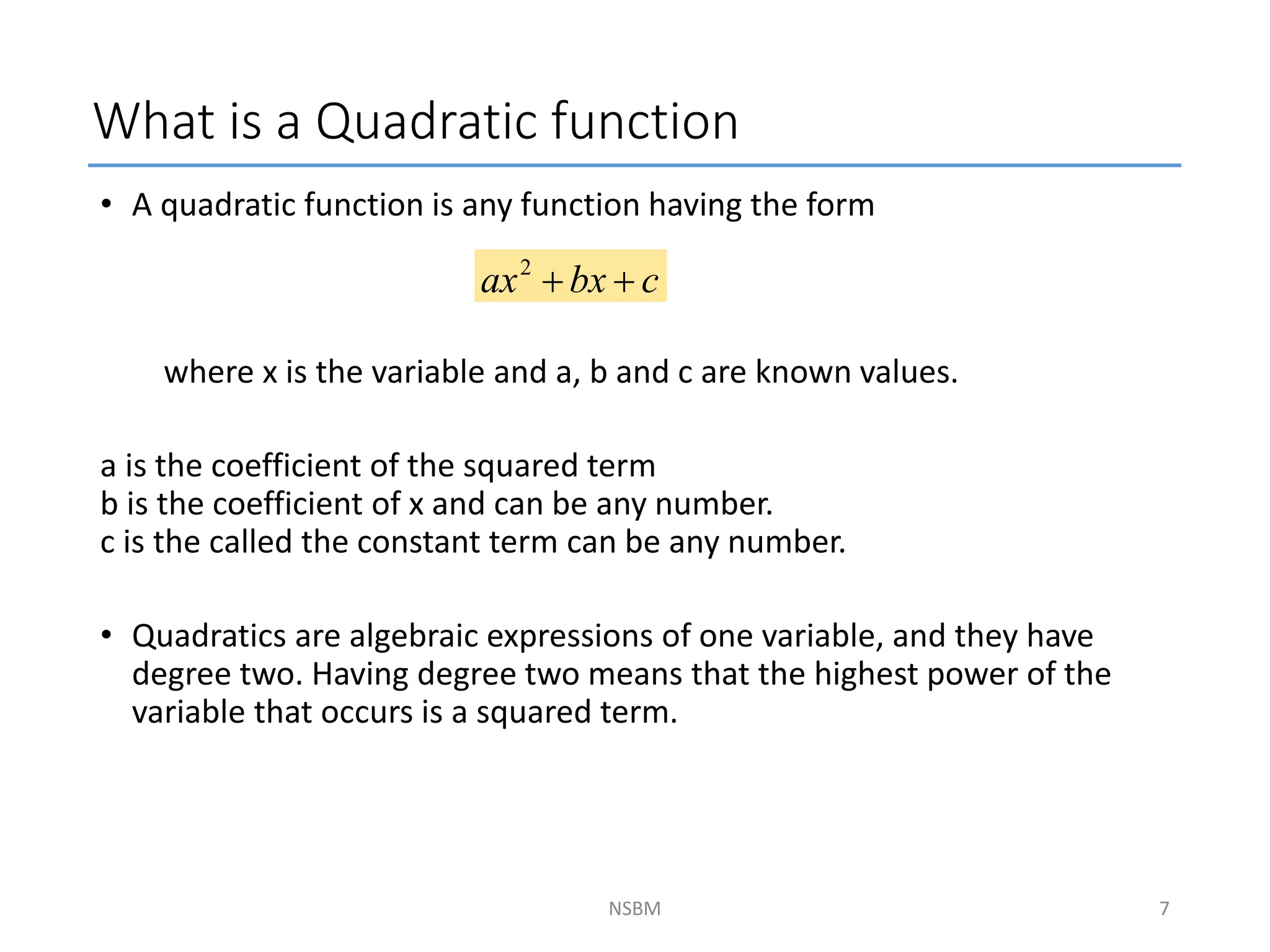
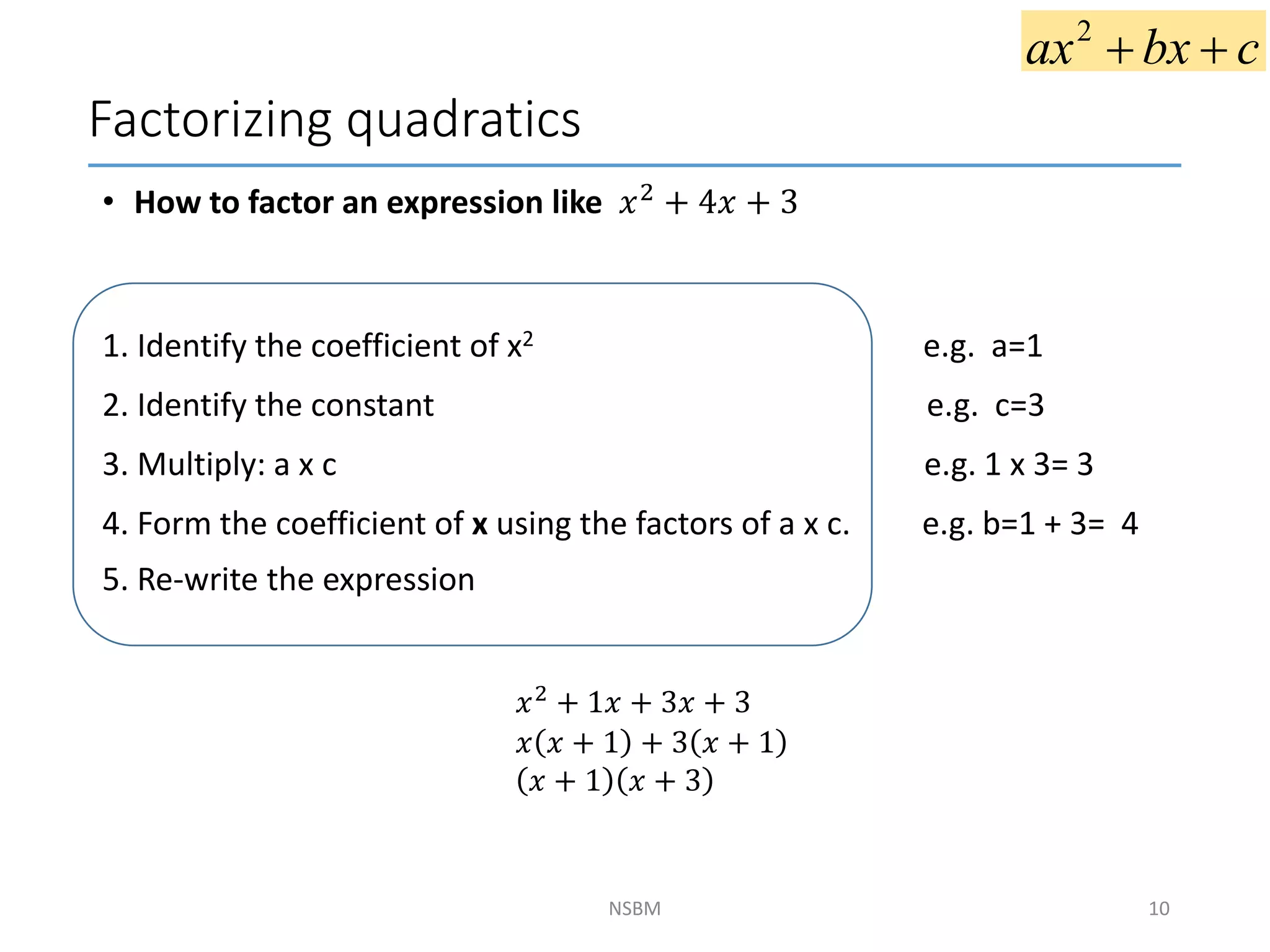
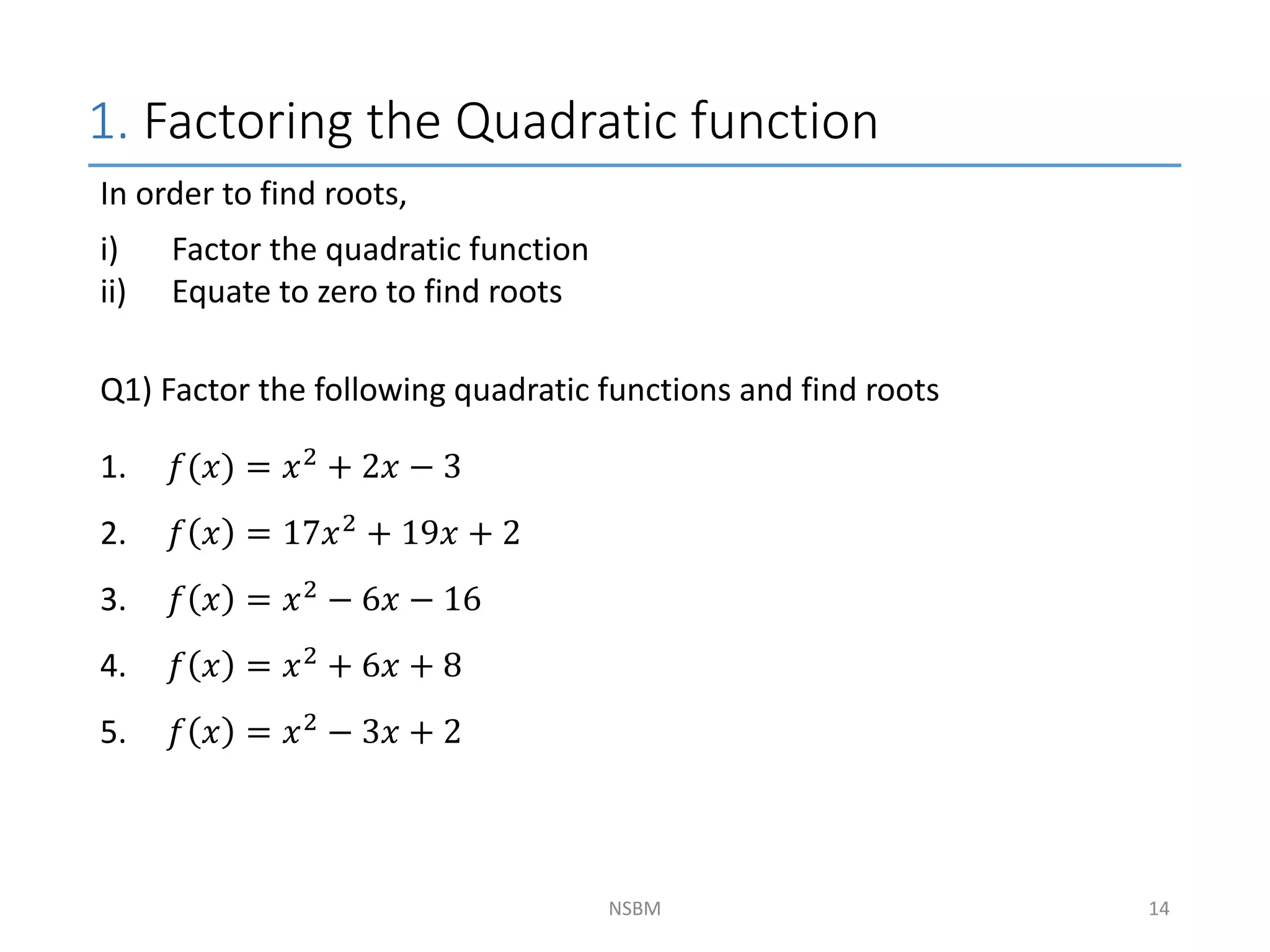
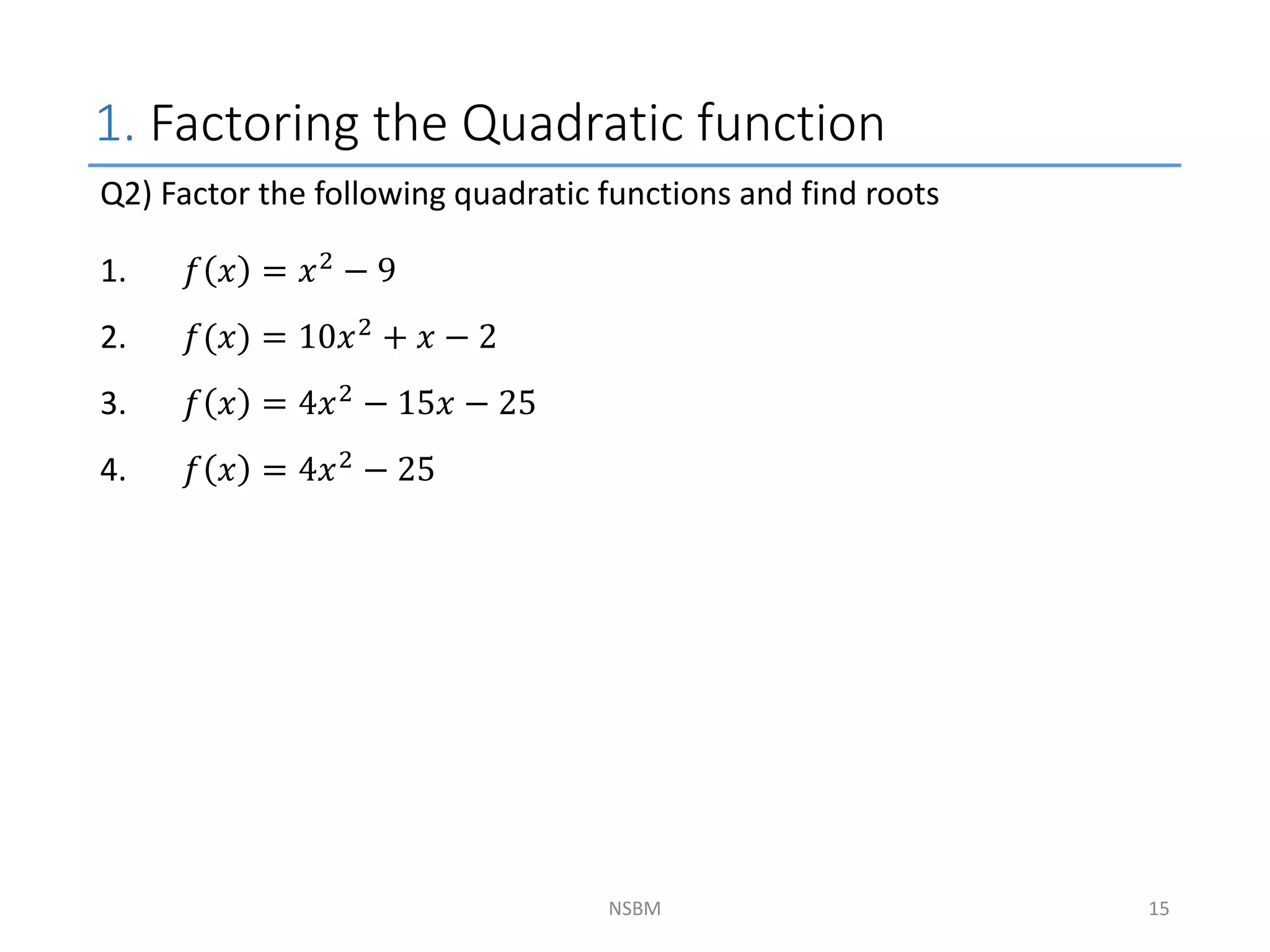
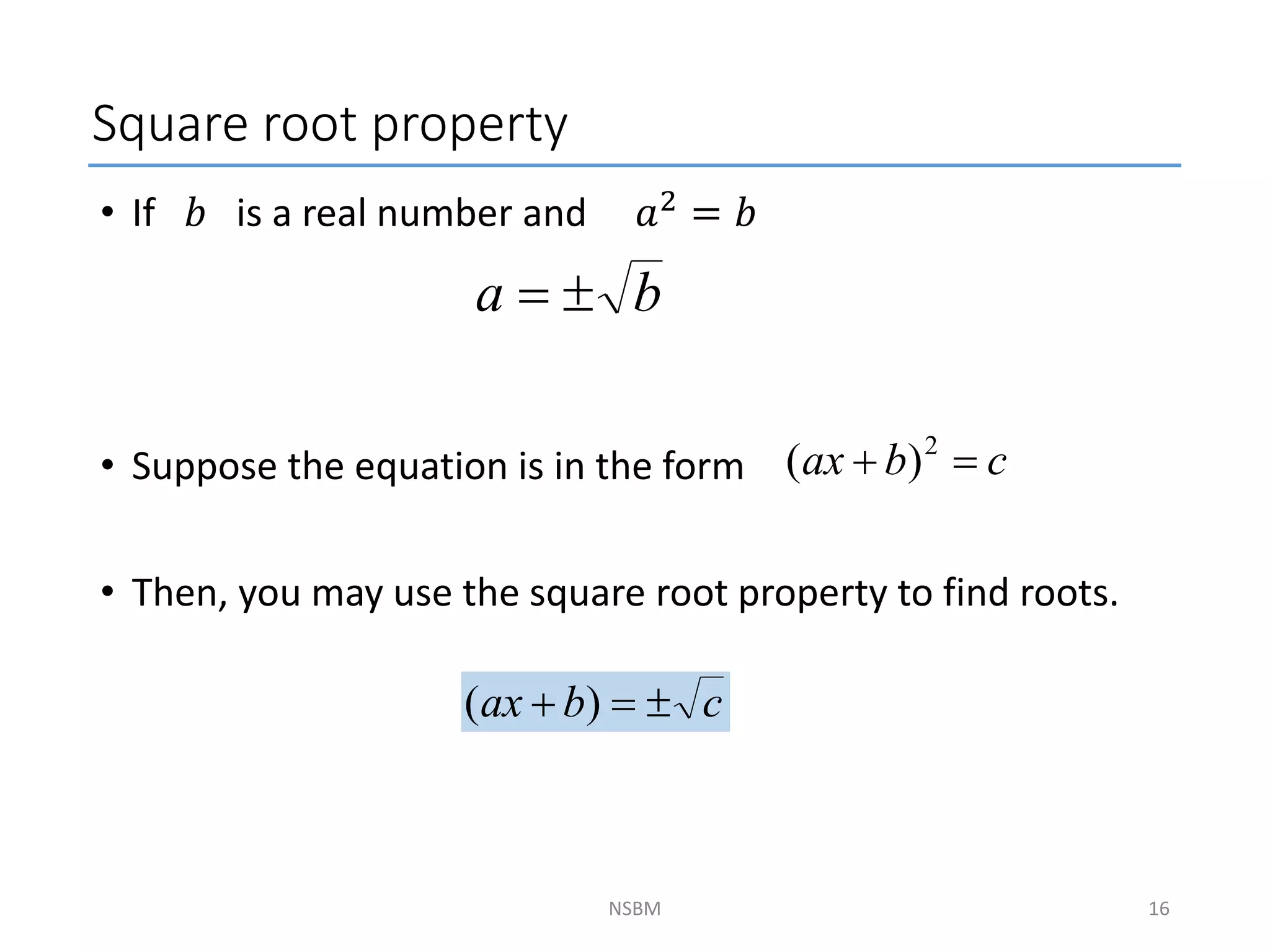
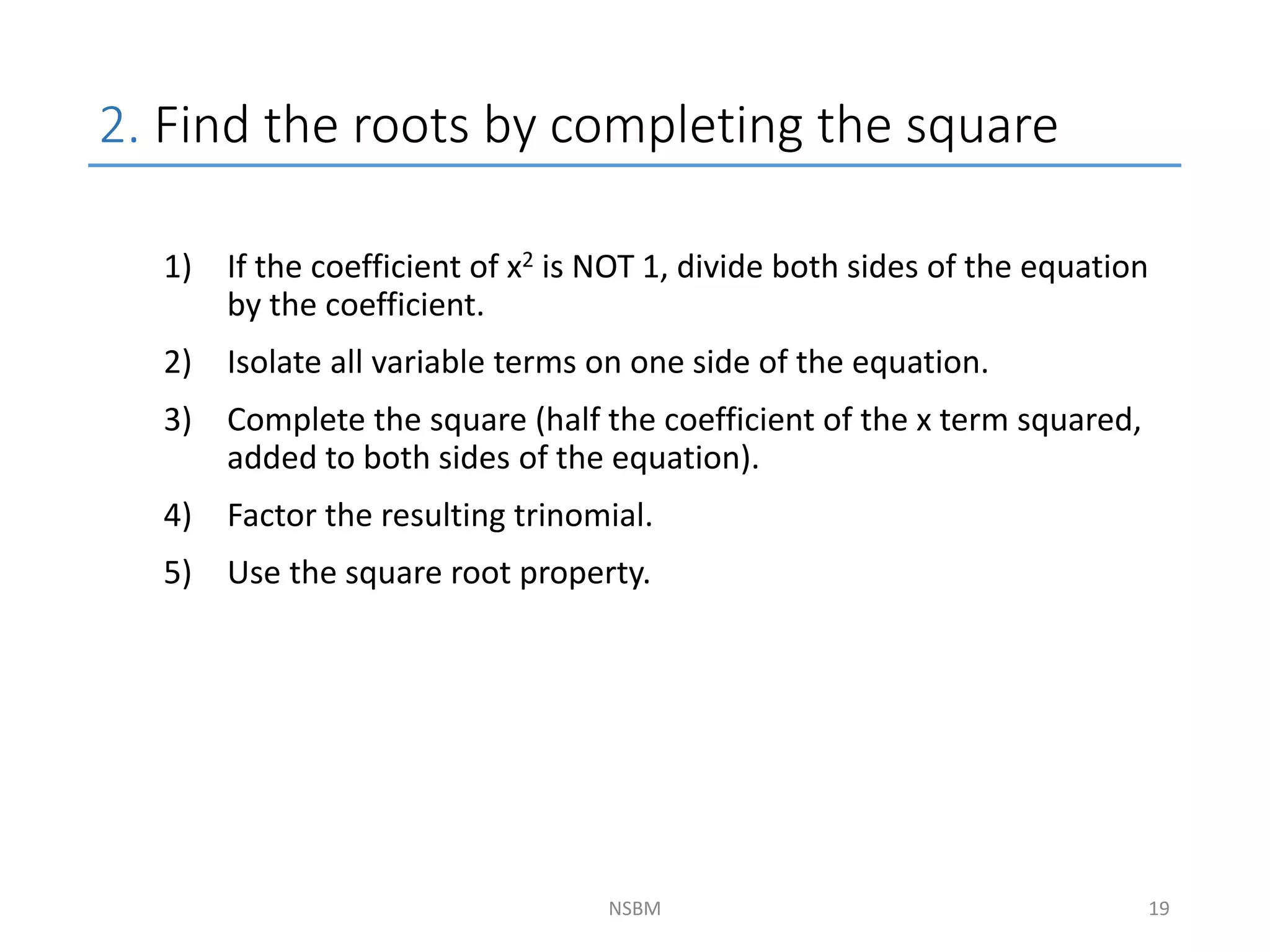
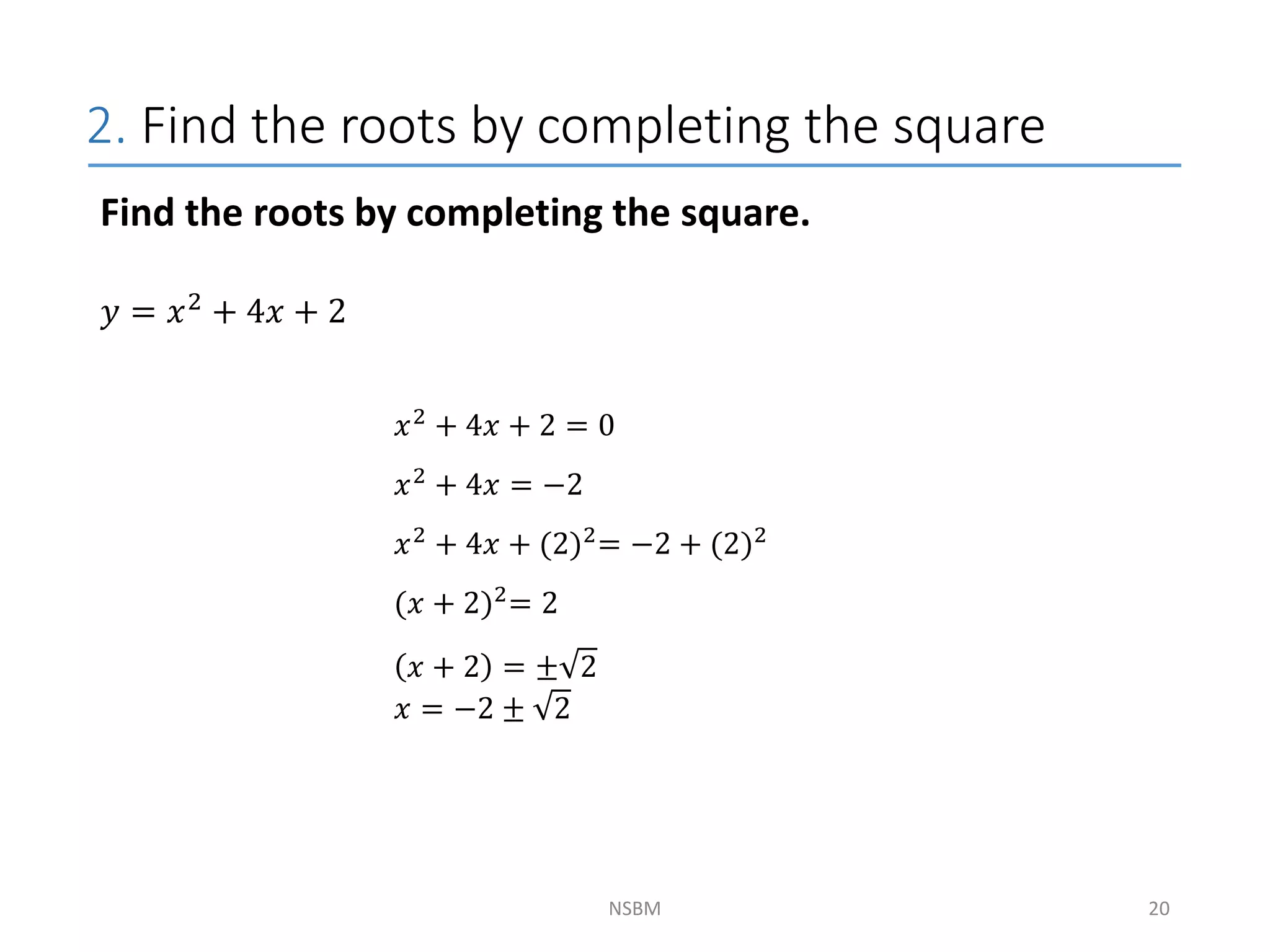
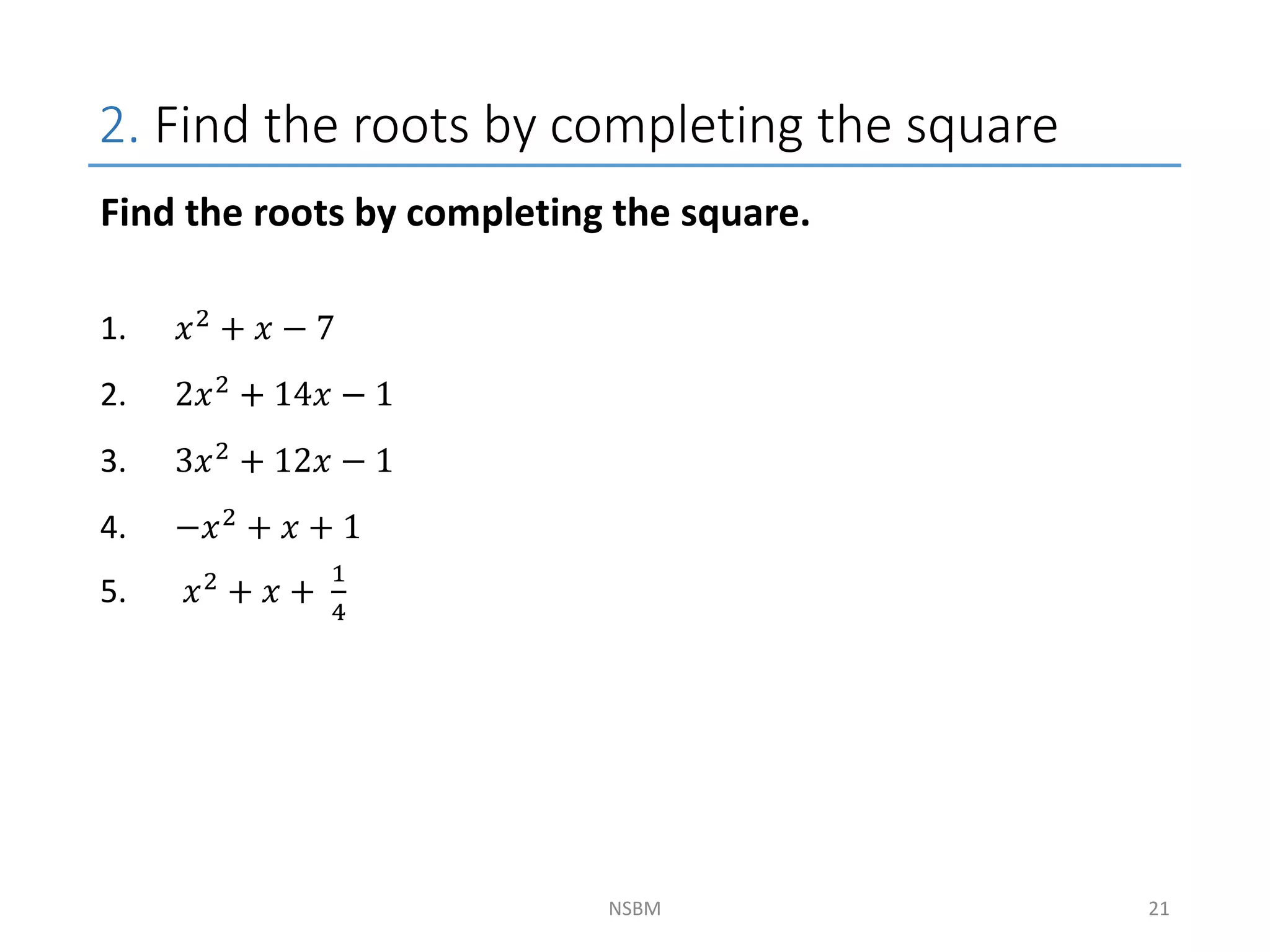
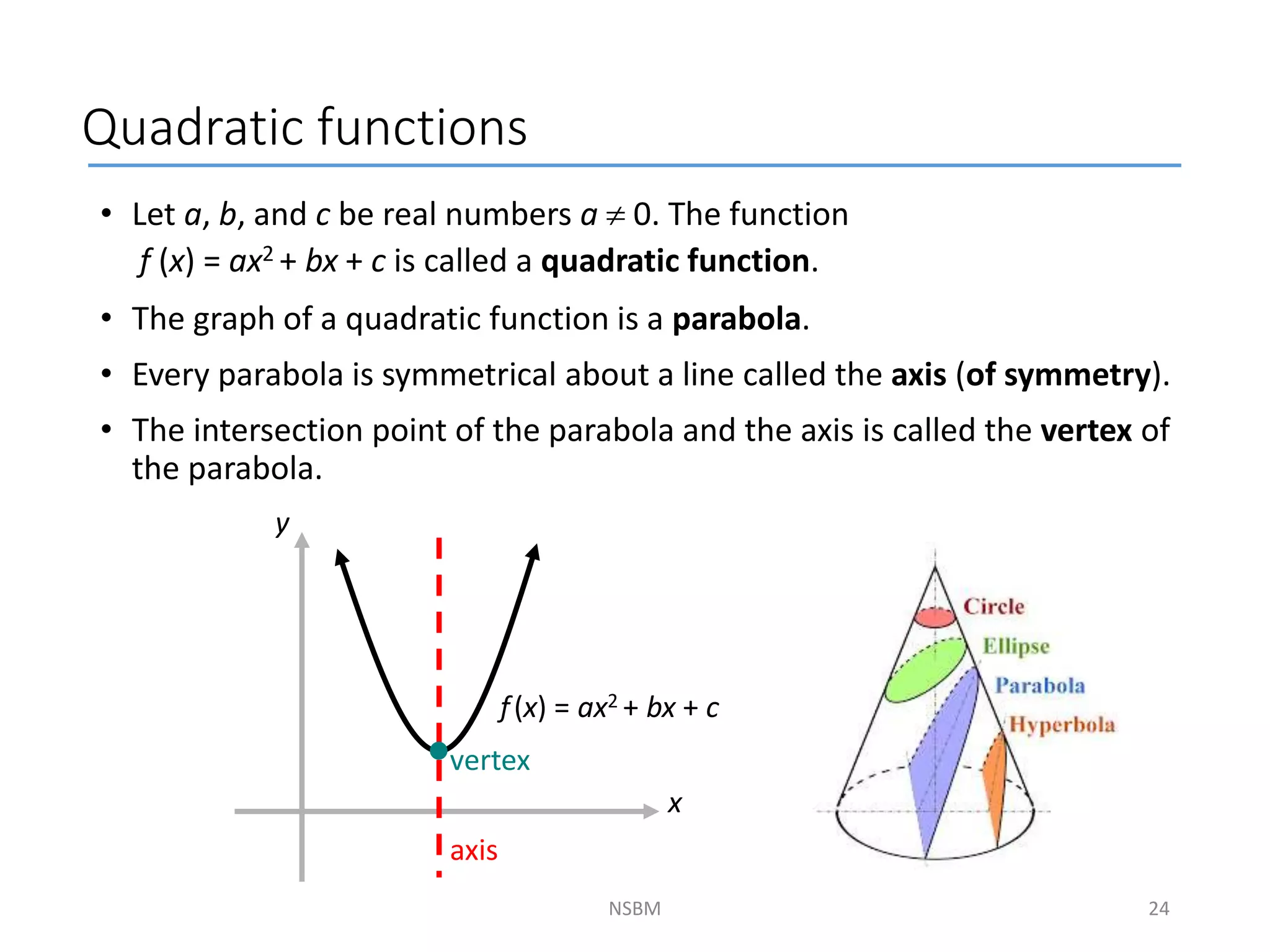
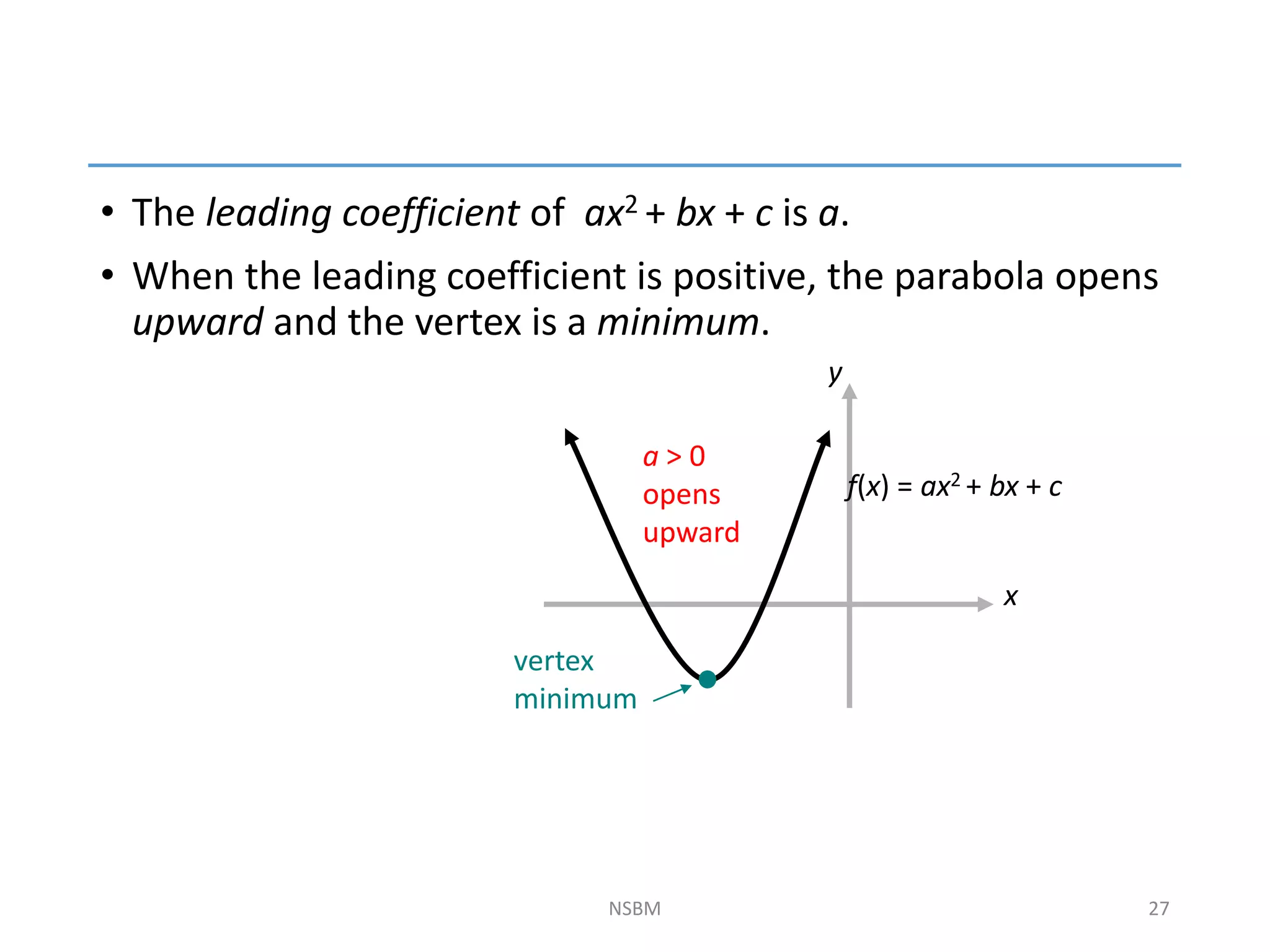
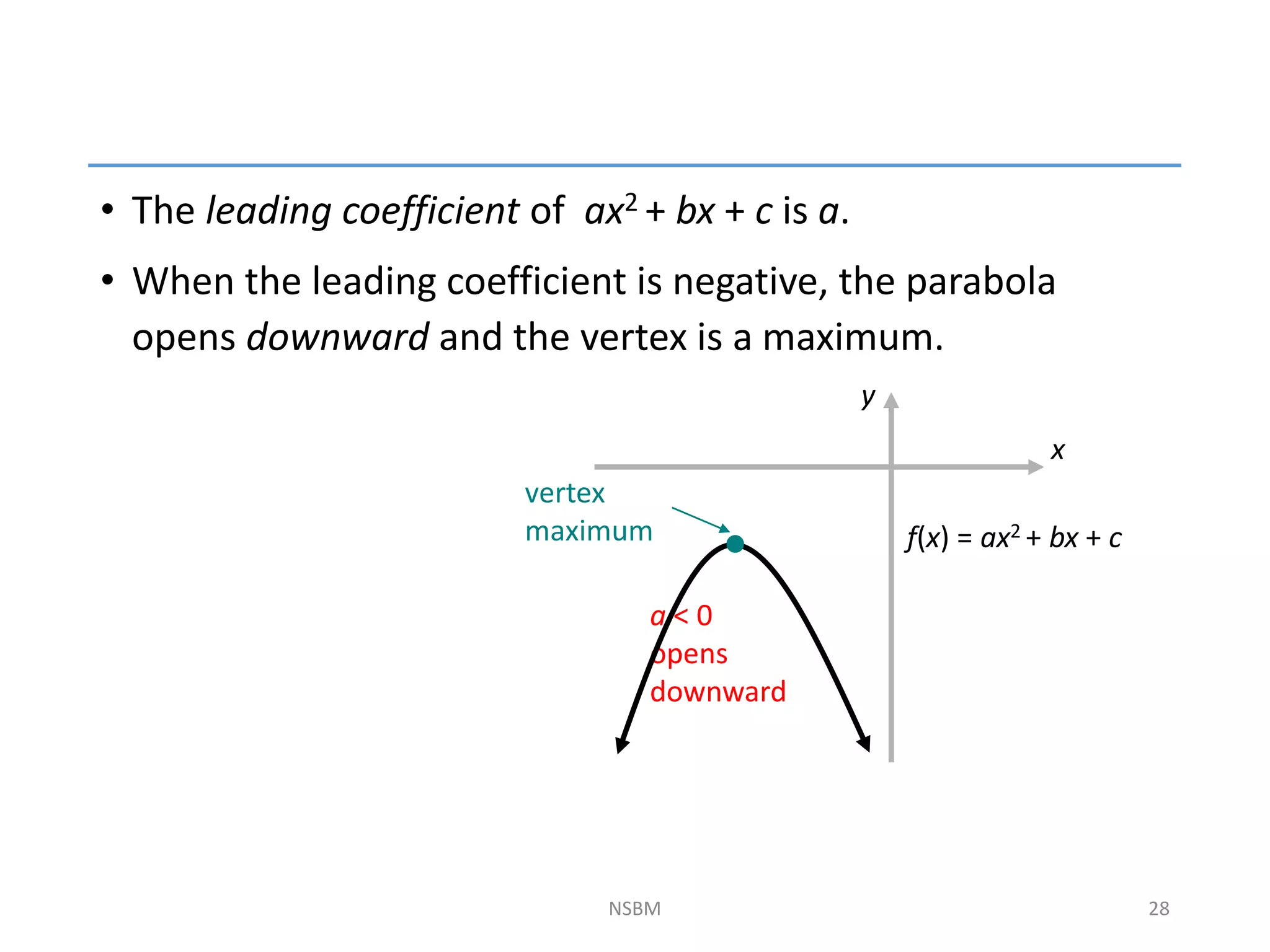
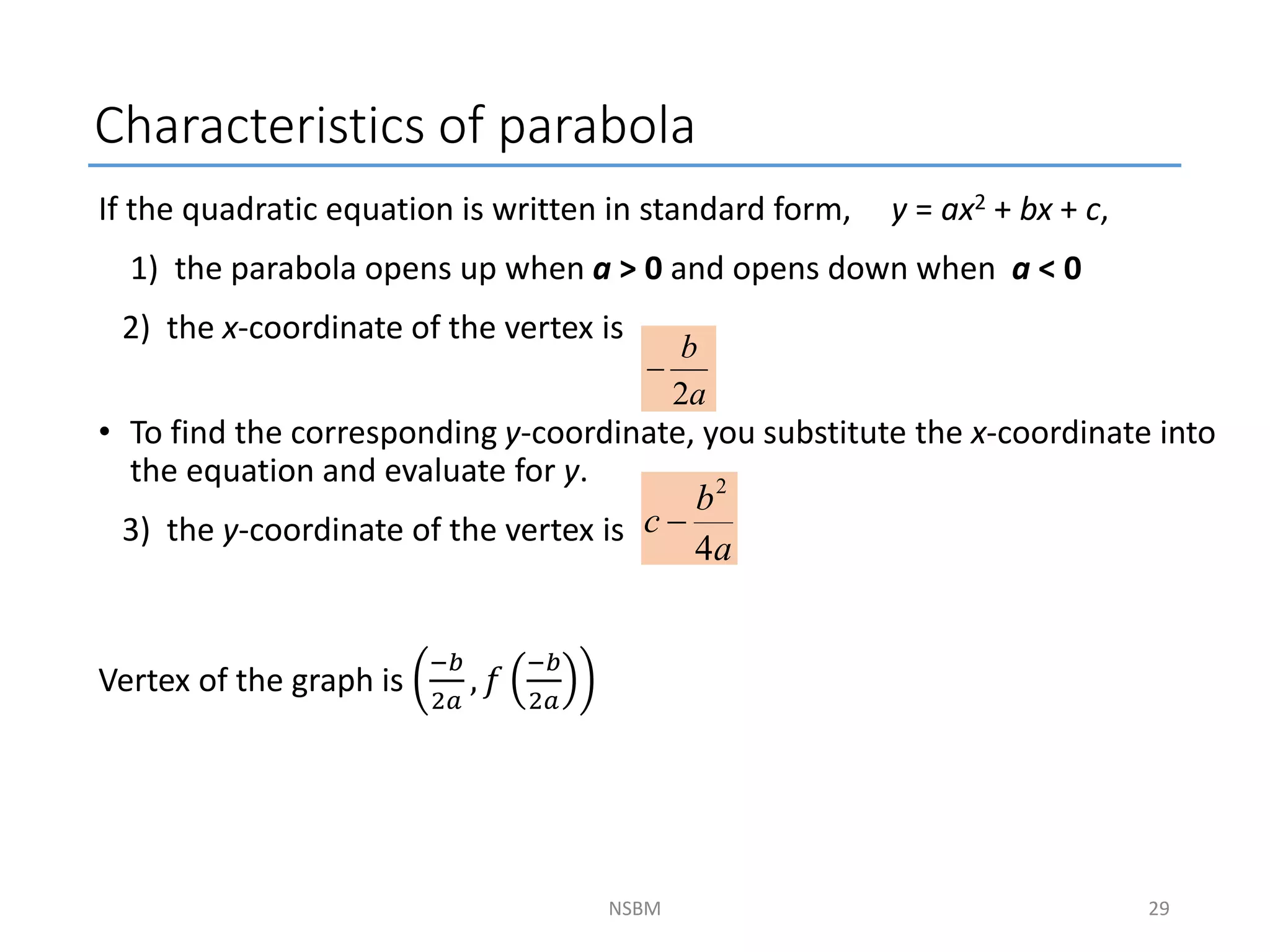
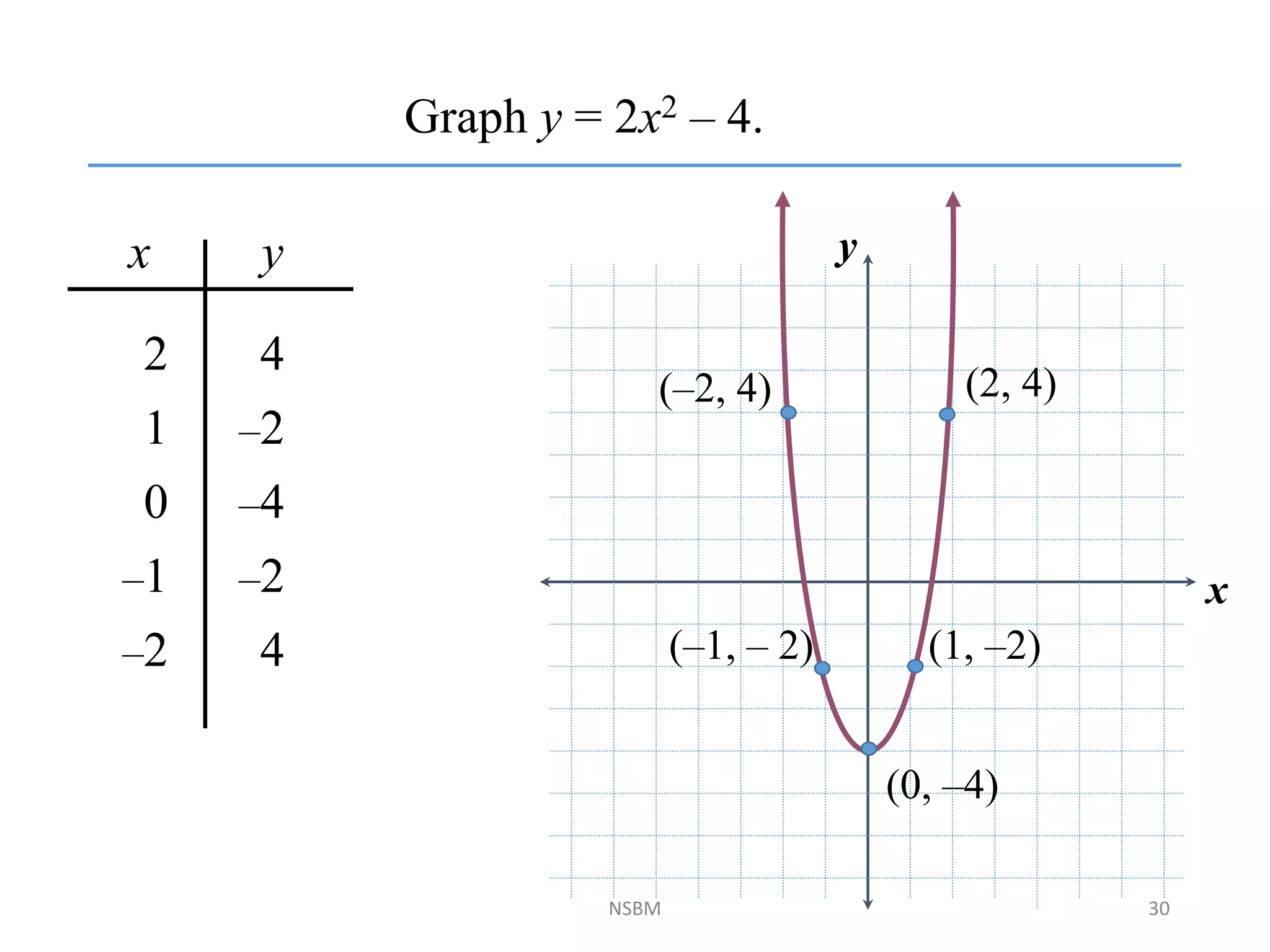
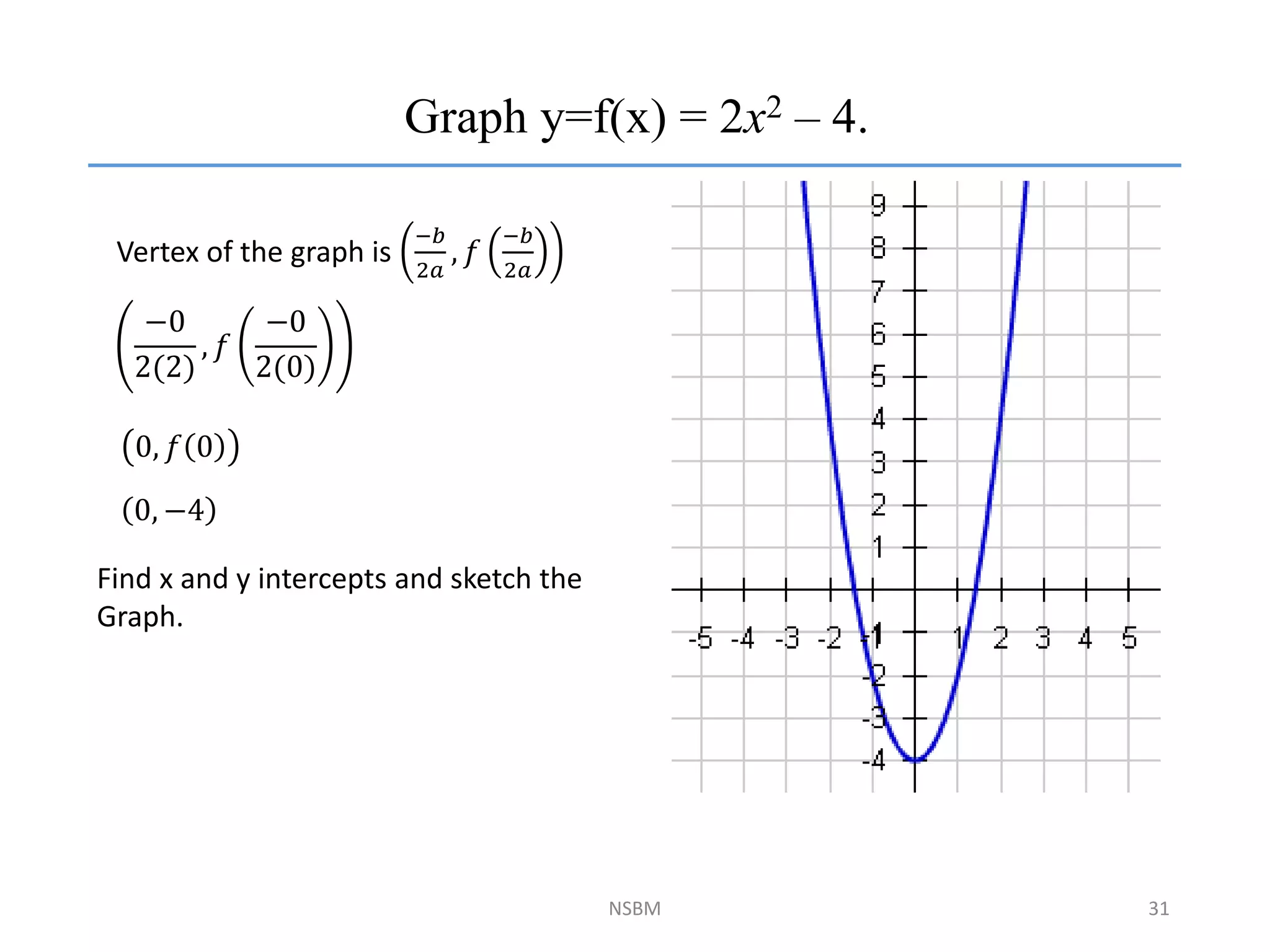
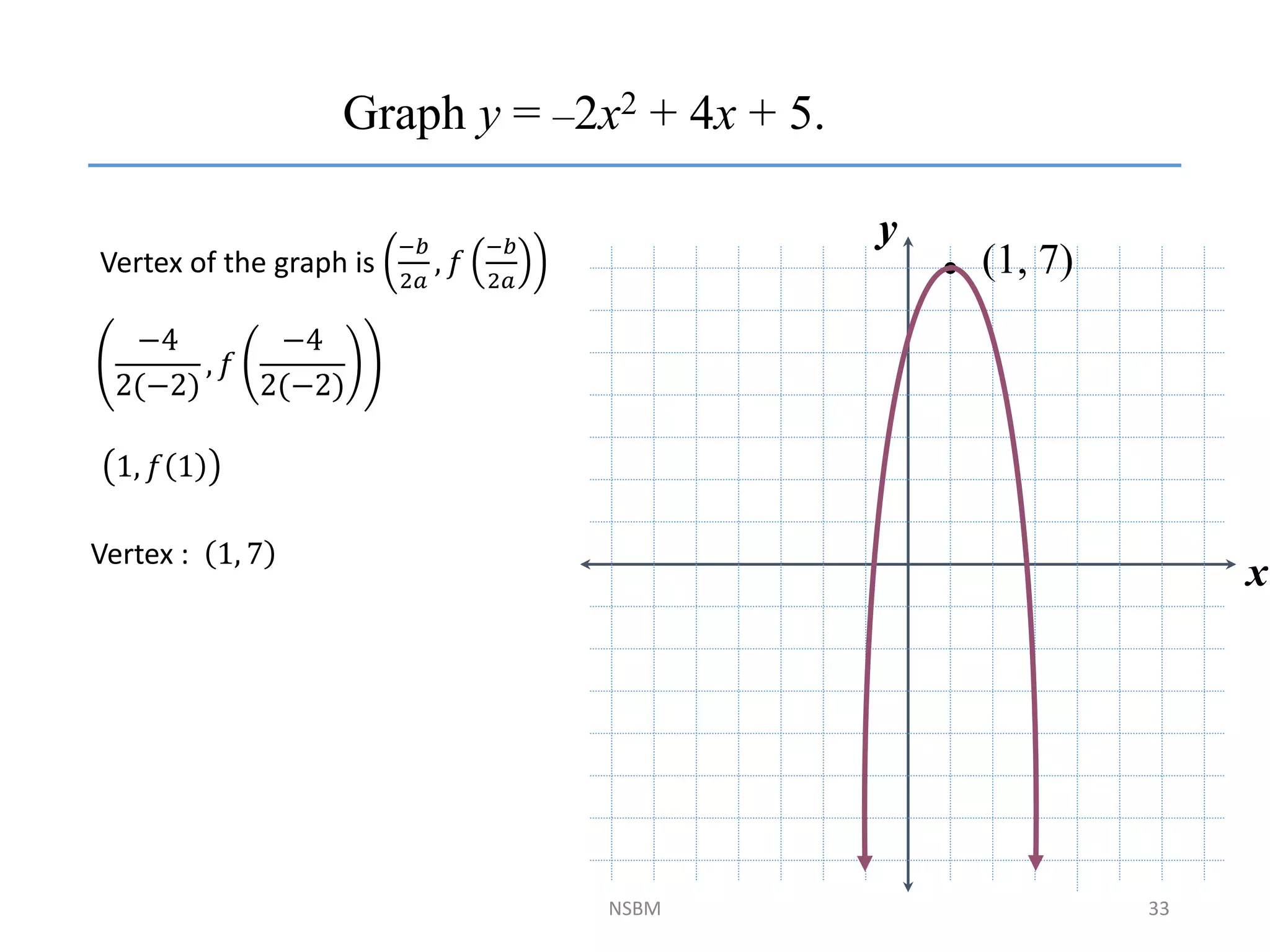
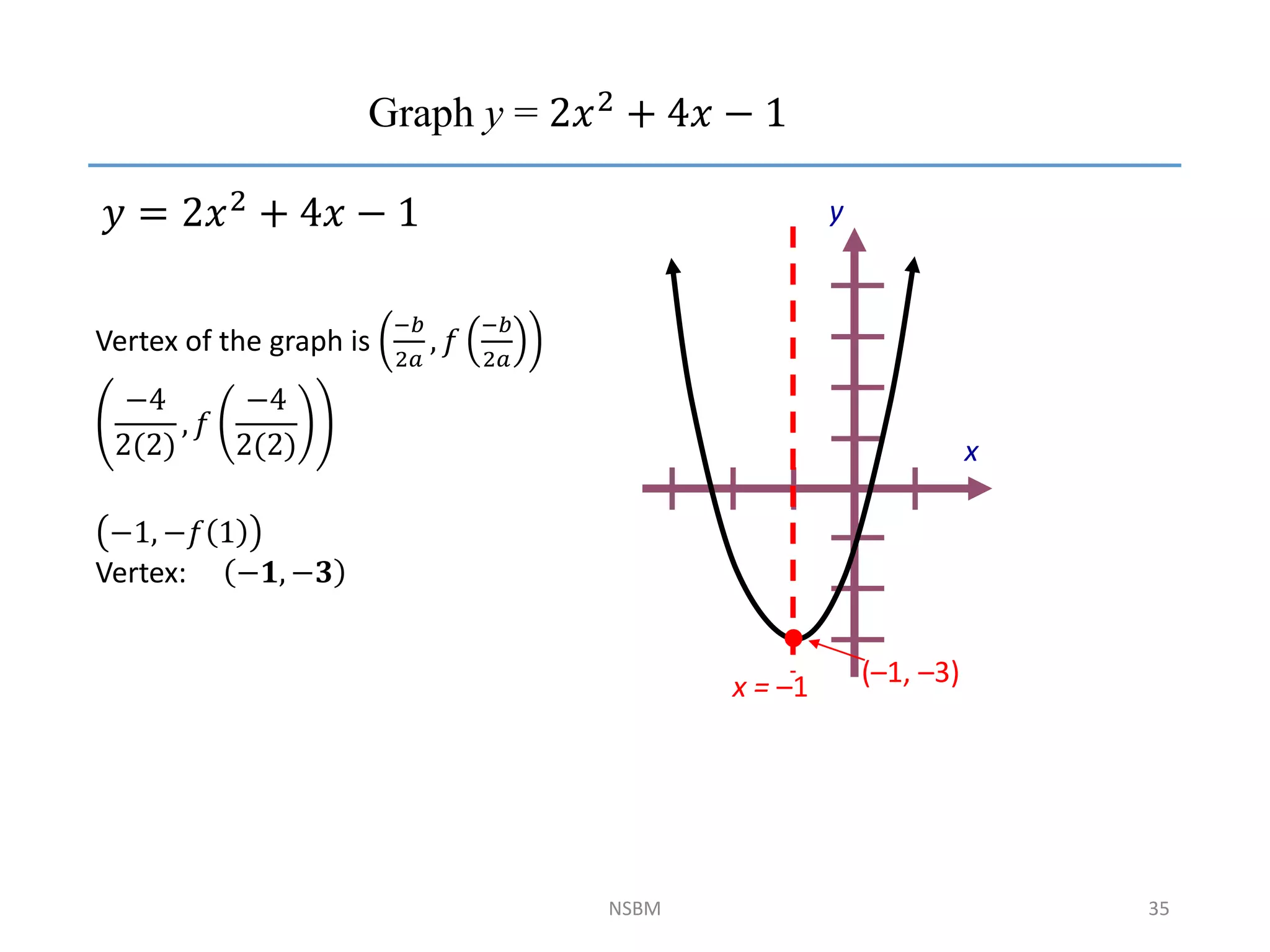
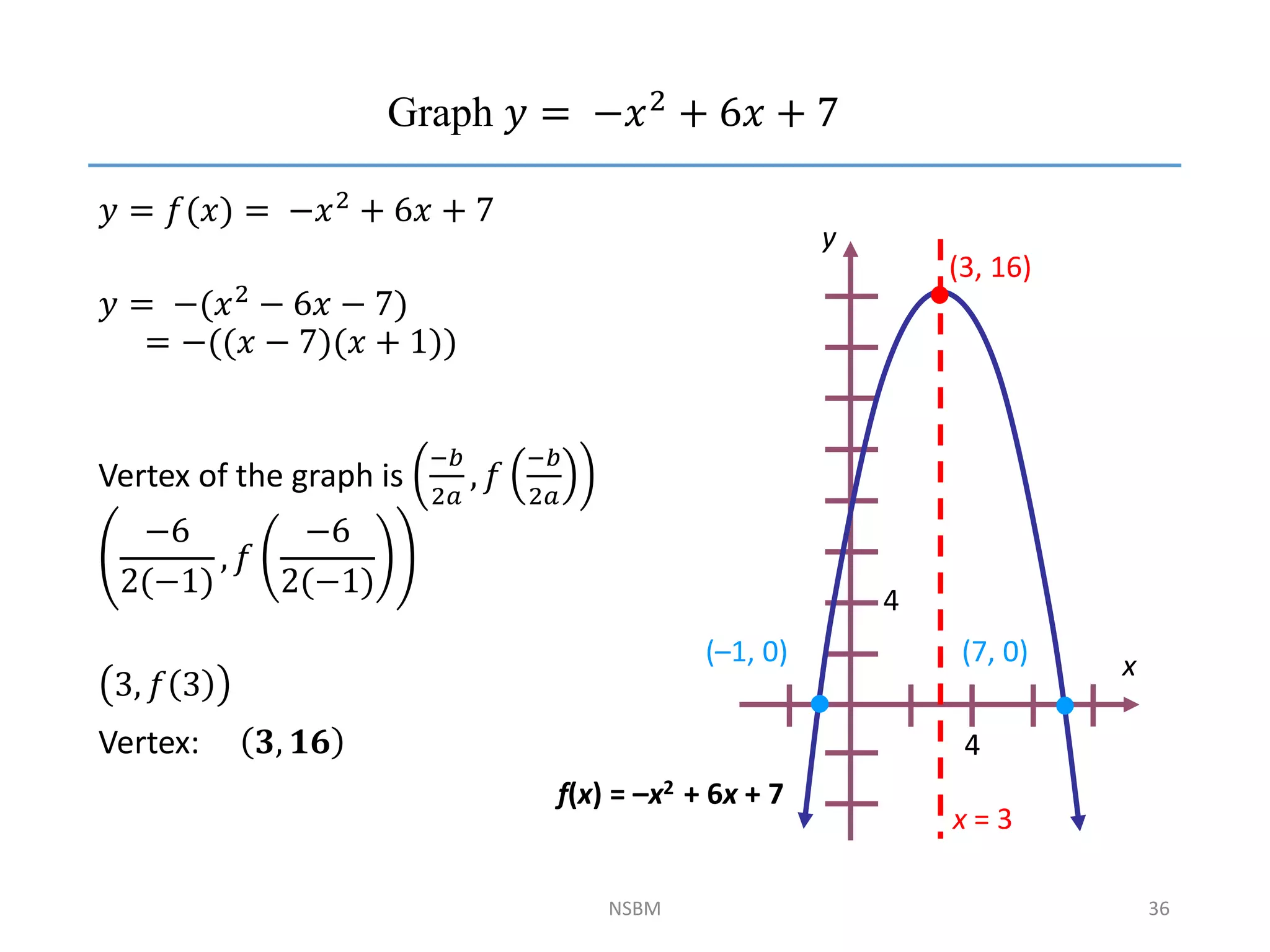
This document discusses factorizing algebraic expressions and quadratic functions. It provides examples of factorizing different types of algebraic expressions like binomials, trinomials and expressions with multiple terms. It also discusses key concepts related to quadratic functions like their standard form, graphing quadratics by finding the vertex, x-intercepts and y-intercepts. Methods to find the roots of a quadratic function include factoring, completing the square and using the quadratic formula.