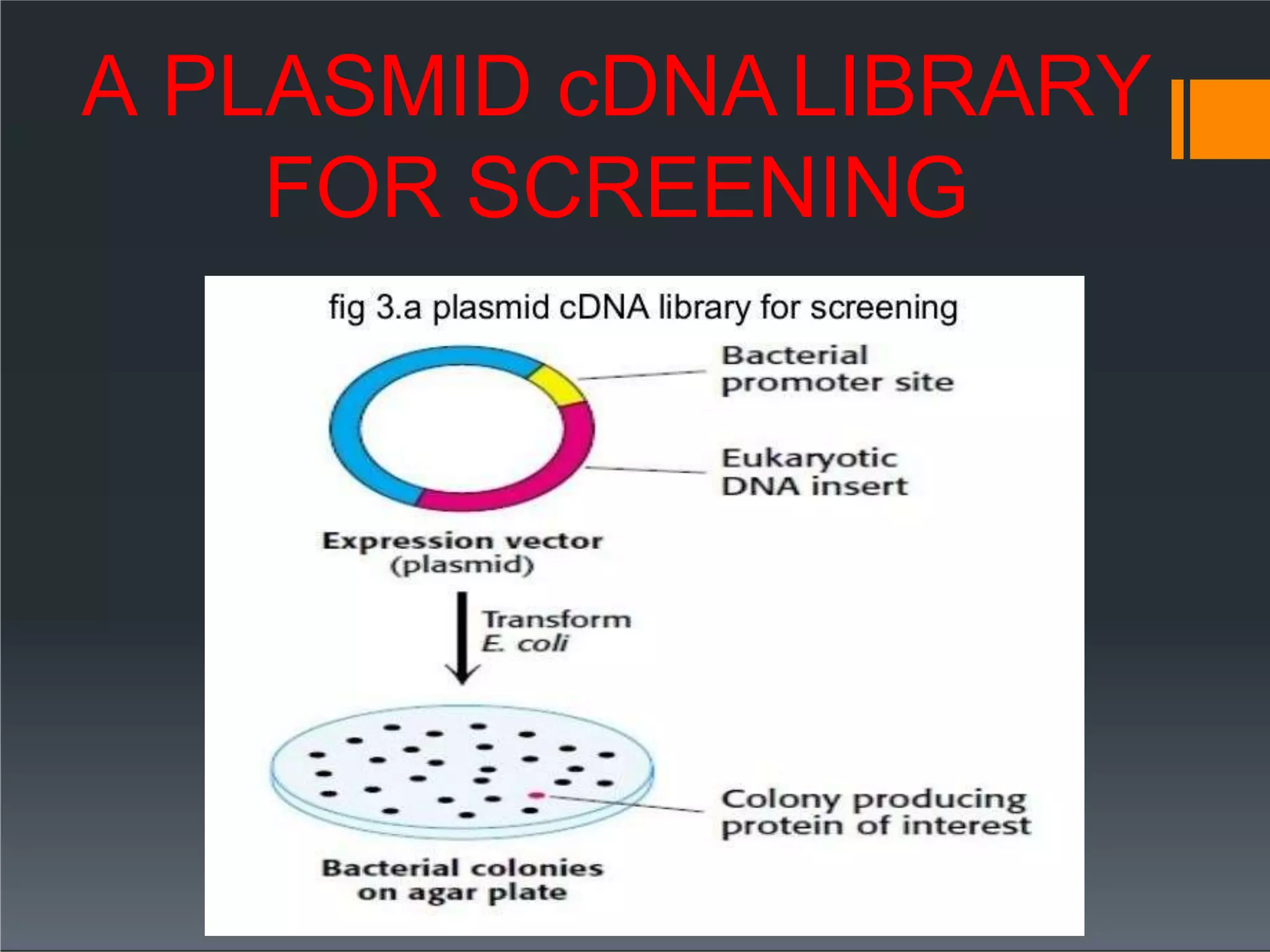
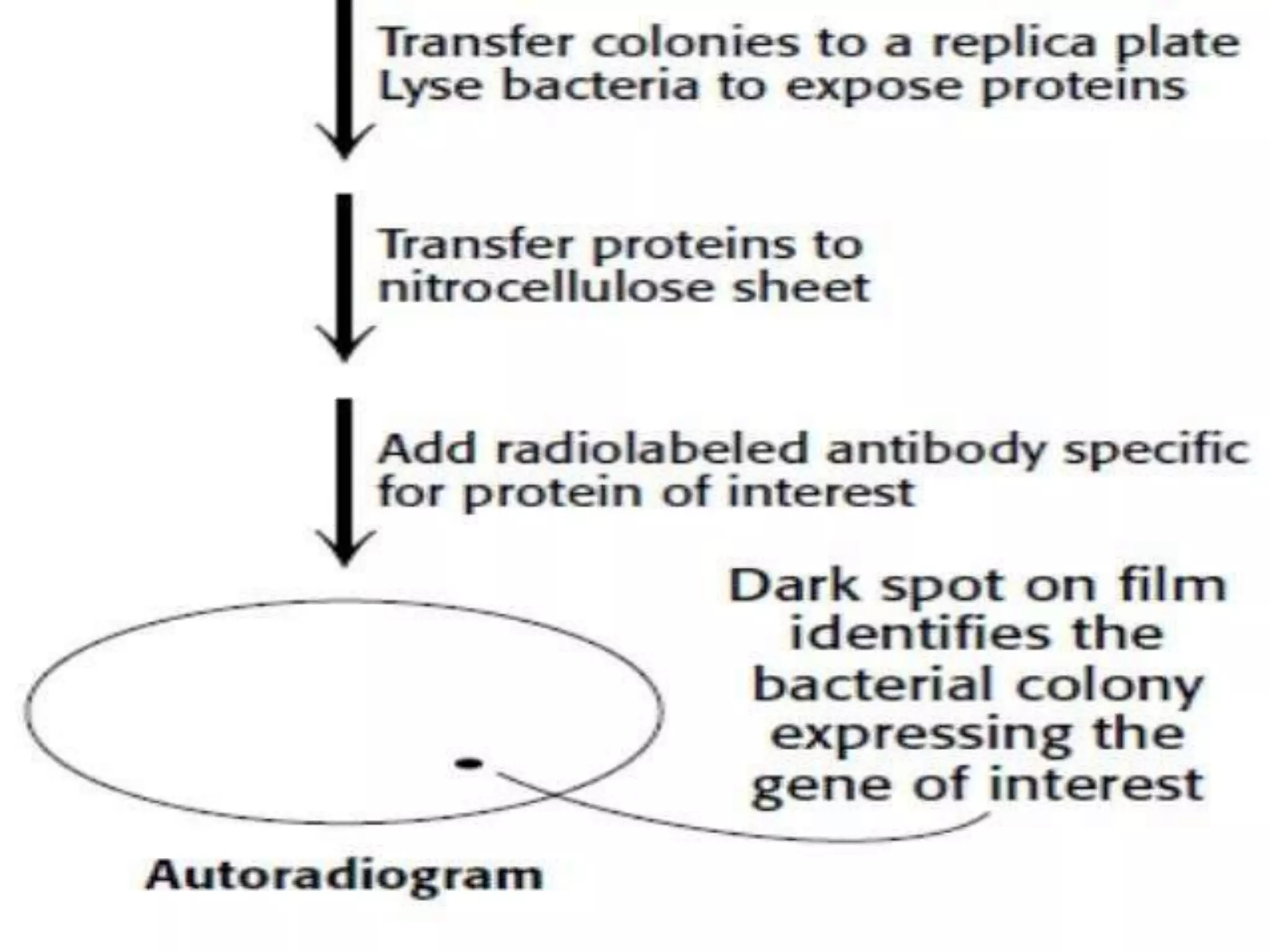
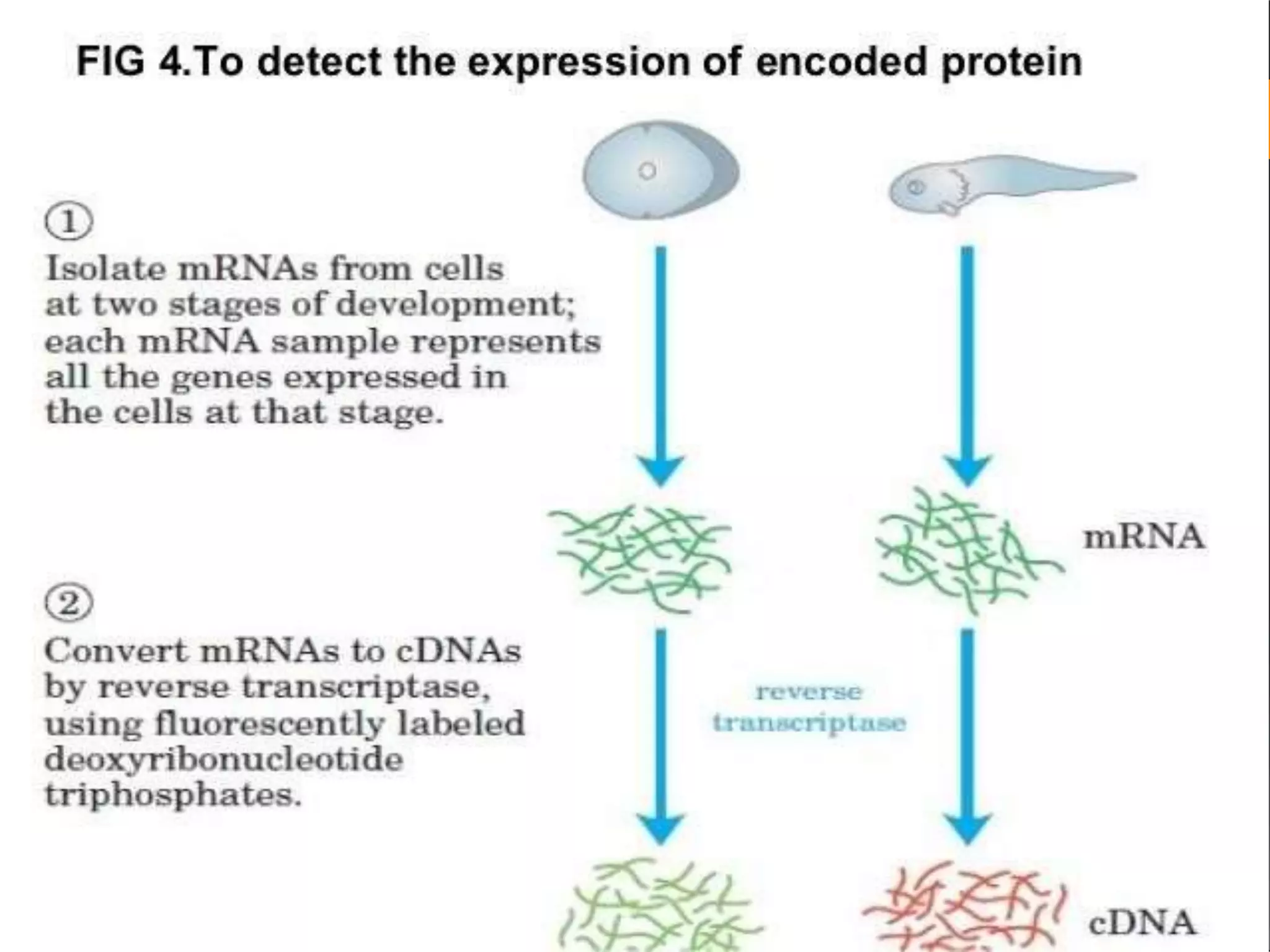
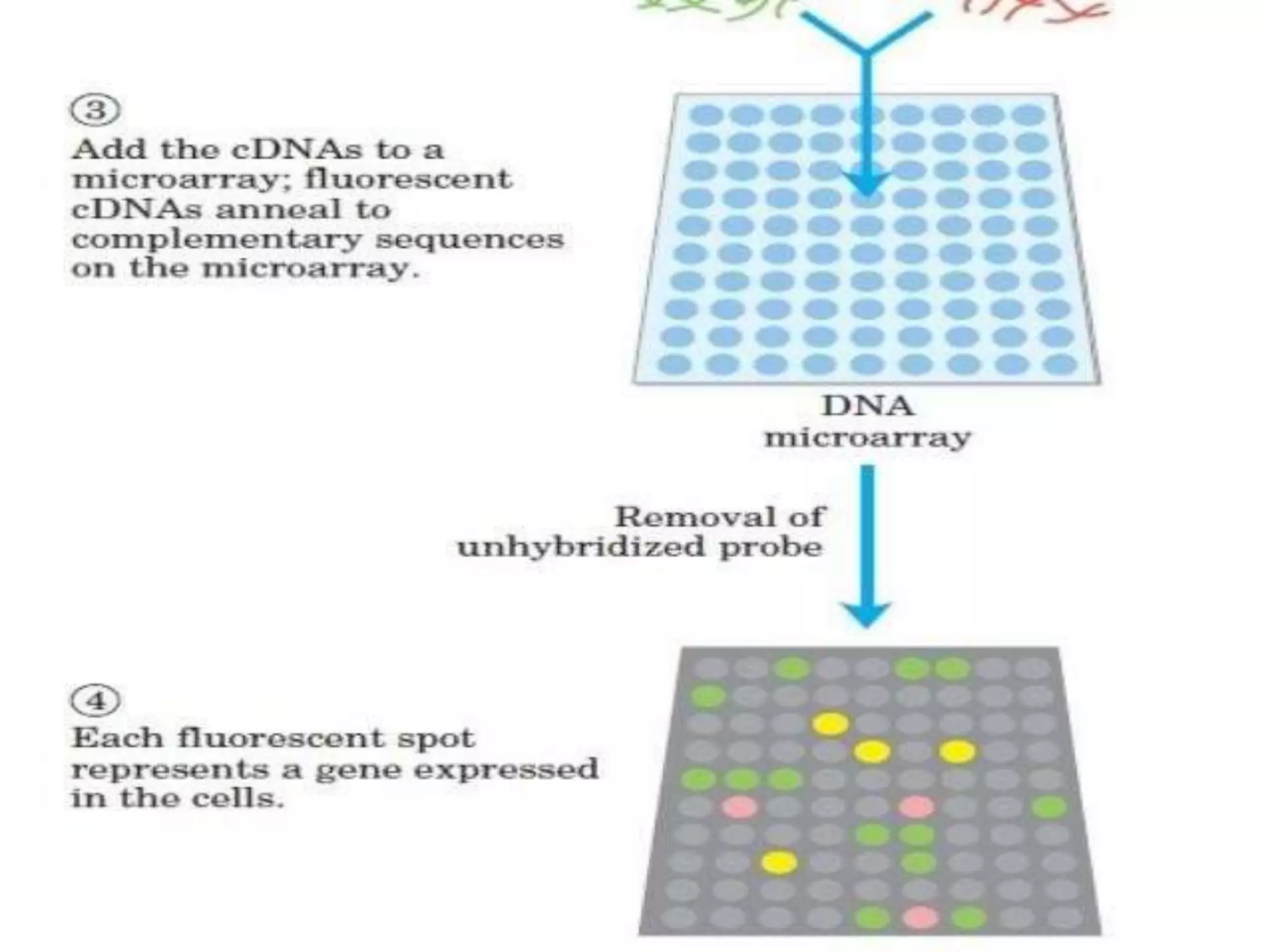
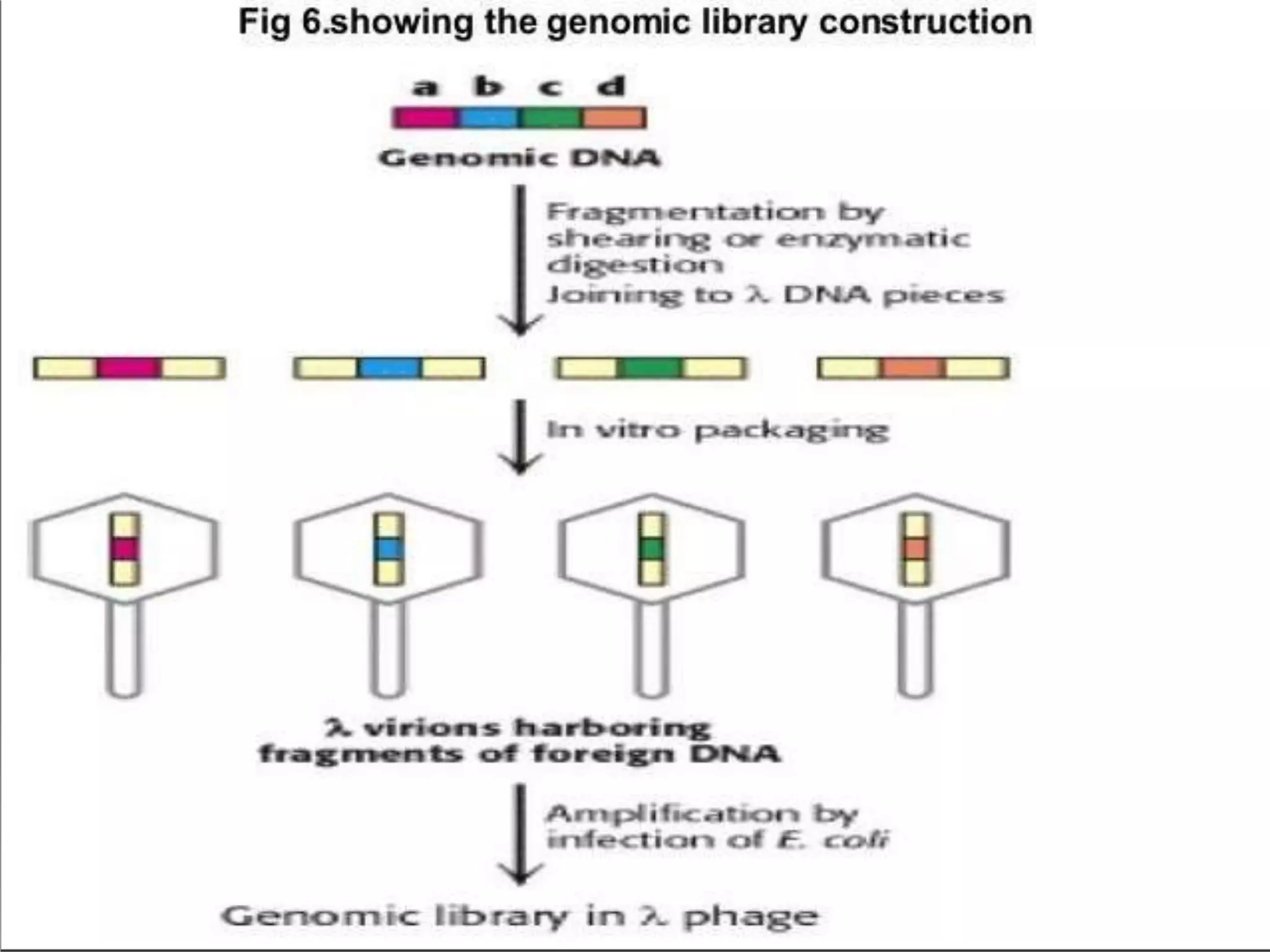
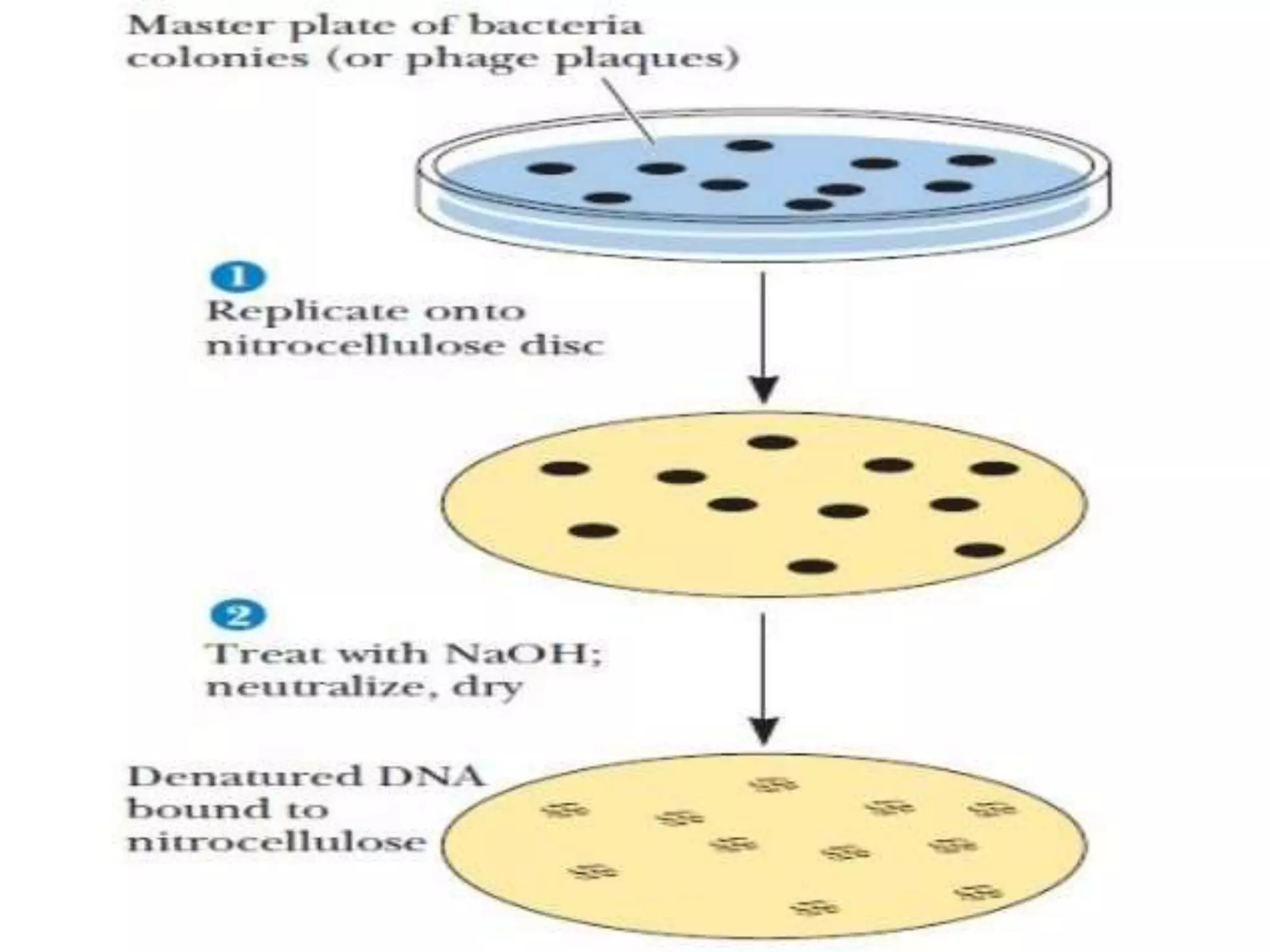
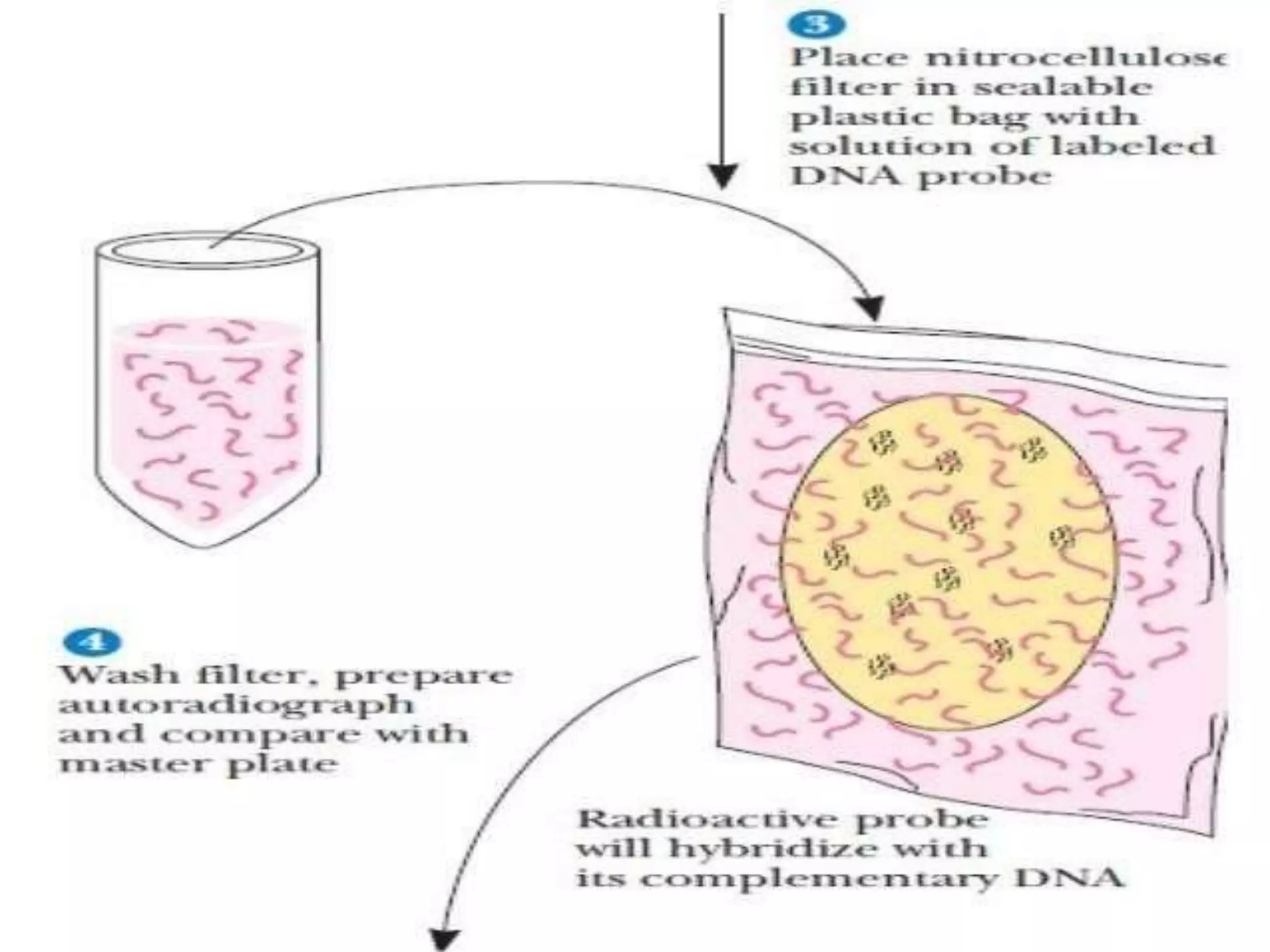
This document discusses cDNA and genomic libraries. It defines cDNA and genomic libraries and explains their key differences. A cDNA library contains only complementary DNA molecules synthesized from mRNA in a cell and represents the genes expressed in that cell. Genomic libraries for prokaryotes are easier to make and contain all genome sequences since prokaryotic mRNA is unstable. cDNA libraries are useful for eukaryotic gene analysis as they contain condensed protein-encoded genes without introns. The document also provides details on the construction, screening, and uses of cDNA and genomic libraries.