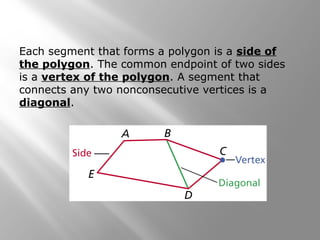
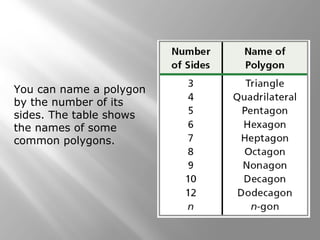
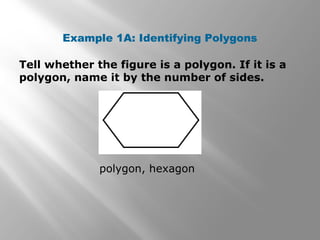
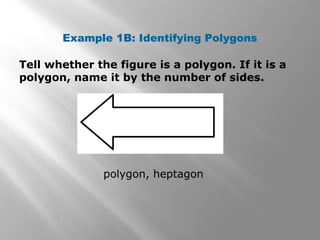
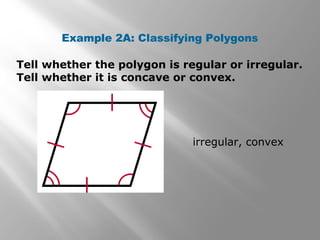
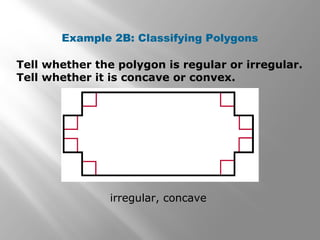
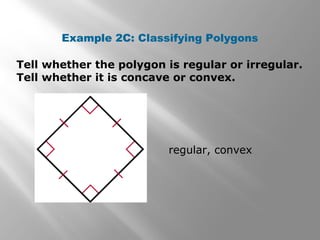
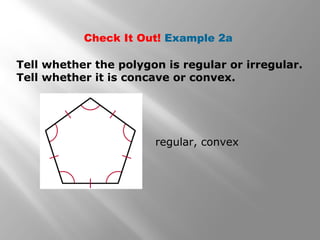
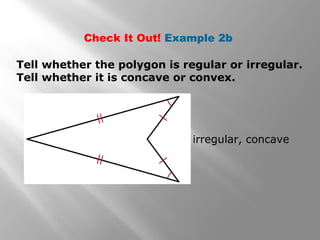
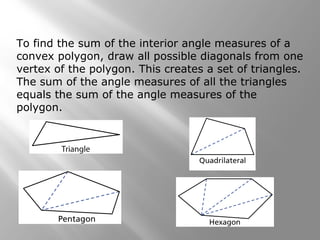
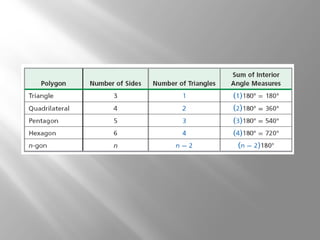
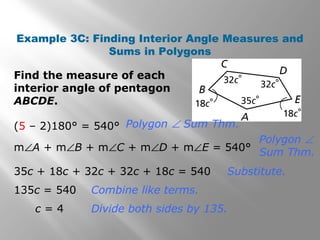
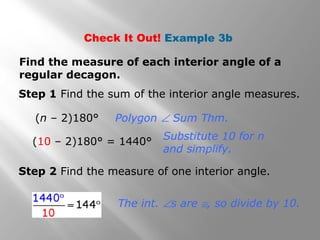
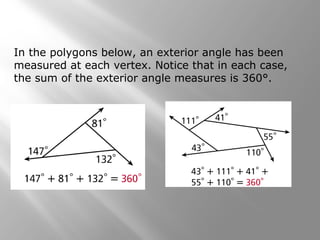
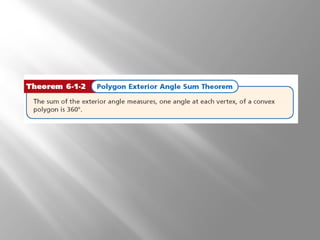
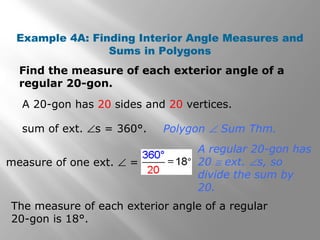
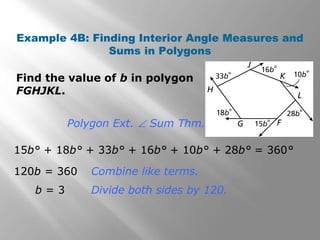
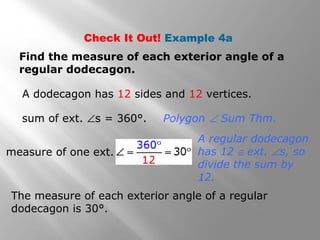
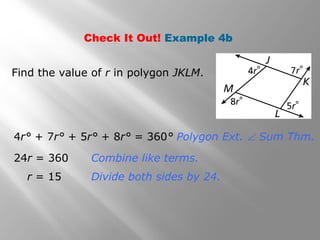
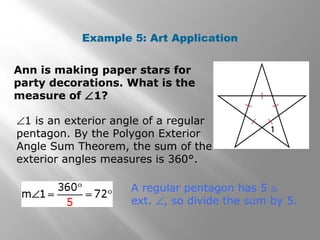
This document provides an overview of polygons and their properties. It begins with objectives and vocabulary related to polygons, such as sides, vertices, diagonals, regular polygons, and convex vs concave shapes. Examples are provided to classify polygons based on their number of sides and whether they are regular, irregular, convex, or concave. The document also discusses finding the sum of interior and exterior angle measures in polygons using theorems. Lesson examples calculate sums and individual angle measures in various polygons.