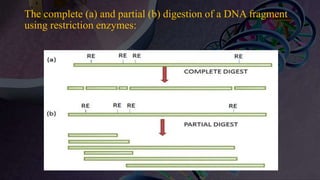
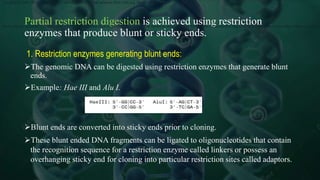
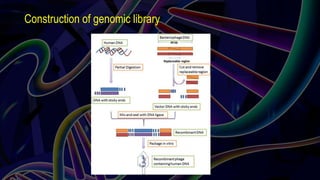
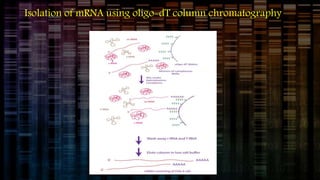
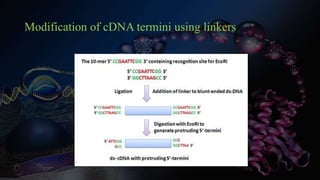
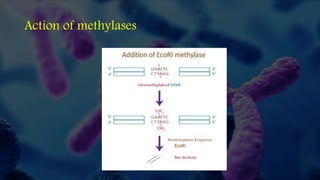
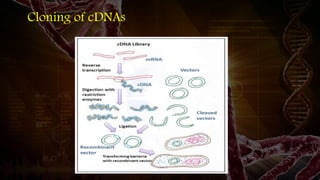
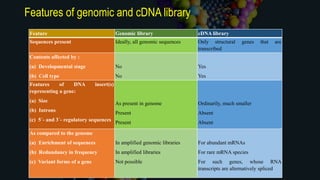
Genomic DNA libraries contain representative copies of all DNA fragments in an organism's genome, including both expressed and non-expressed sequences. They are constructed by isolating genomic DNA, fragmenting it, and cloning the fragments into suitable vectors like lambda phage or BACs. cDNA libraries contain only expressed sequences, as they are constructed by isolating mRNA from tissues, reverse transcribing it to cDNA, and cloning the cDNA fragments. Both library types are useful for gene discovery, sequencing, mapping genomes, and studying regulatory sequences.