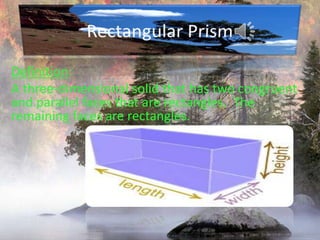
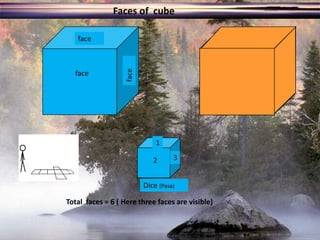
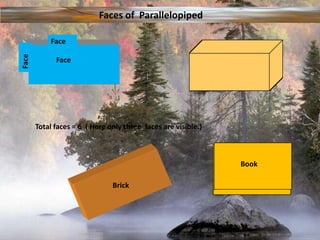
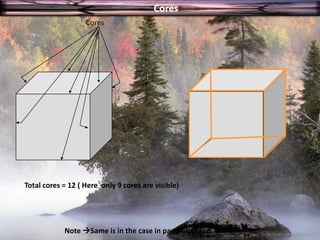
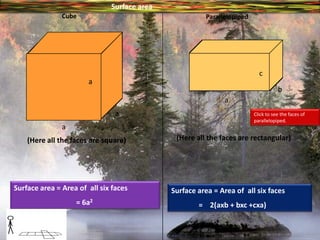
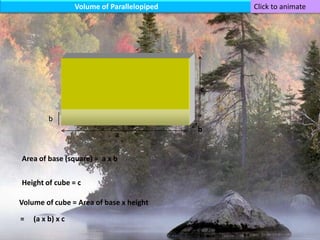
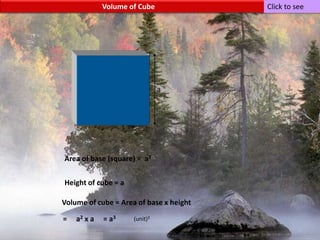
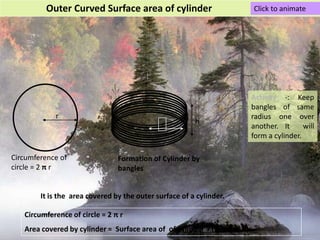
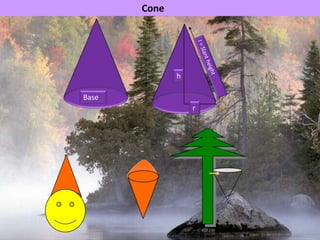
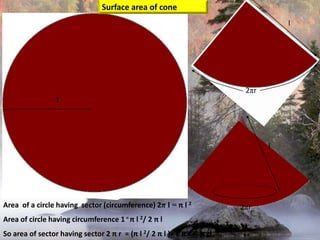
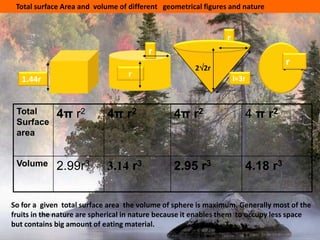
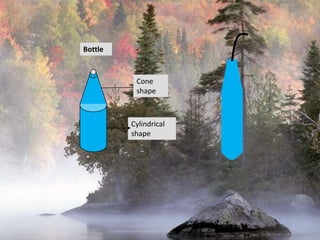
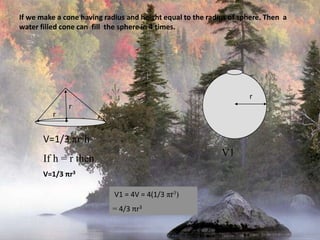
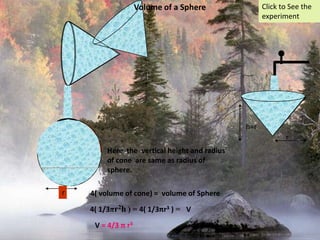
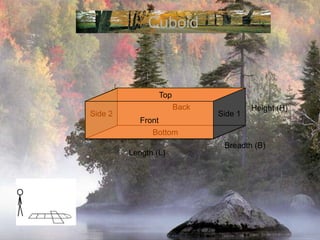
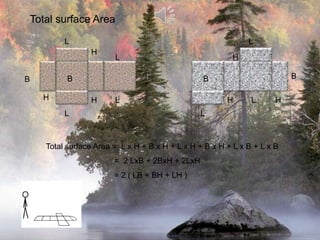
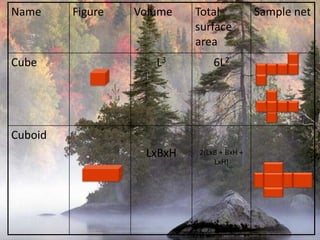
The document provides information on surface area and volume formulas and calculations for basic 3D shapes including prisms, cubes, cylinders, cones, and spheres. It defines key terms like surface area and volume and provides example calculations and formulas for finding the surface area and volume of cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Diagrams and examples are included to illustrate the different shapes and how to set up the surface area and volume calculations.