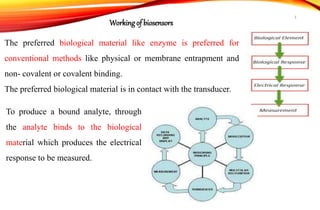
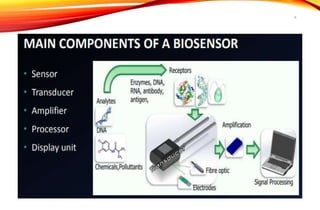
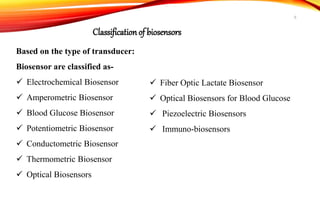
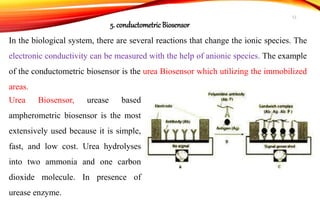
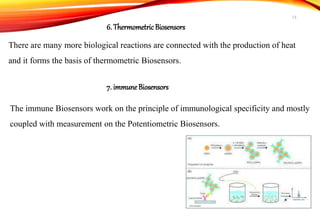
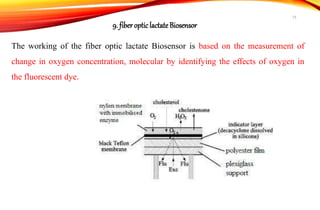
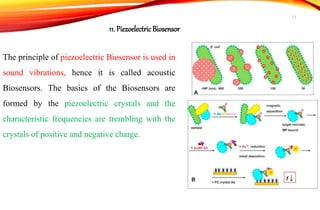
Biosensors are analytical devices that convert a biological response into an electrical signal. They have a biological sensing element and a transducer that converts the biological response into electrical signals. There are several types of biosensors classified based on their transducer, including electrochemical, optical, thermometric, and piezoelectric biosensors. Important applications of biosensors include monitoring blood glucose levels, detecting chemicals and pollutants, and quality control testing in food and medical industries.