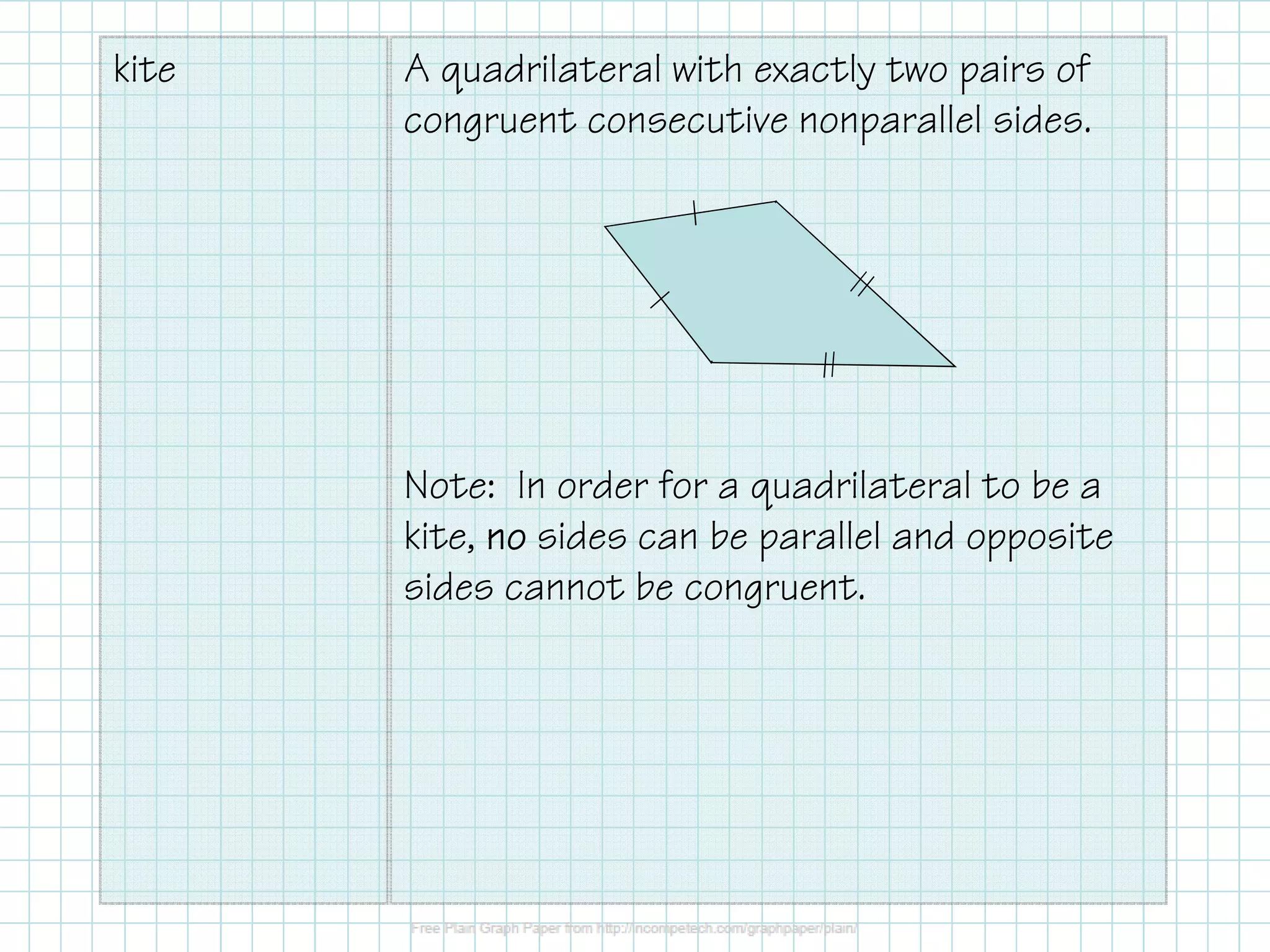
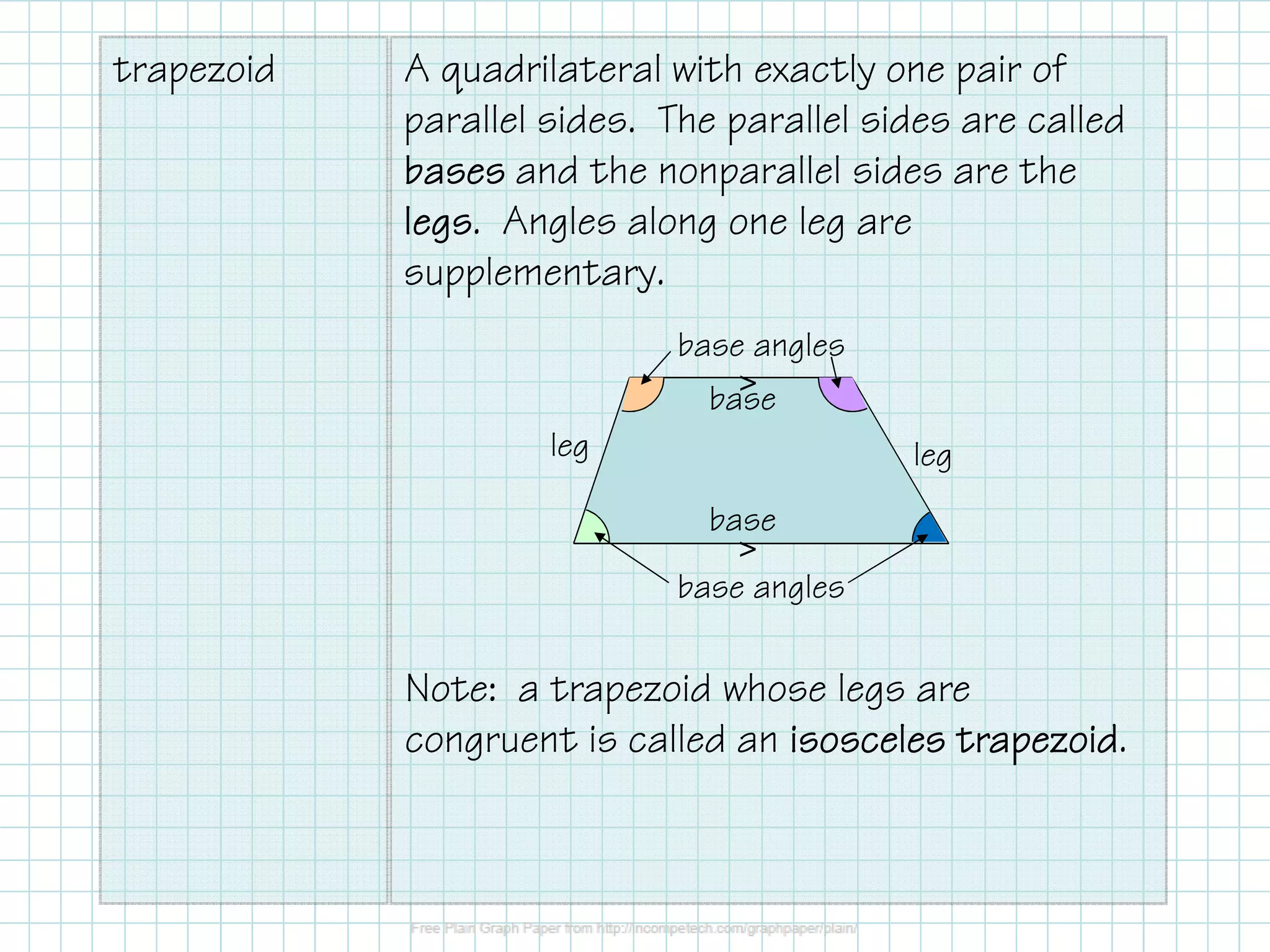
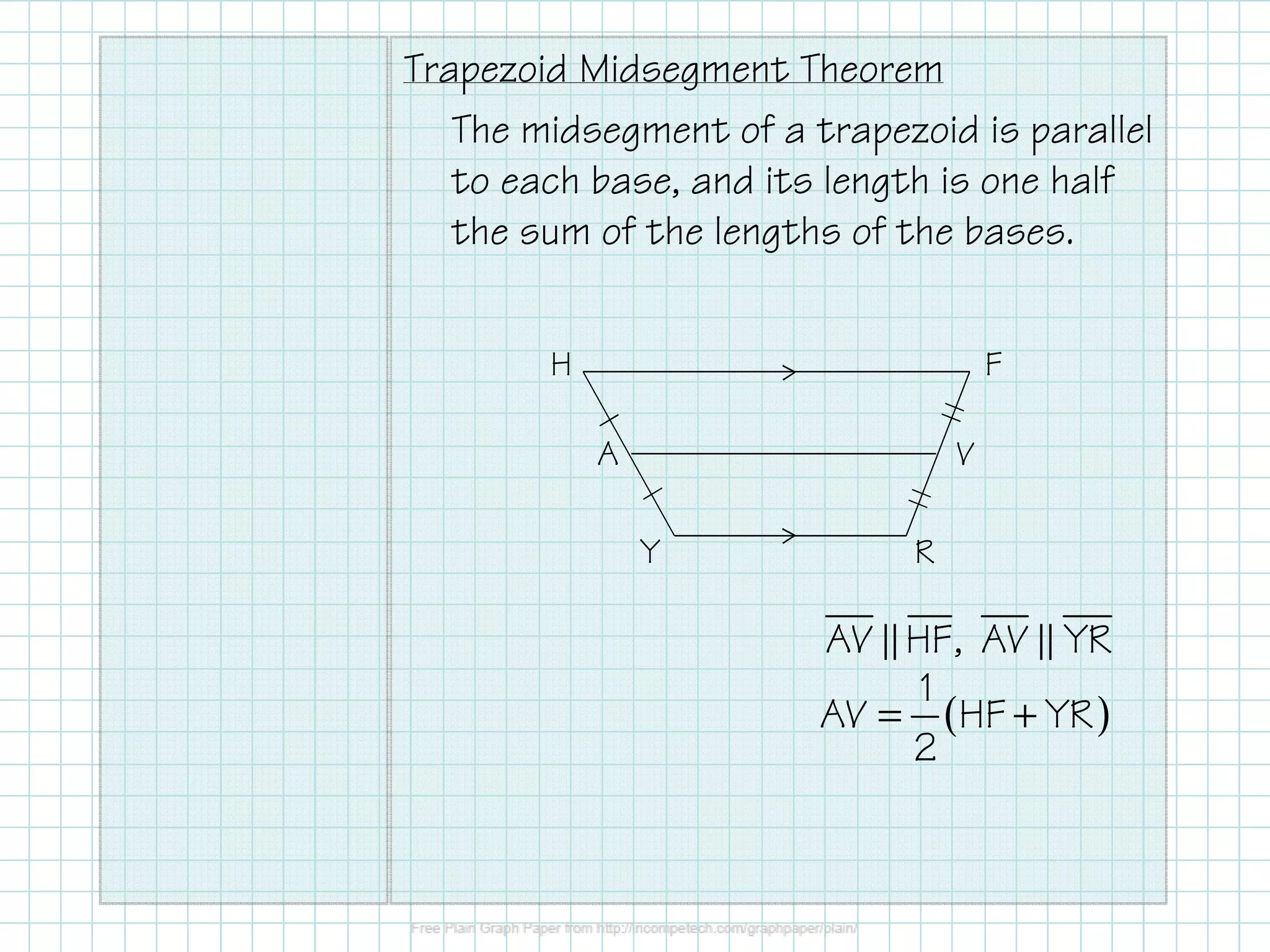
This document defines and provides properties of kites and trapezoids. It states that a kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of congruent consecutive sides, and its diagonals are perpendicular. A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides called bases, and the nonparallel sides are legs. An isosceles trapezoid has two congruent base angles. The midsegment of a trapezoid is parallel to the bases and is half the sum of the base lengths. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving problems using properties of kites and trapezoids.