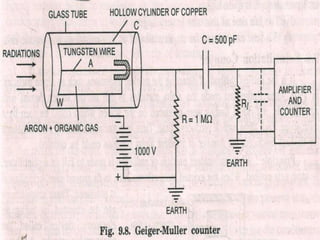
The Geiger-Muller counter is a device that detects and measures all types of radiation such as alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. It consists of a pair of electrodes with a high voltage between them. The gas used is usually helium or argon. When radiation particles enter the chamber, they ionize the gas atoms. This produces electrons that accelerate toward the anode and cause further ionization, creating an avalanche effect. To prevent continuous pulses, quenching is used to stop the successive avalanche amplification, such as by connecting an external resistance or using a specific gas. The electric field strength is calculated based on parameters like the anode voltage, wire and cylinder radii.