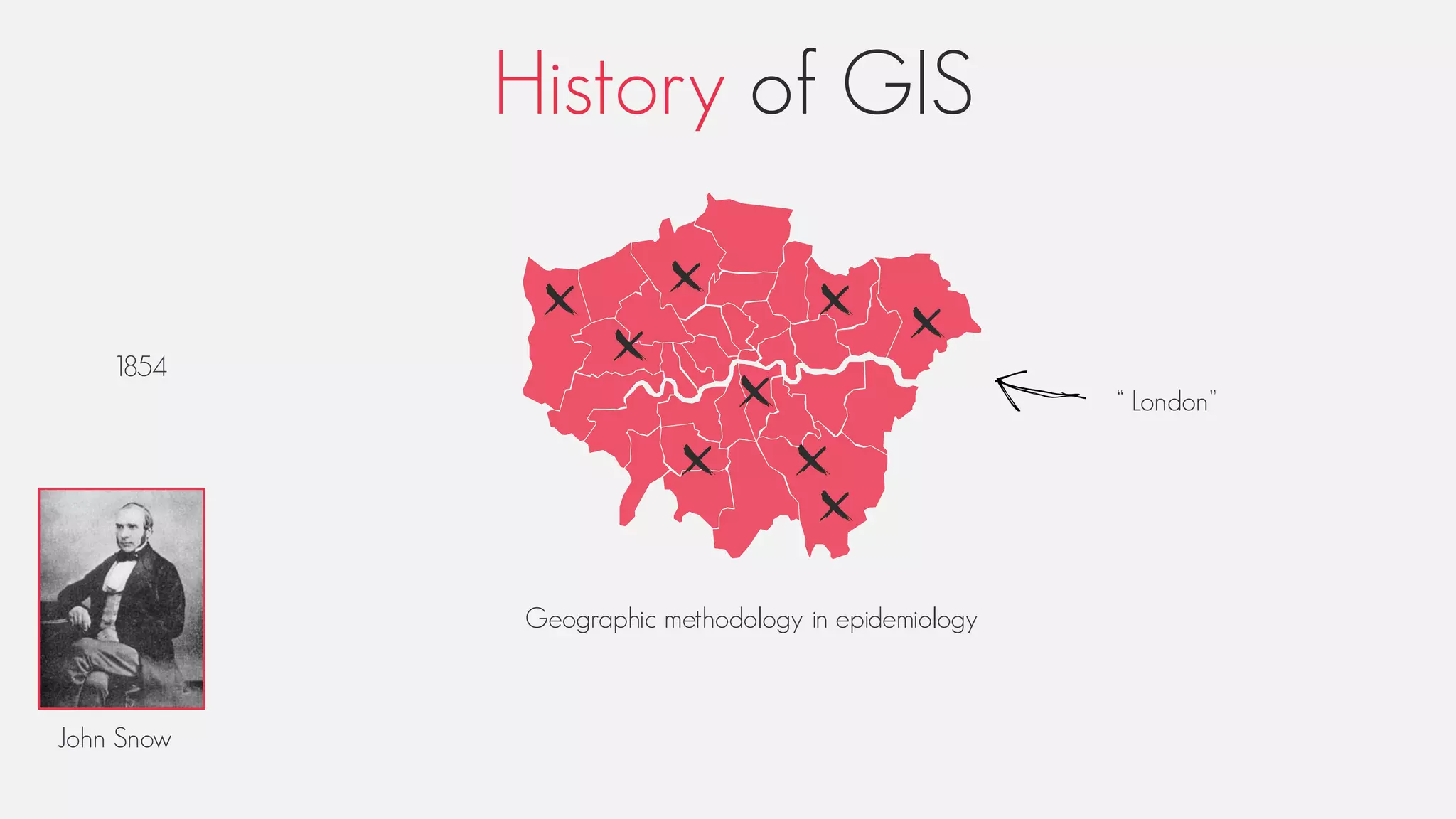
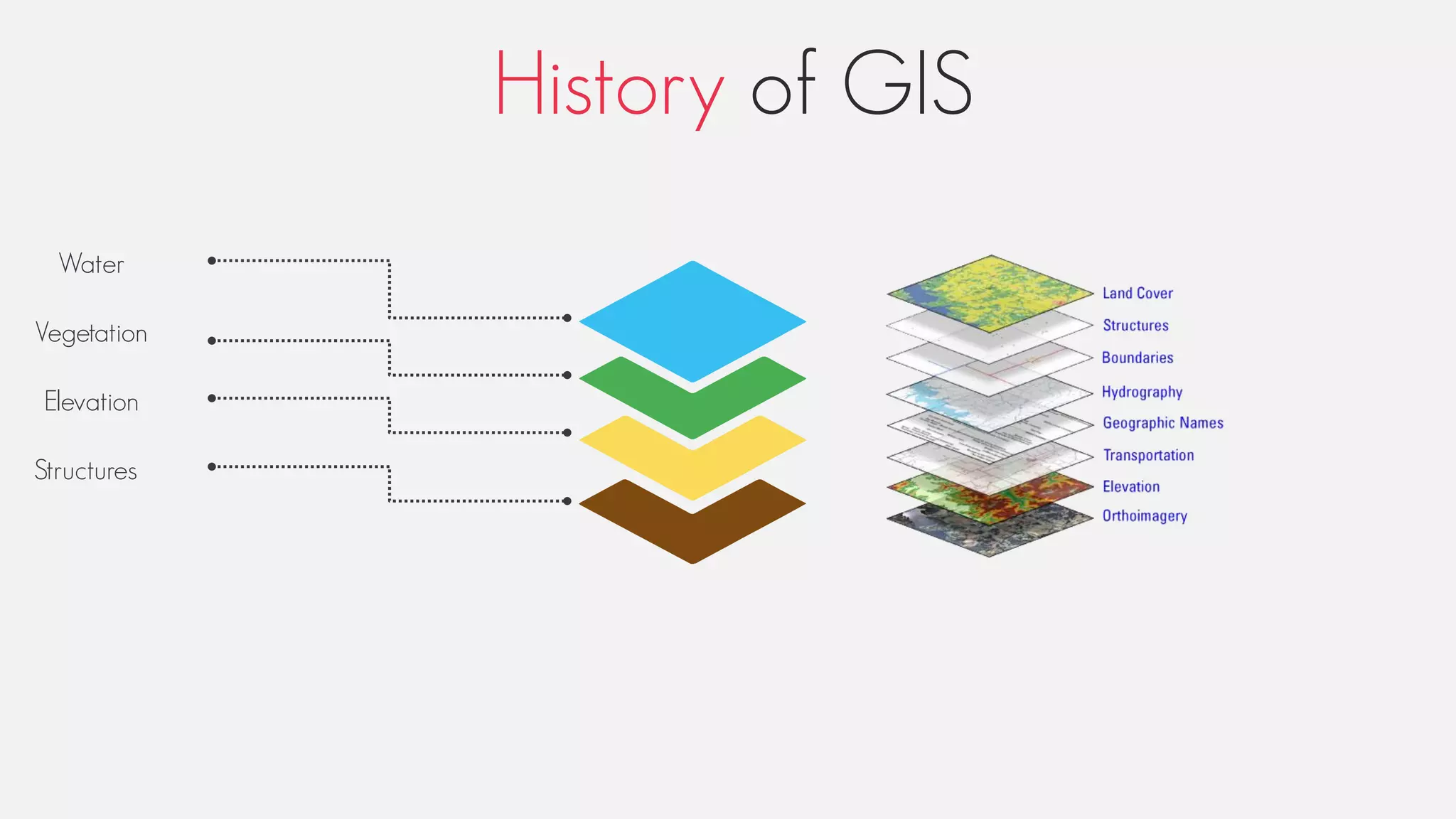
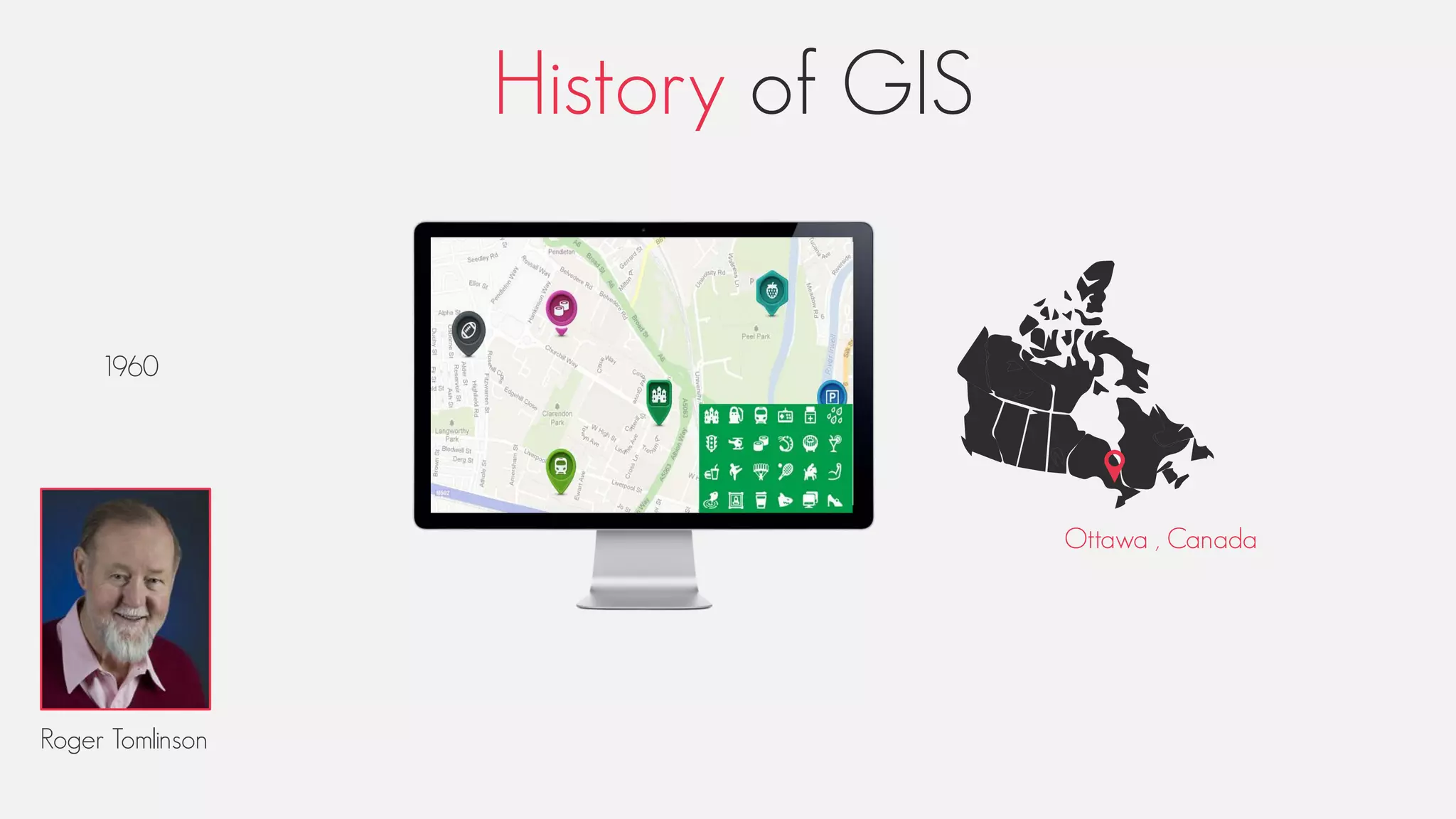
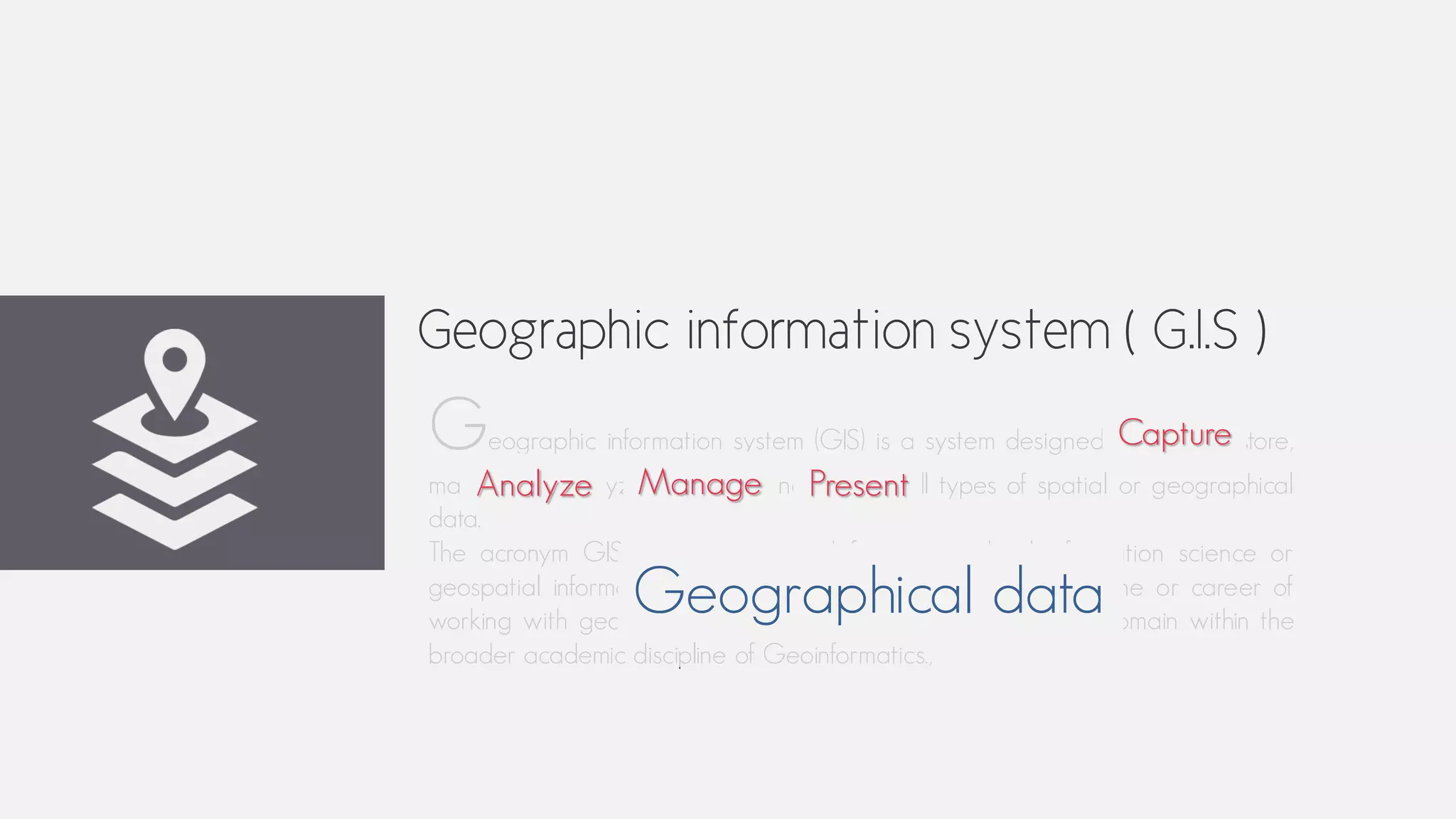
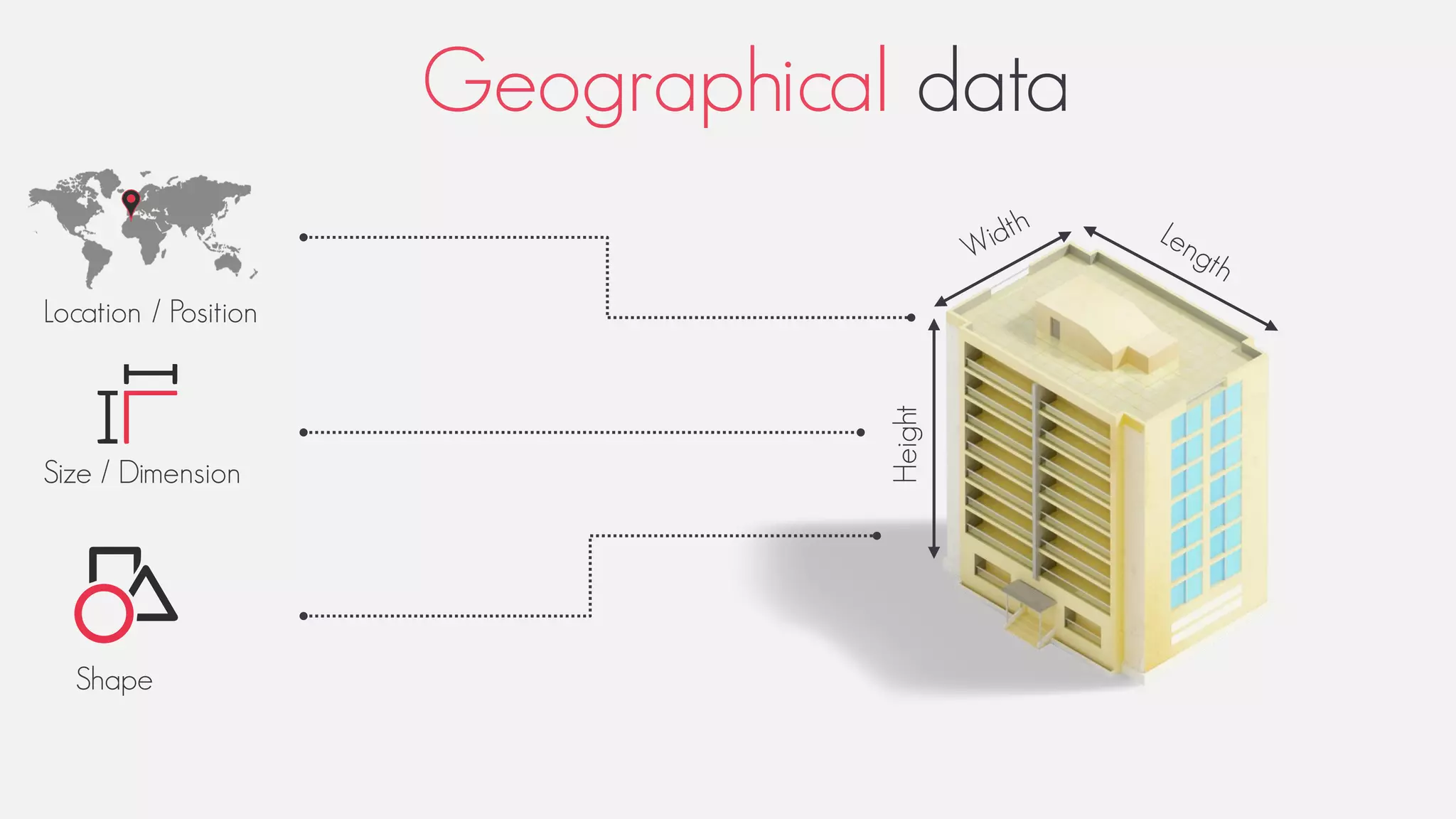
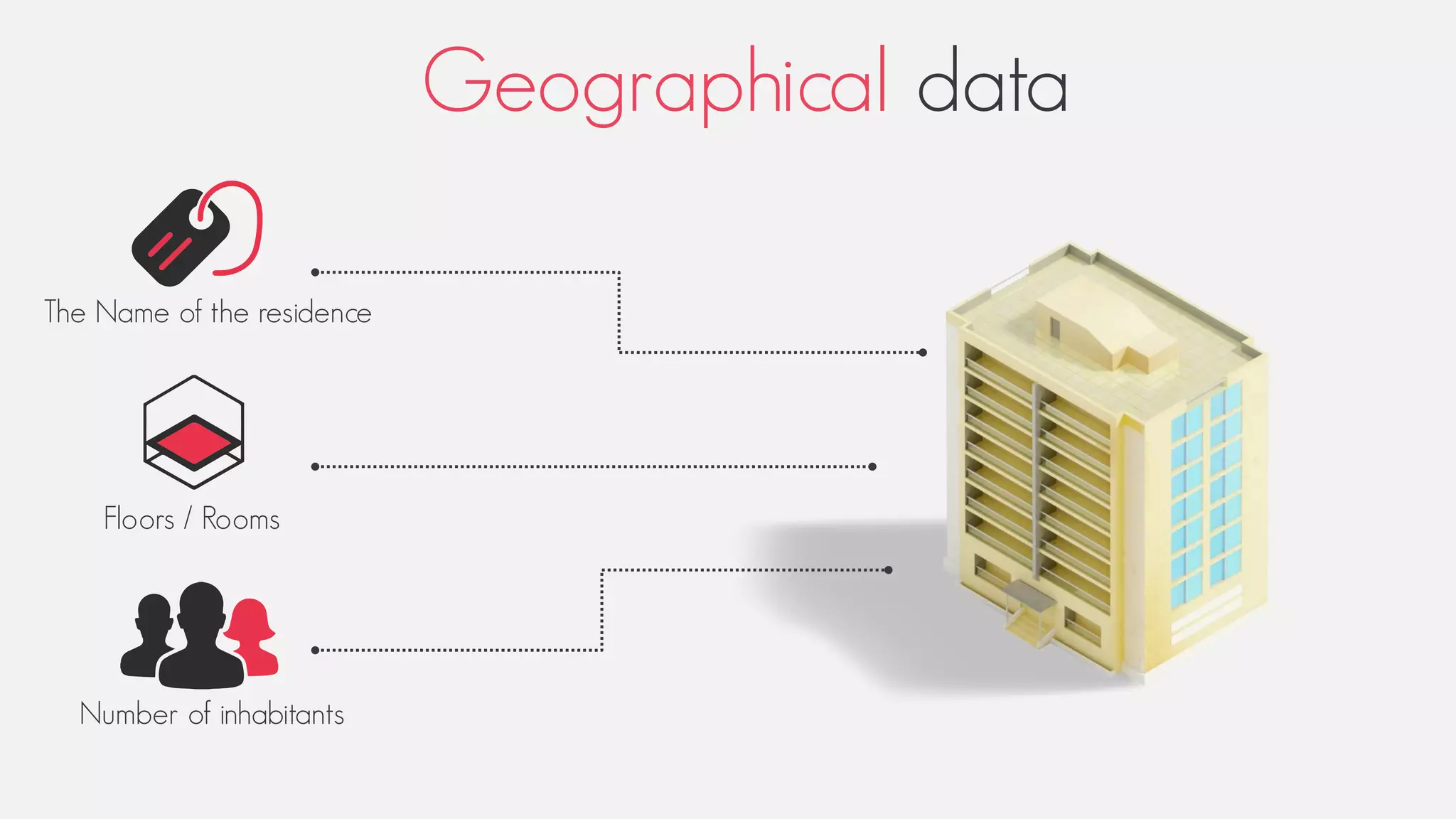
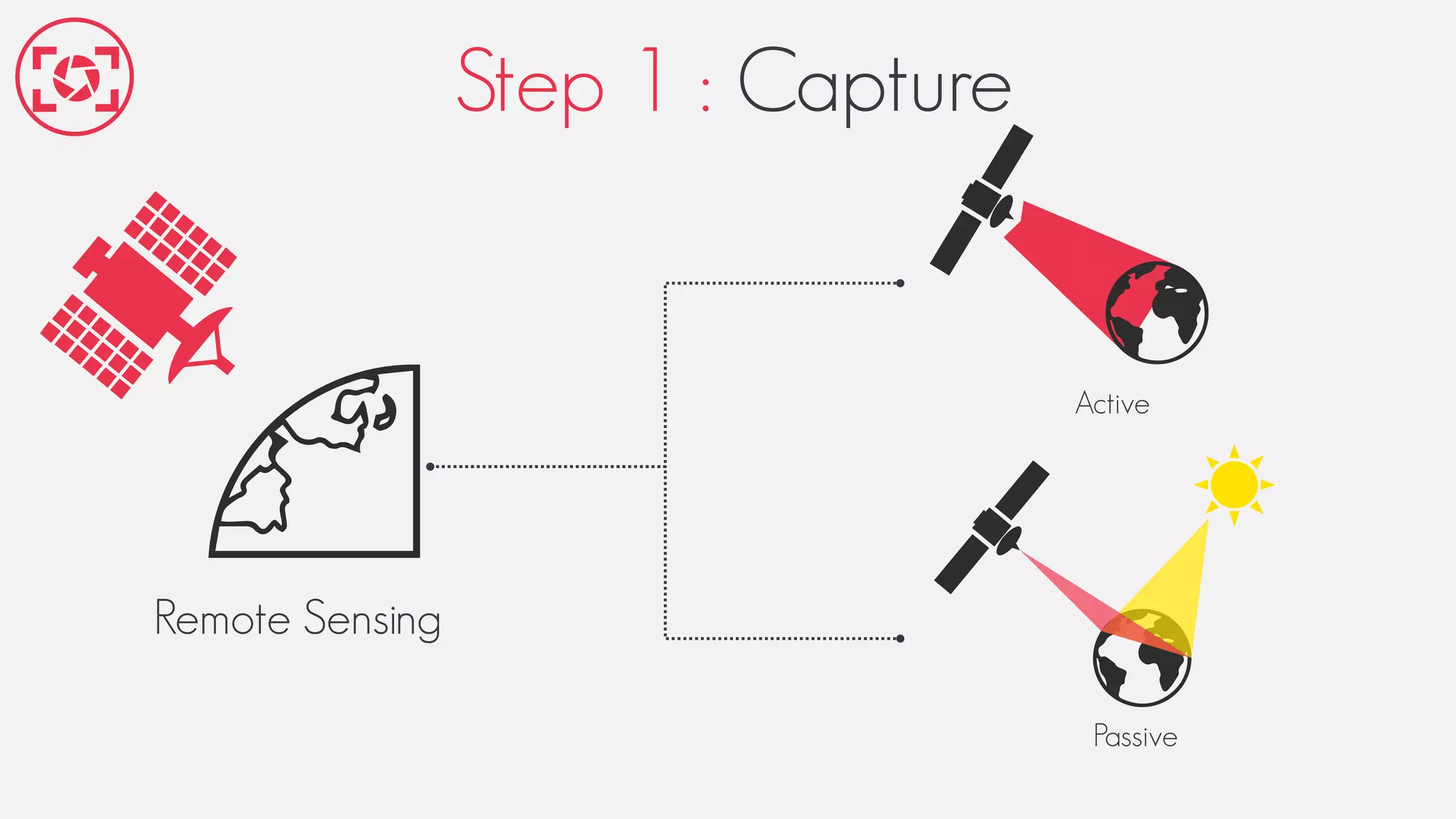
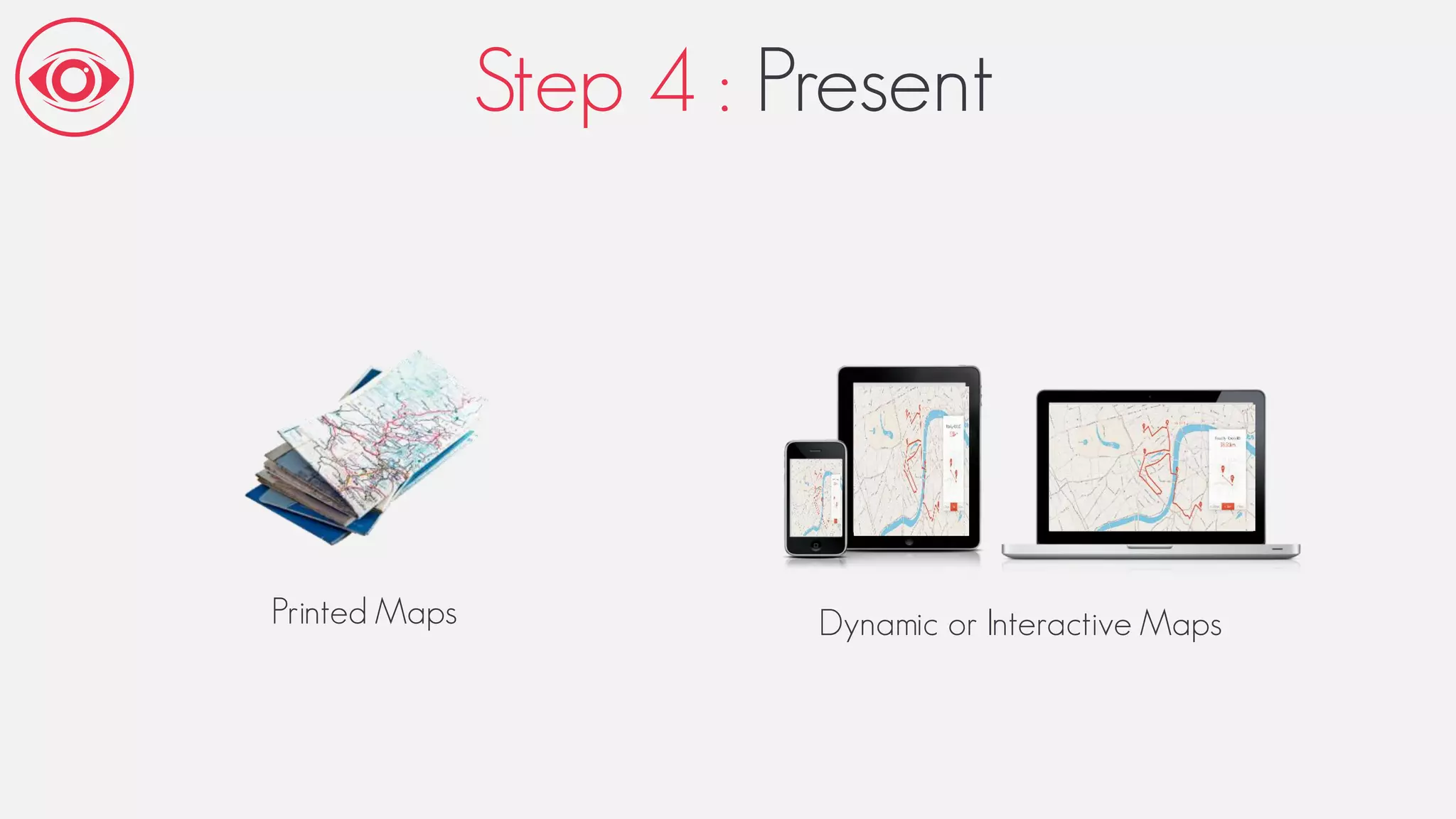
This document provides an overview of geographic information systems (GIS). It discusses the history of GIS, defines what GIS is, describes what types of geographical data are used in GIS, and outlines the key GIS processes of capture, manage, analyze and present. It also provides some examples of GIS applications such as crime mapping, hydrology and health services. The overall document provides a high-level introduction to what GIS is and how it works.