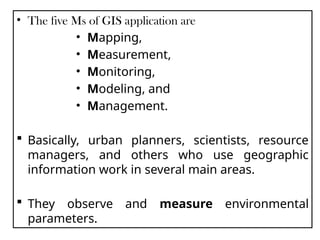
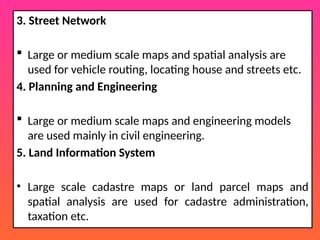
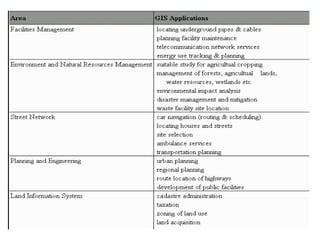
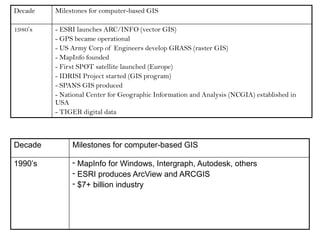
Example of GIS Applications
Environmental Studies: Monitoring deforestation, climate change impacts.
Urban Planning: Designing roads, water supply, and housing.
Health: Tracking disease outbreaks (e.g., mapping COVID-19 cases).
Agriculture: Precision farming, crop monitoring.
Disaster Management: Flood risk mapping, earthquake preparedness.
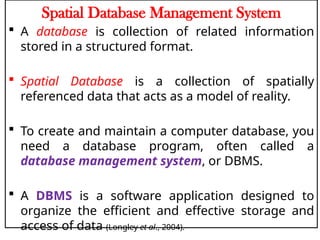
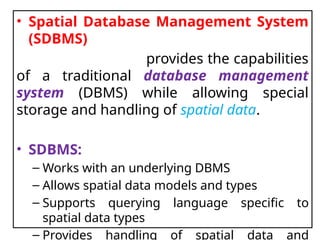
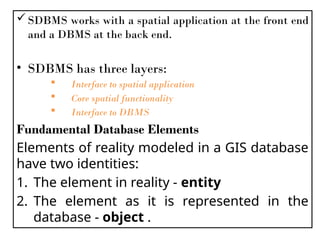
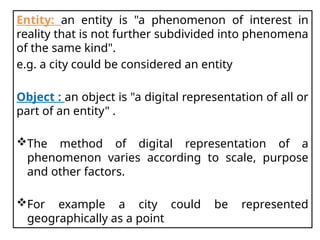
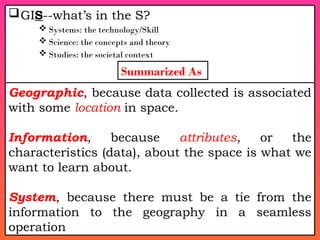
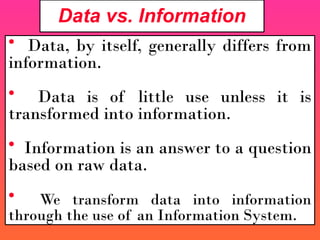
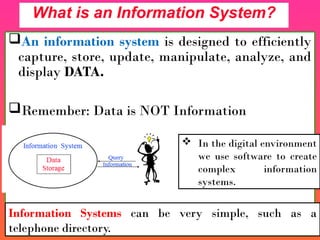
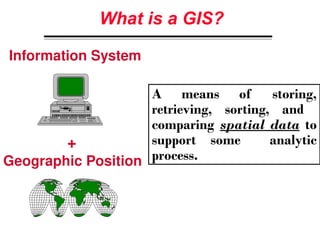
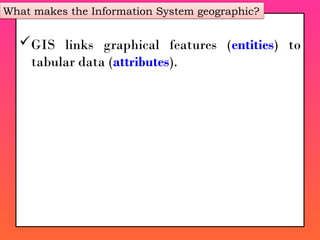
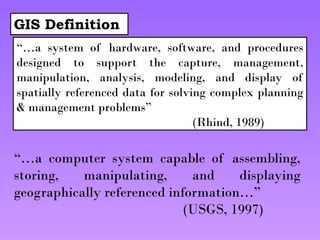
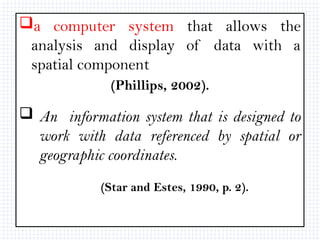
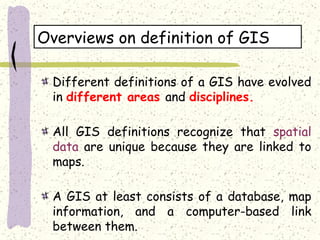
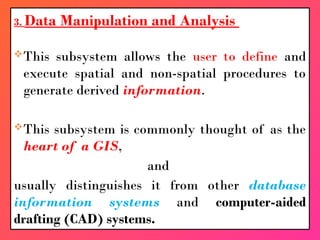
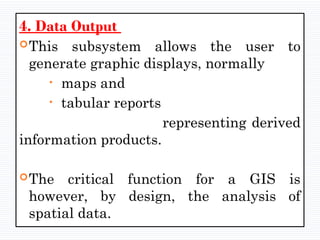
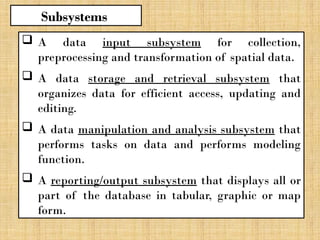
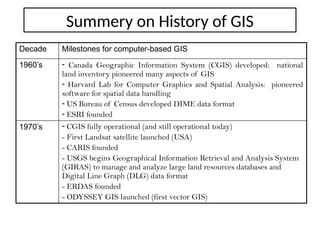
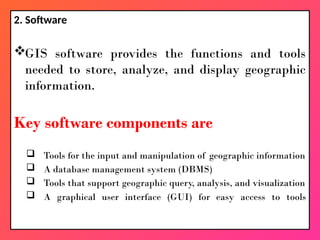
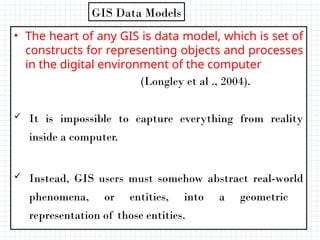
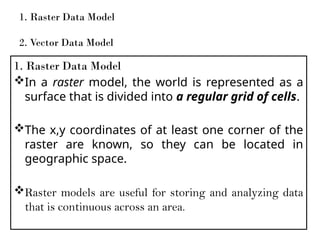
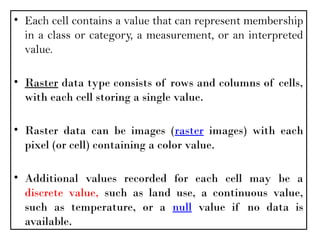
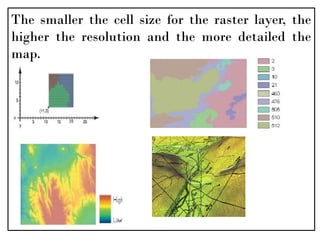
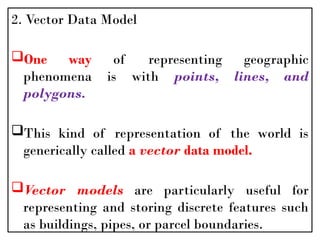
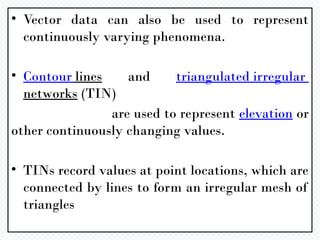
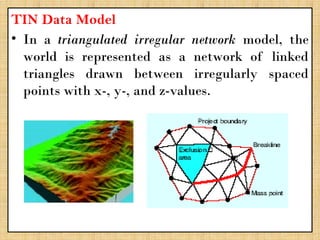
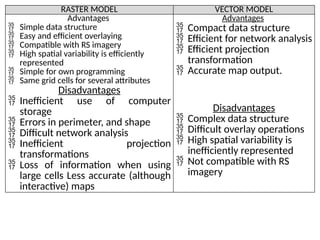
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a technological framework that allows users to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and visualize geographic data. Unlike traditional maps, GIS is dynamic: it integrates location (spatial data) with descriptive information (attribute data), enabling users to perform complex analyses and generate insights that support decision-making across multiple fields.
GIS is not just software—it’s a system that combines data, tools, and human expertise to answer questions such as:
Where is a feature located?
How are multiple features related in space?





























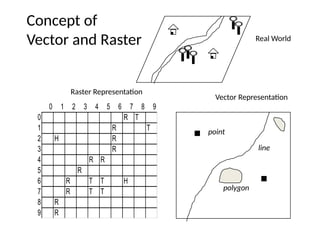

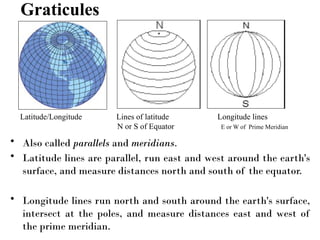
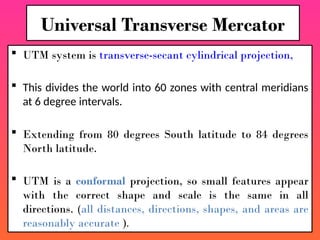
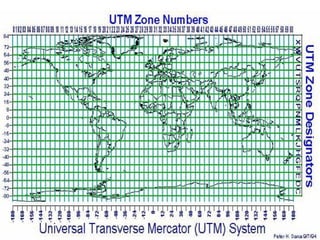
![• A coordinate is a number set that denotes a
specific location within a reference system.
• Typical coordinates are
the x-y set ([x, y]), which is used in a two-
dimensional system,
and
the x-y-z set ([x, y, z]), which is used in a three-
dimensional system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geographicinformationsystemsgis-1-250828092258-e7dbcc46/85/Geographic-Information-Systems-GIS-1-pptx-66-320.jpg)