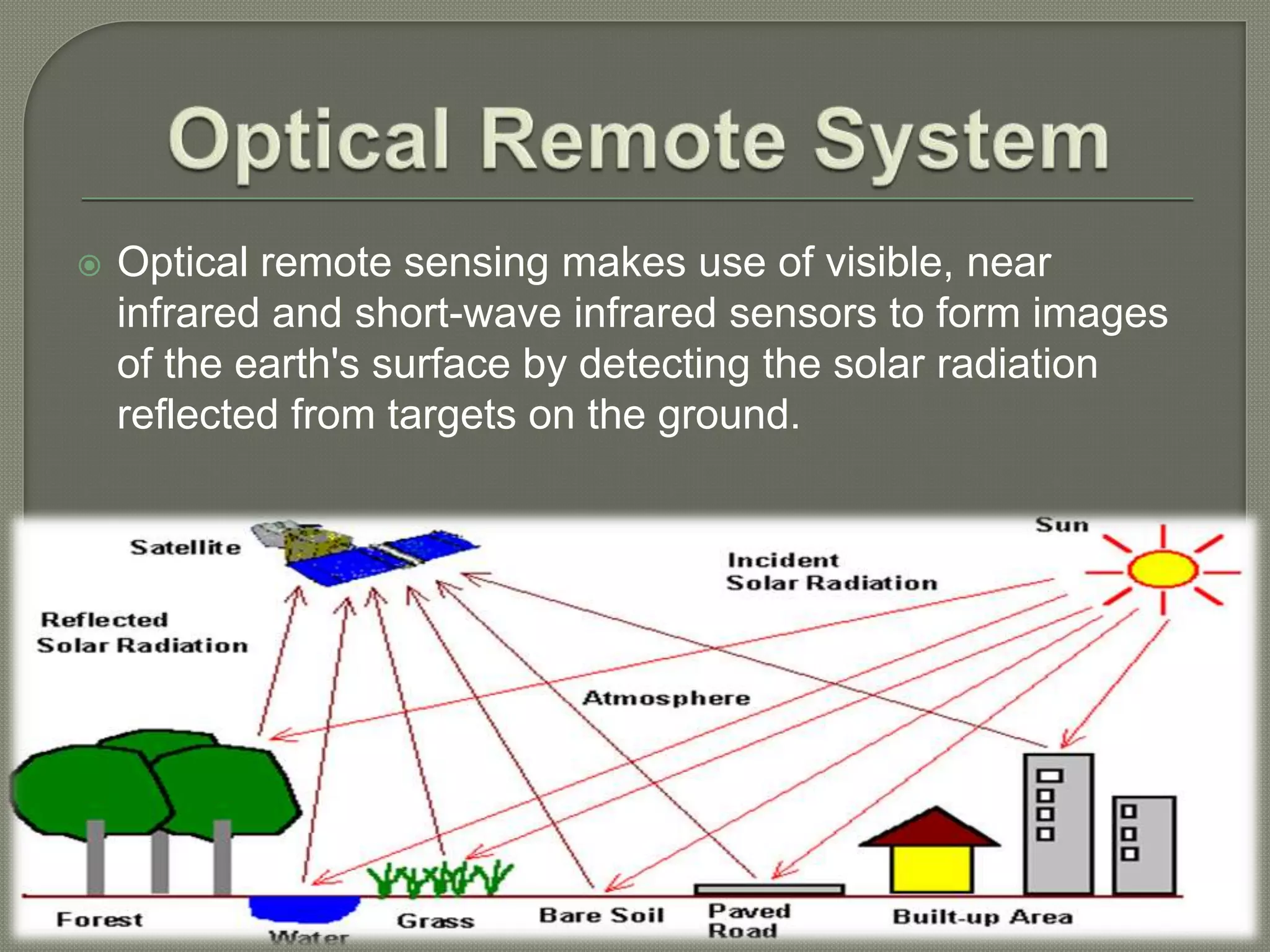
This document provides an overview of remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS). It discusses that remote sensing involves gathering information about objects from a distance using sensors, including passive techniques like photography and active techniques like radar. It also outlines key remote sensing concepts and different sensor types. The document then defines GIS as a system for inputting, storing, analyzing and outputting geospatial data to support decision-making. It lists some common GIS functions and applications.