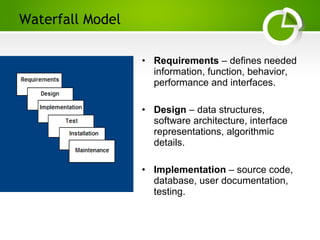
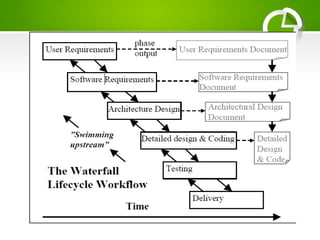
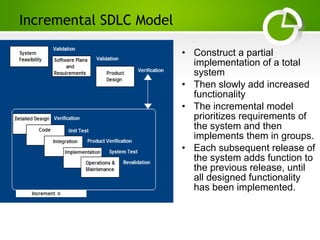
The document provides an overview of various Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) models, including Waterfall, V-Shaped, Incremental, Spiral, and Agile methods. It discusses each model's strengths, weaknesses, and ideal scenarios for use, emphasizing the importance of adapting the models to specific project needs. Additionally, it highlights the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) as a benchmark for measuring organizational software process maturity across five levels.