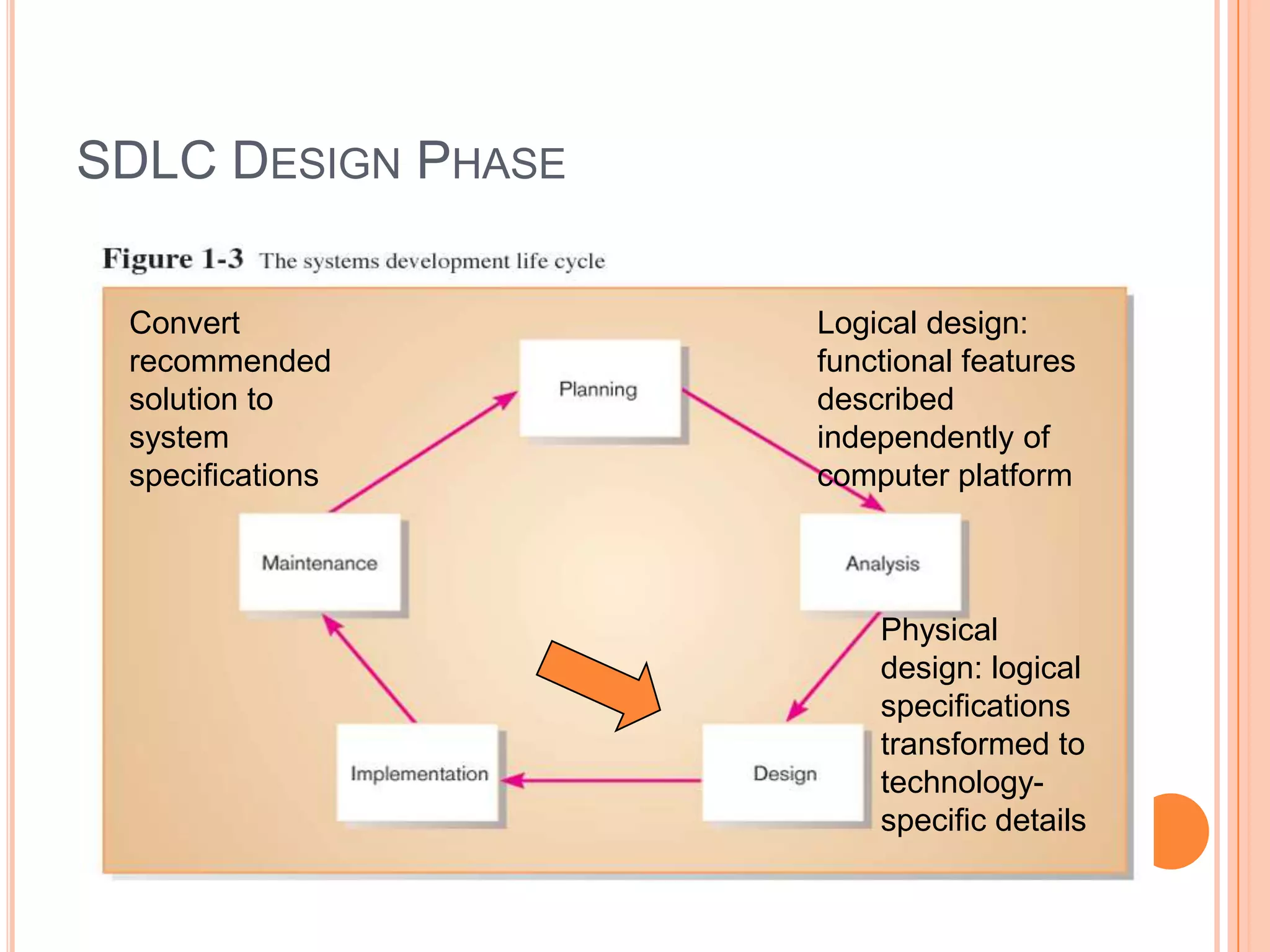
Information systems analysis and design involves developing and maintaining computer-based information systems through a system development life cycle (SDLC) with phases like planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. Analysis involves breaking down a system to understand its components and functionality, while design creates a blueprint for how the system will be developed based on requirements. Key concepts in analysis and design include requirement analysis, abstraction, refinement, modularity, and tools like data flow diagrams and data dictionaries.