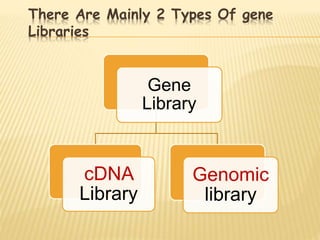
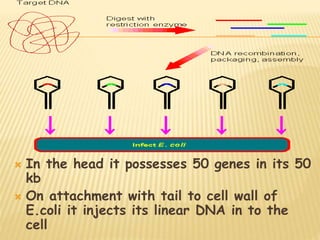
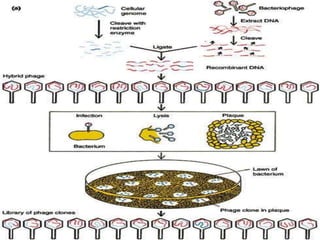
This document discusses gene libraries and their construction. There are two main types of gene libraries: cDNA libraries which contain only expressed DNA sequences, and genomic libraries which contain both coding and non-coding DNA fragments representing an organism's entire genome. The procedure to create a genomic library using lambda phage involves isolating and purifying genomic DNA, cutting it into fragments using restriction enzymes, ligating the fragments into lambda phage vectors, and transforming the recombinant DNA into a bacterial host to generate a library of clones representing the entire genome.