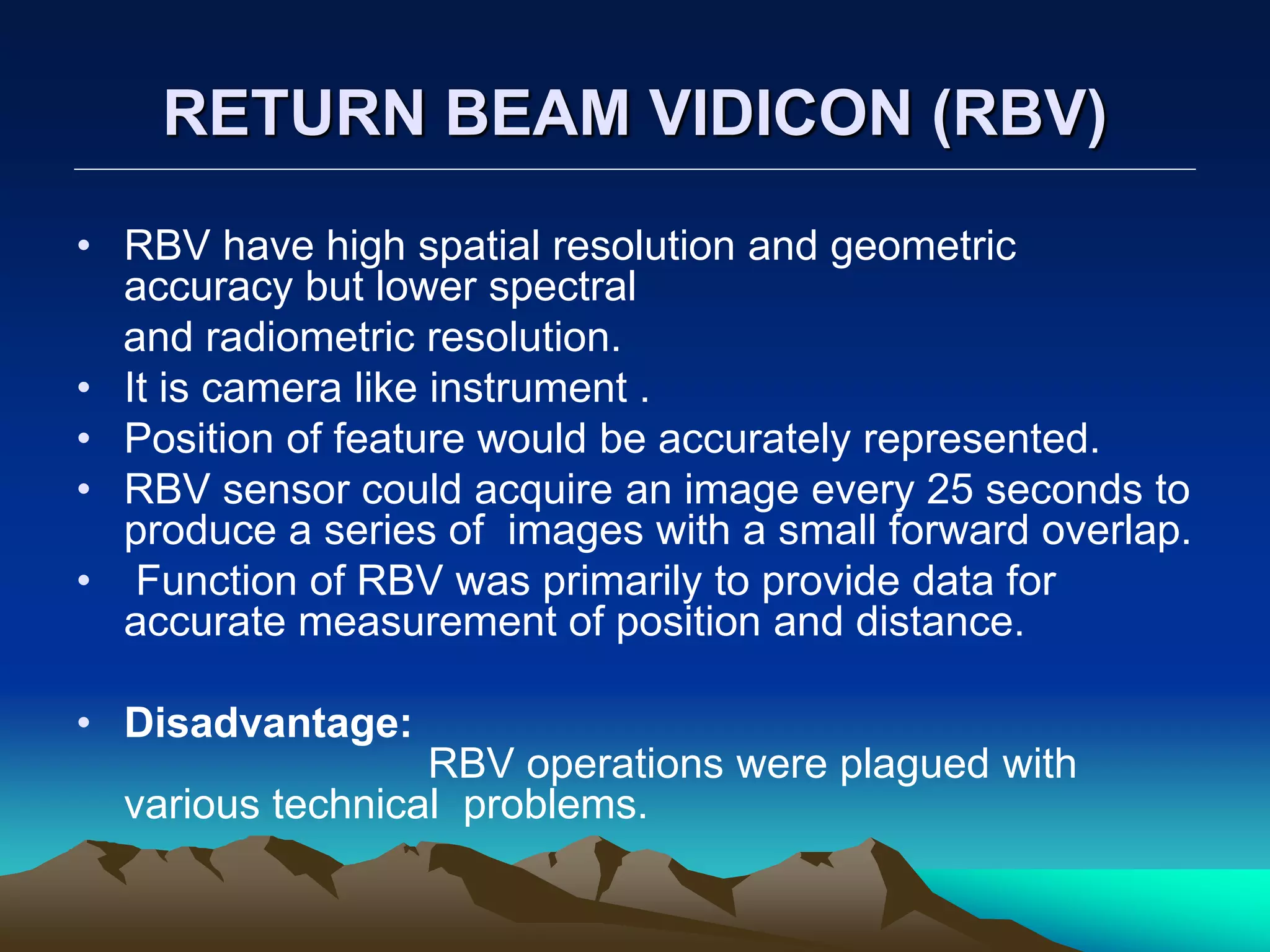
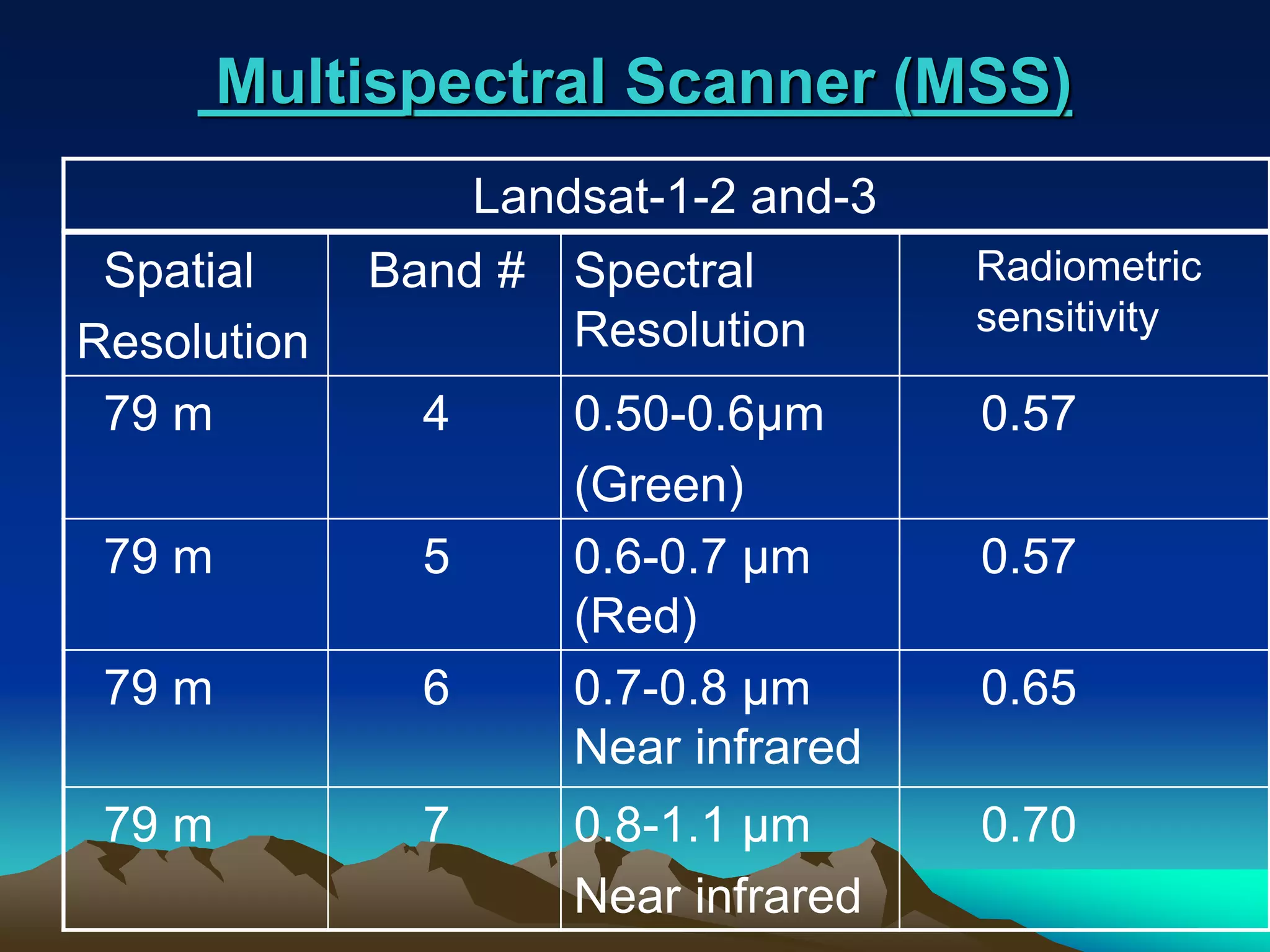
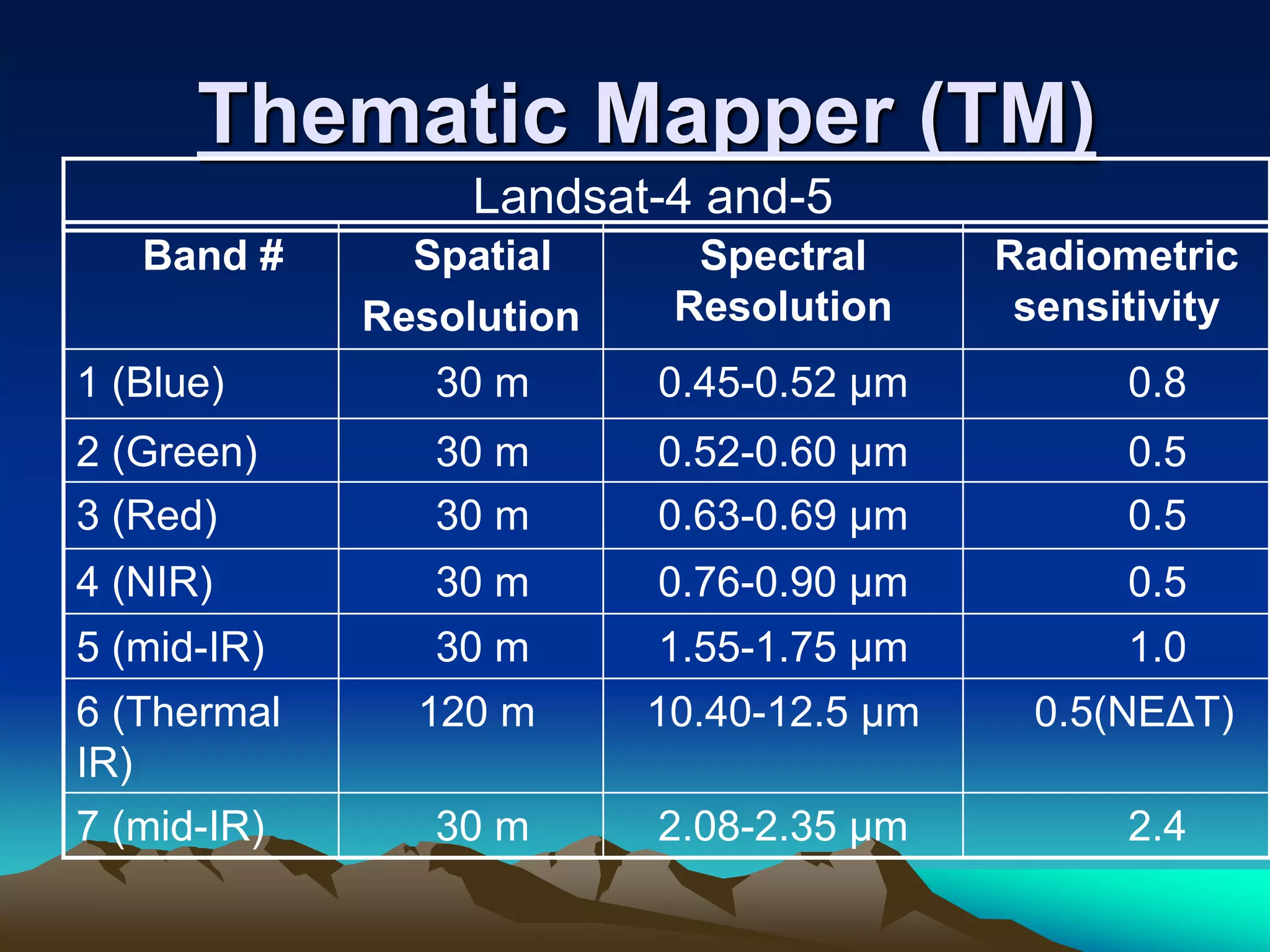
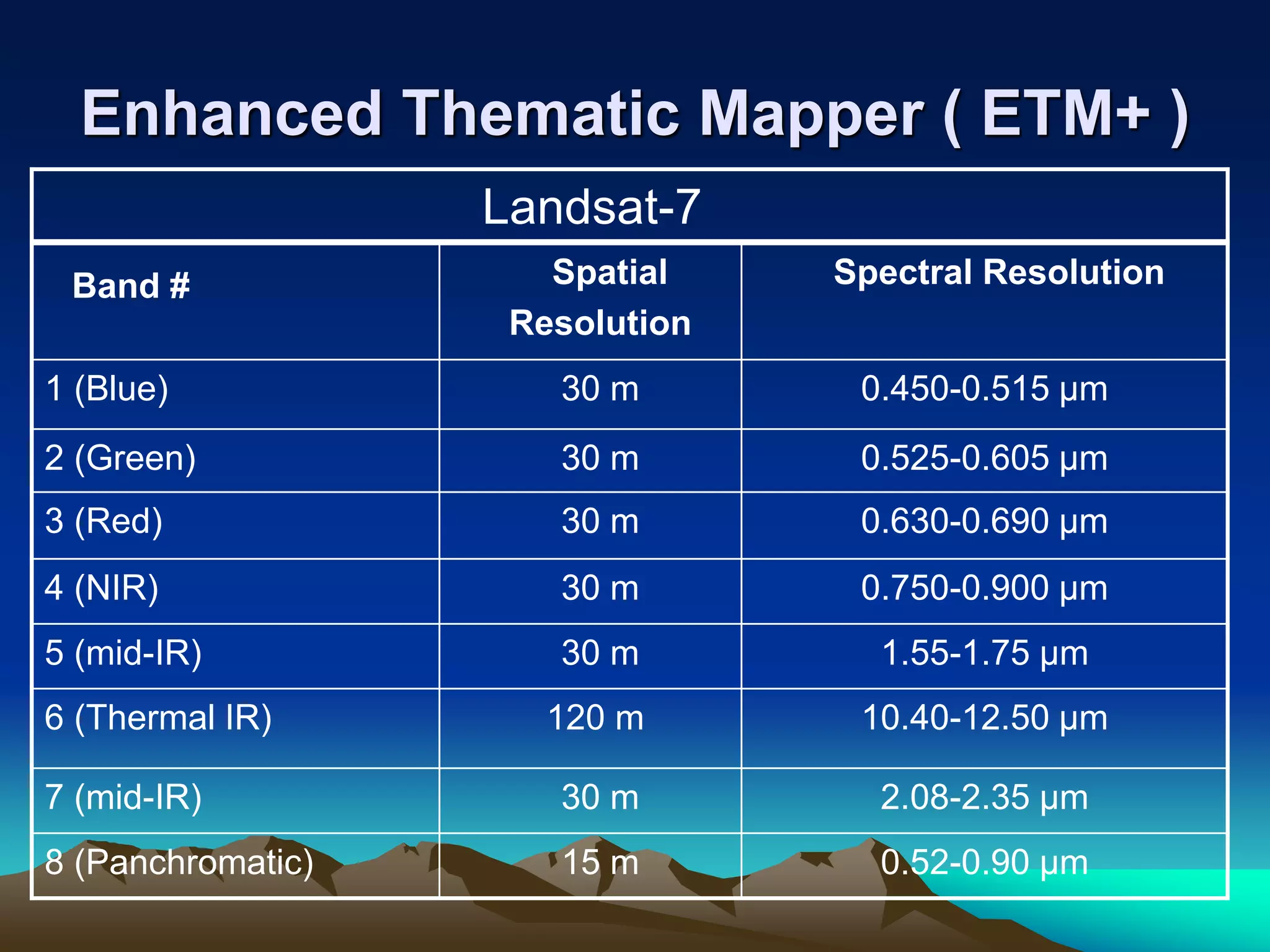
Landsat is a series of Earth observation satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. The first Landsat satellite was launched in 1972 and subsequent satellites were launched through 2013 to acquire global land data. Landsat satellites carry imaging sensors to collect medium-resolution multi-spectral images of the Earth's surface on a 16-day repeat cycle. The images are used to observe changes in land use, monitor deforestation, and detect water pollution among other applications. Six Landsat satellites have been launched to date, each carrying improved sensors from the Multi-Spectral Scanner to the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus. Landsat provides the longest continuous space-based record of Earth's surface.