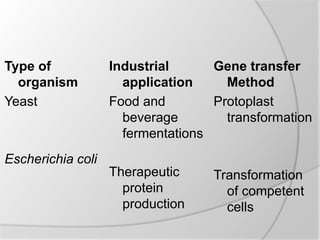
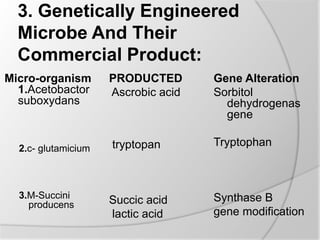
Genetic engineering involves altering an organism's genetic material, employing tools like vectors, restriction enzymes, and selection mechanisms. It has various industrial applications across food, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, enhancing product yield through methods like overcoming rate-limiting steps and eliminating feedback regulation. Genetically engineered microbes have been developed to significantly improve health, agriculture, and environmental outcomes.