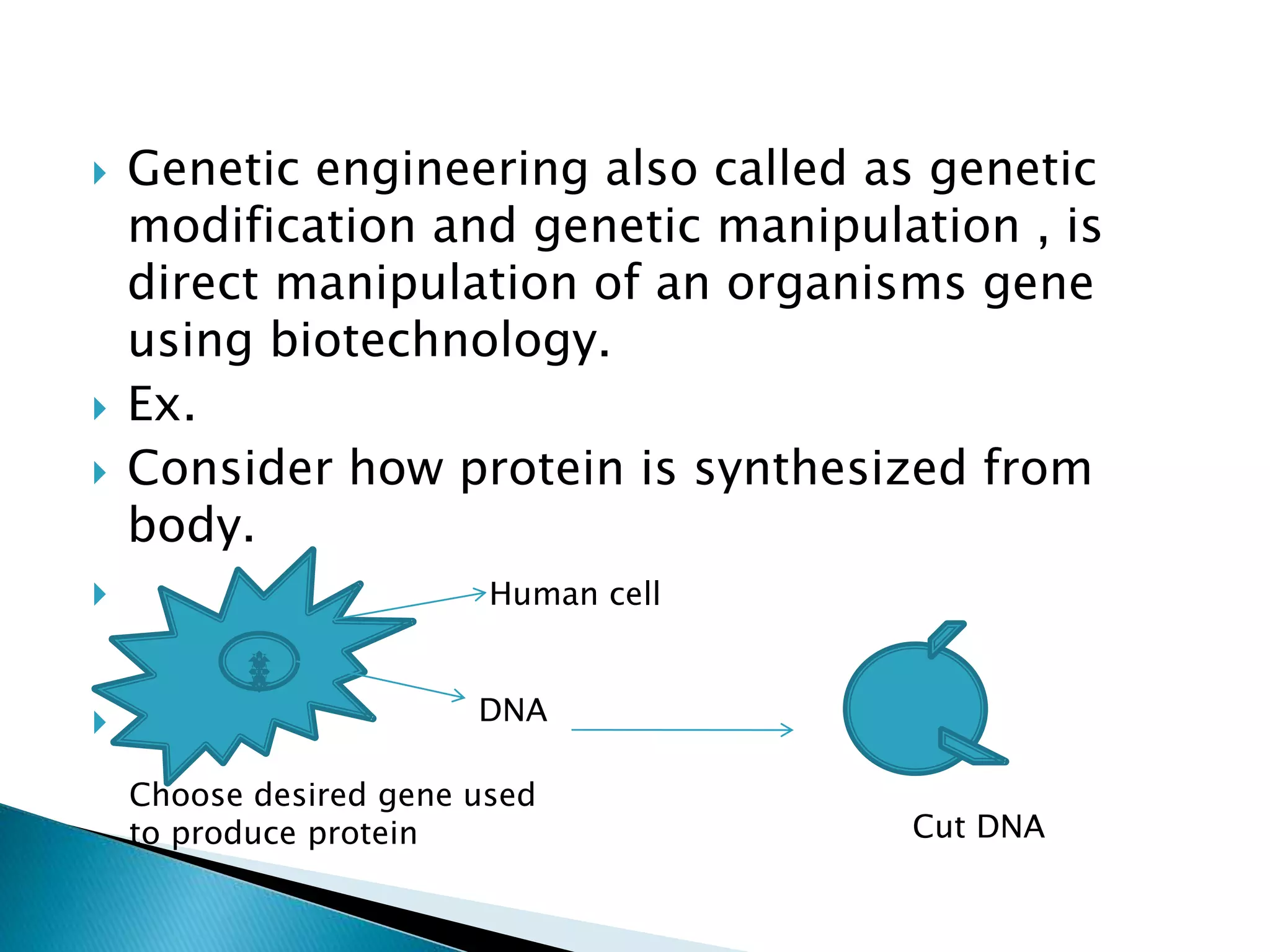
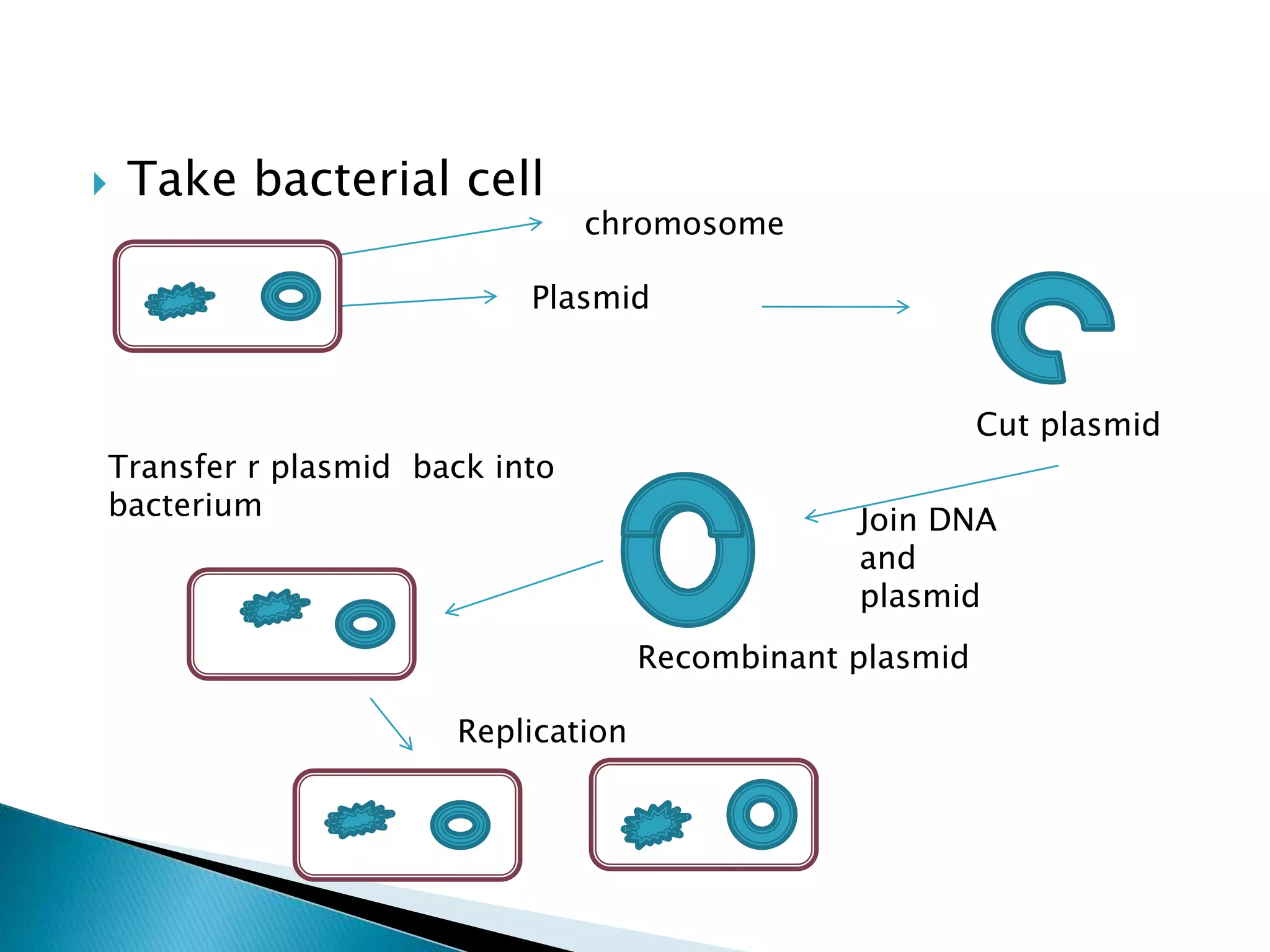
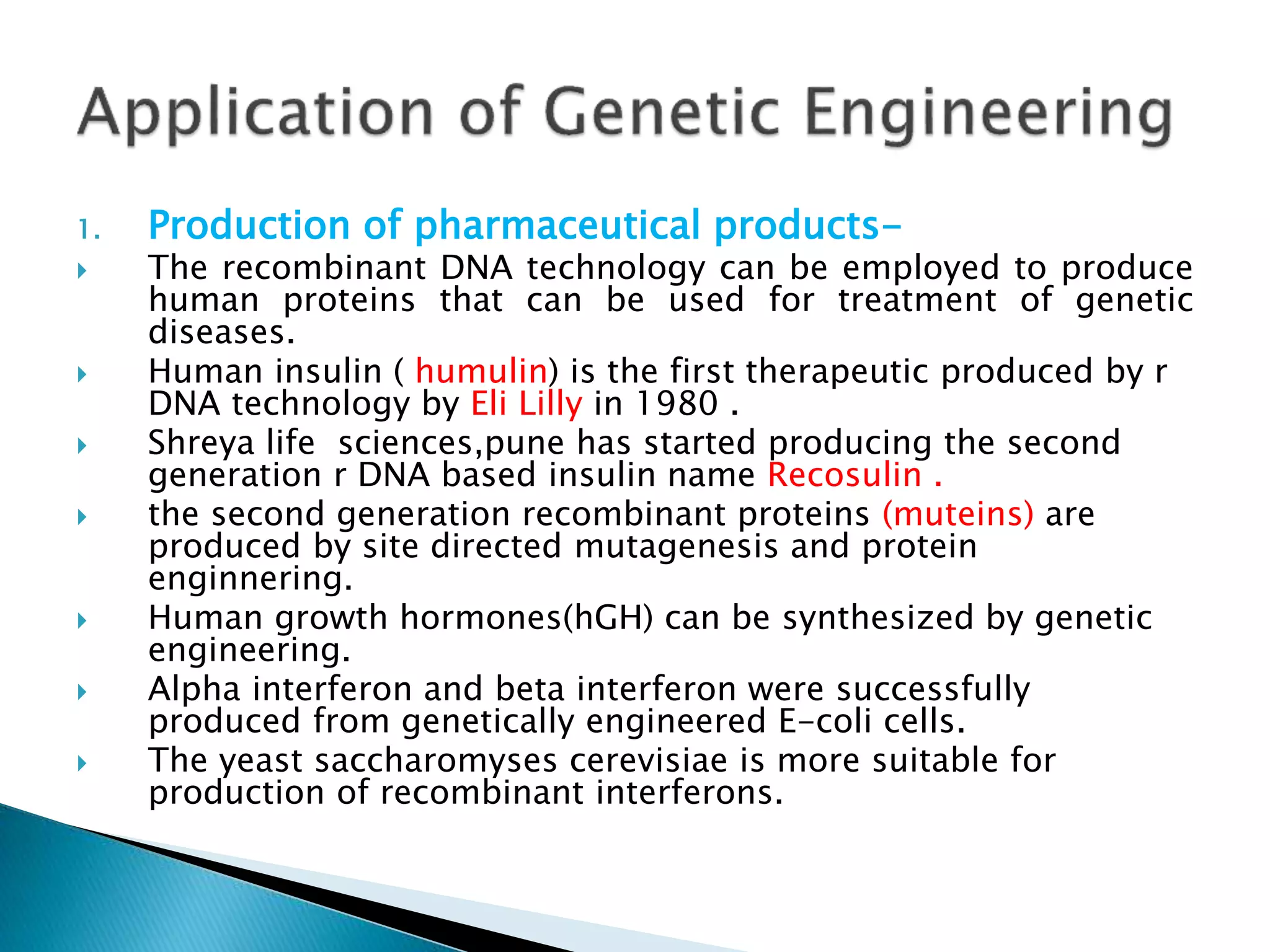
Genetic engineering involves modifying an organism's genetic material, primarily through techniques such as recombination, where new genes are inserted into bacterial DNA. This process enables the production of valuable pharmaceutical products, including human insulin and vaccines, and facilitates crop improvement for higher yields and disease resistance. Additionally, gene therapy and the development of transgenic plants and animals showcase the broad applications and benefits of genetic engineering in medicine and agriculture.












![ Agrobacterium is bacteria that uses a
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) to cause
tumers in plants .
Agrobacterium used in biotechnology for
plant improvemet.
HGT is the transfer of DNA between different
genomes
[Pop up: A genome is the complete set of
genetic material present in an organism].
HGT can occur in bacteria through
transformation, conjugation and
Transduction. .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticengineering-230619065958-8db35207/75/GENETIC-ENGINEERING-pptx-16-2048.jpg)

