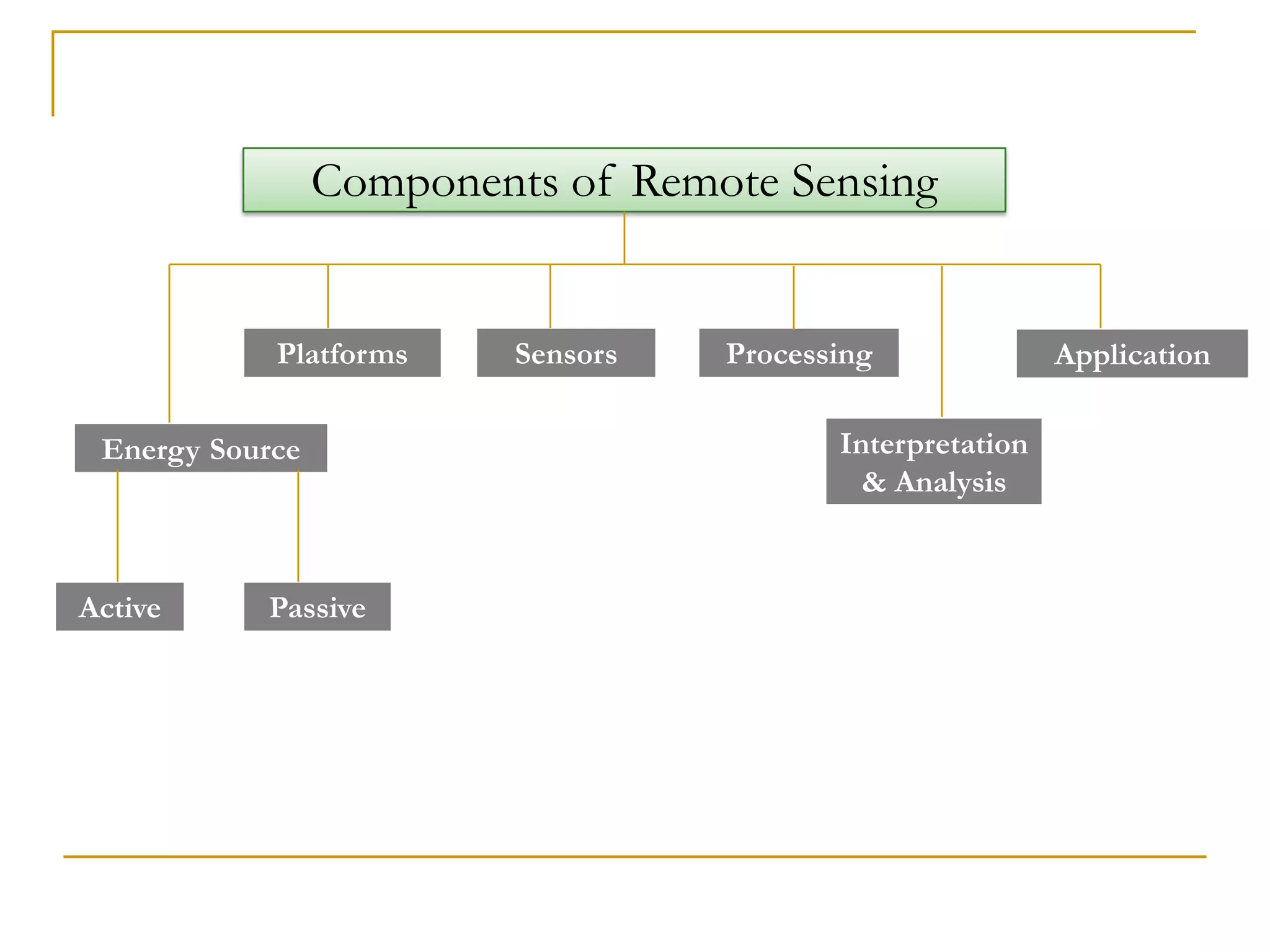
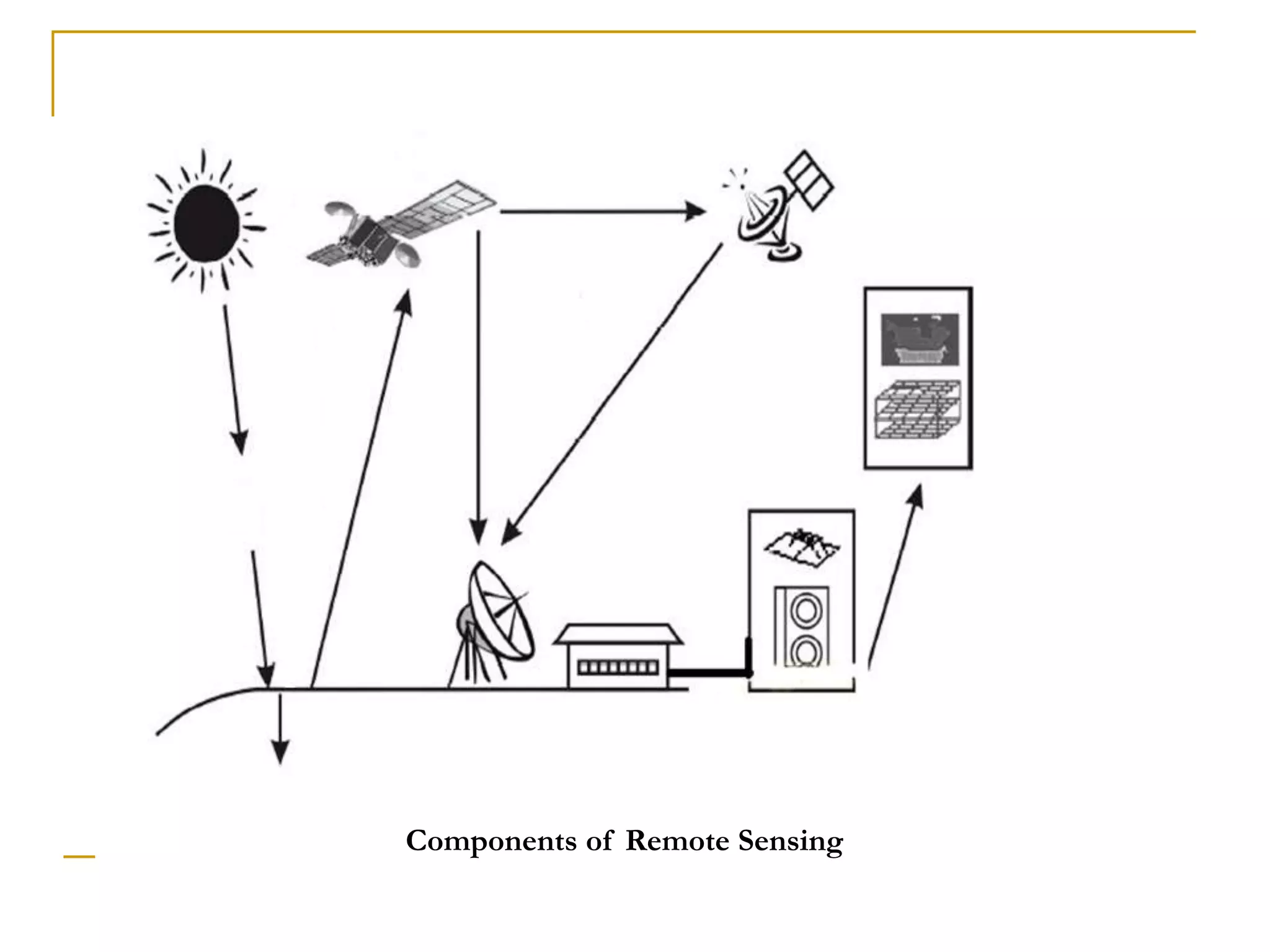
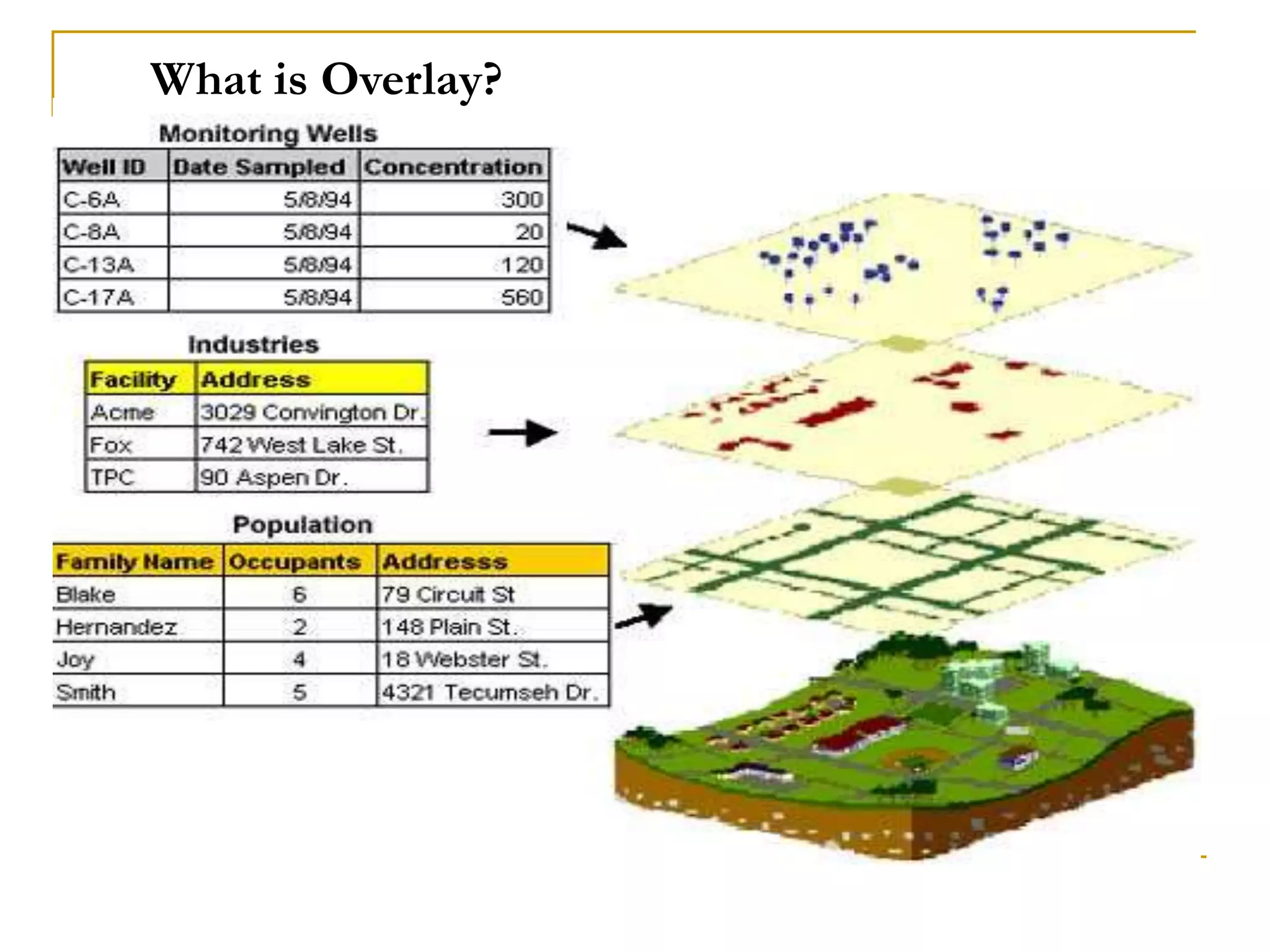
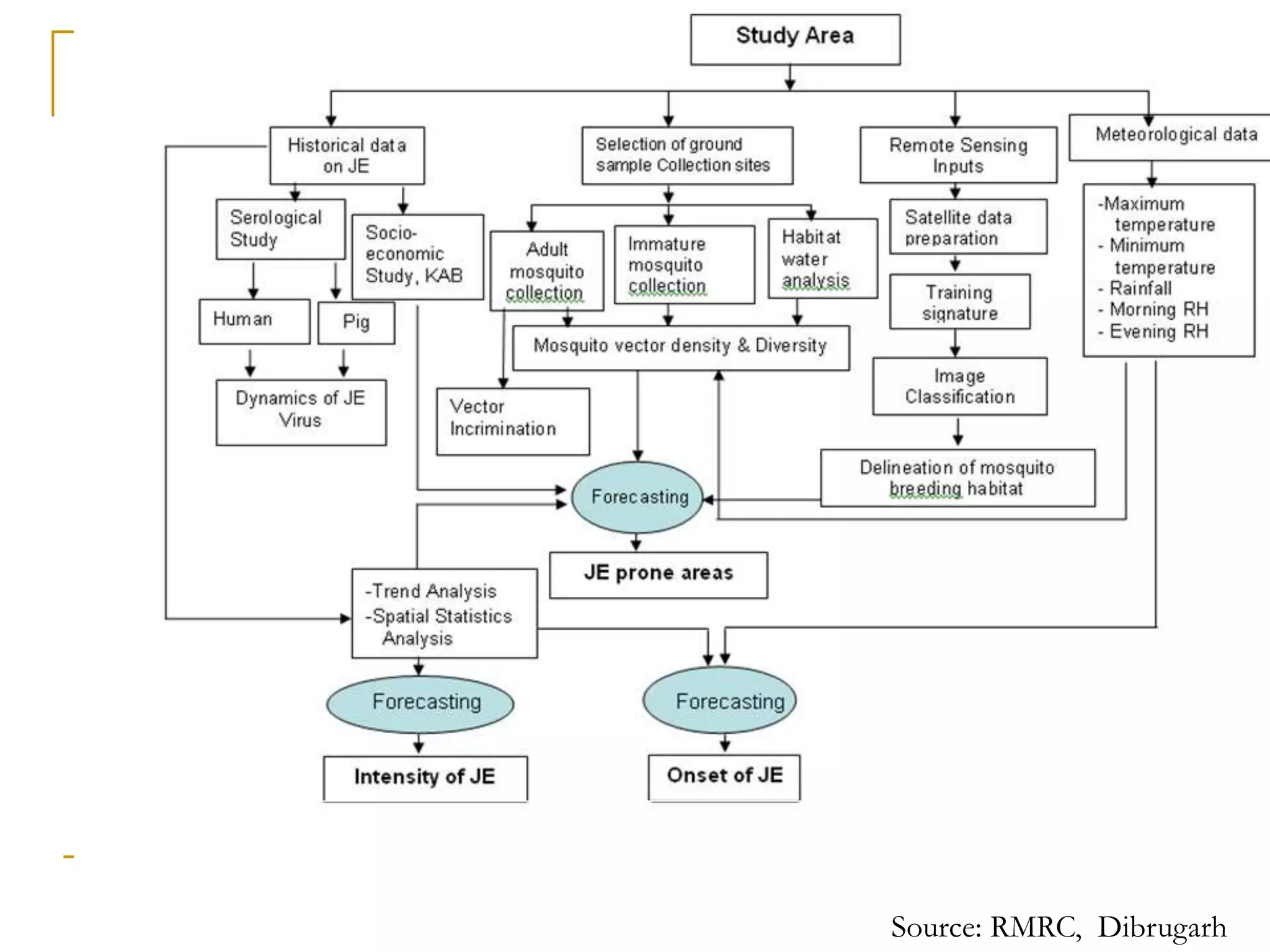
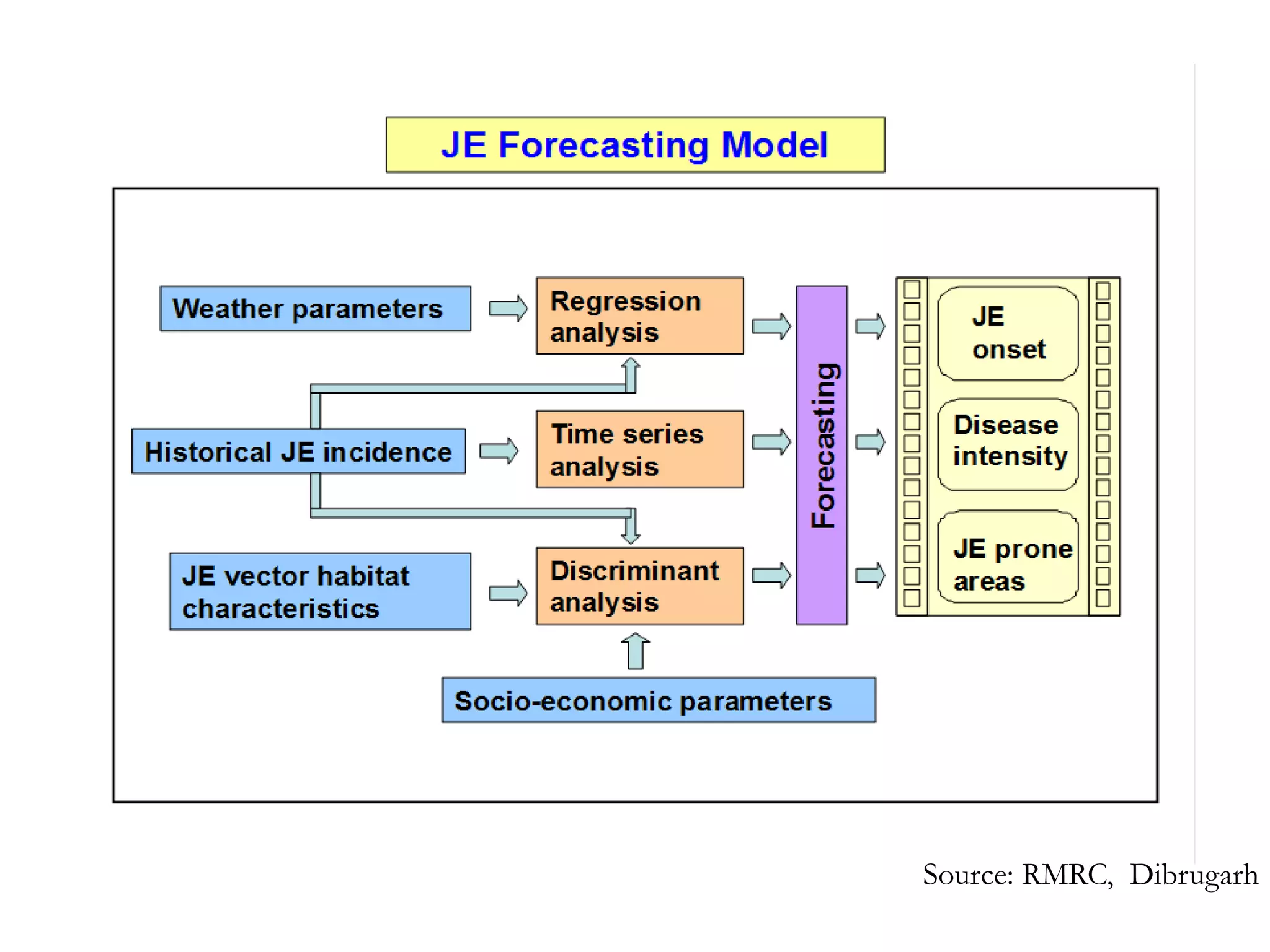
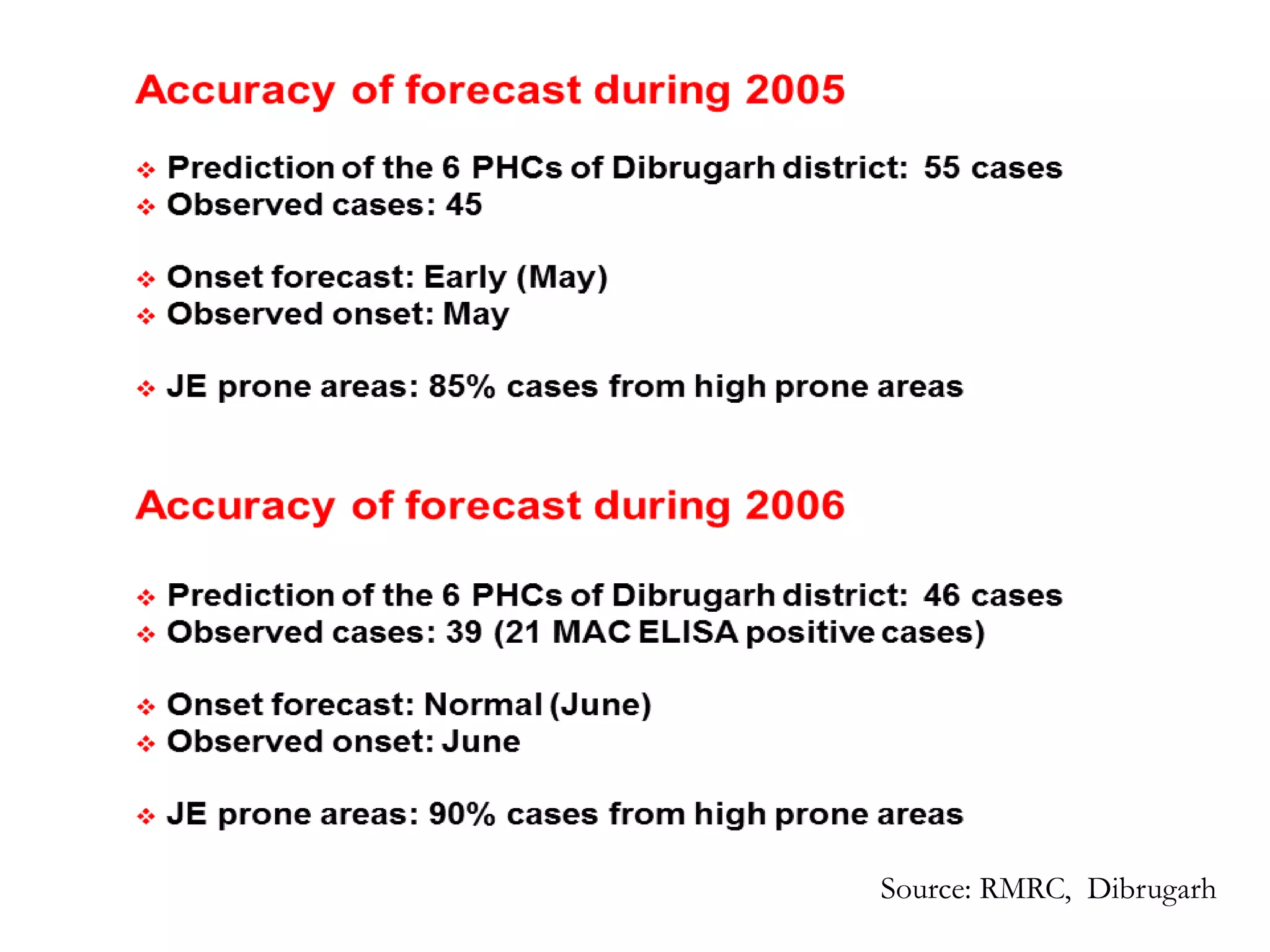
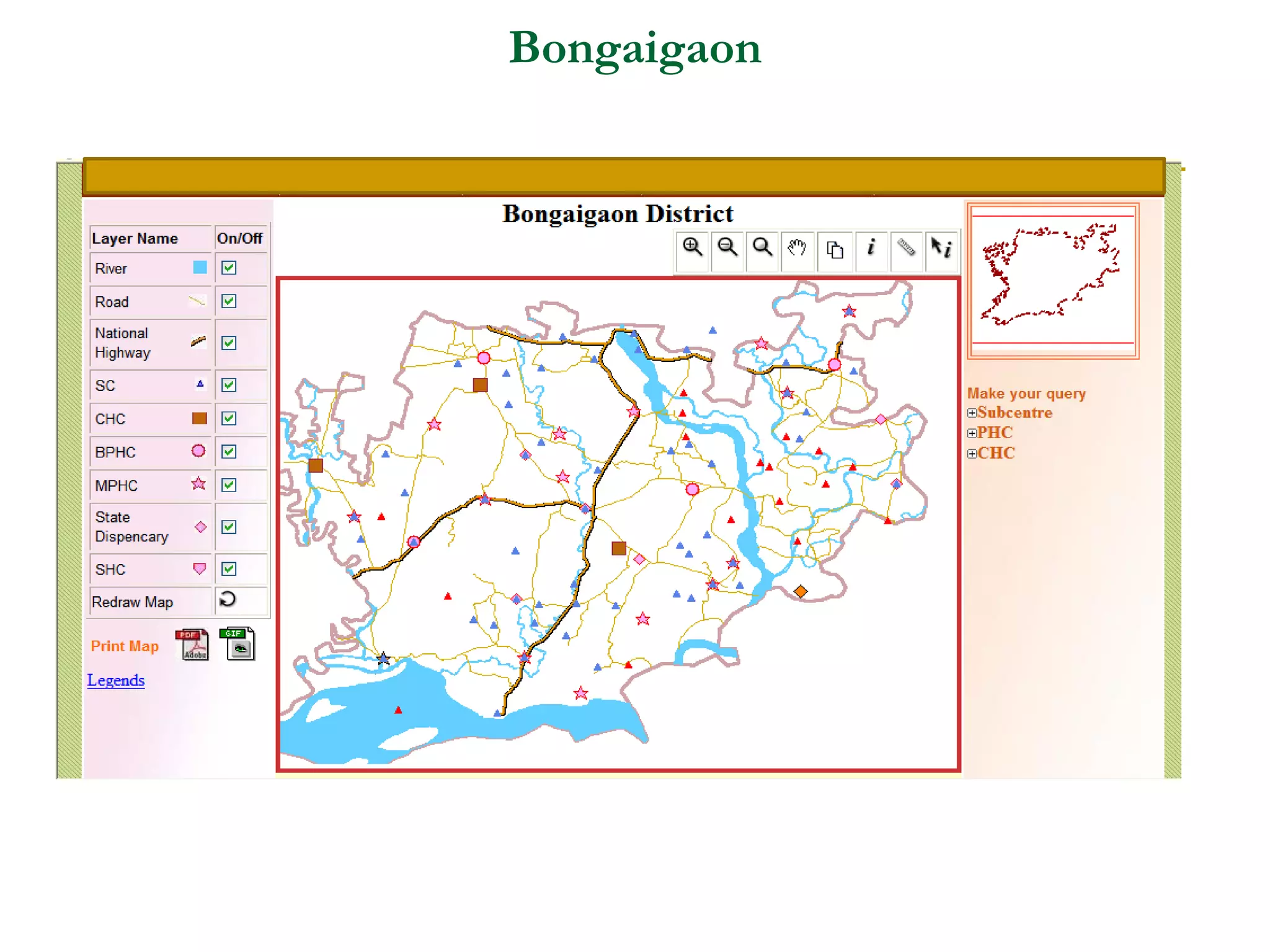
Remote sensing uses sensors to acquire information about objects or areas without direct contact. It can be passive, using natural radiation sources, or active, using artificial sources. GIS organizes spatial data in databases and allows for visualization and analysis. Both tools have many applications in public health, including disease surveillance, outbreak prediction and response, health resource allocation, and monitoring interventions over time. In Assam, a project used remote sensing and GIS along with epidemiological data to develop an early warning system for Japanese encephalitis outbreaks from 2002-2006. The NRHM in Assam has also created a web-based GIS system for health facility planning and management. Overall, remote sensing and GIS are valuable tools for improving public health when