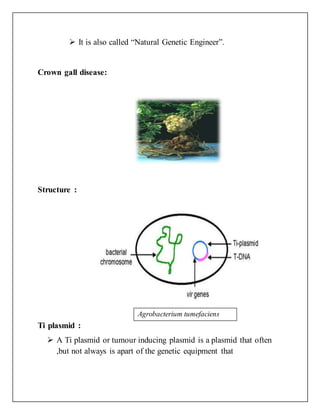
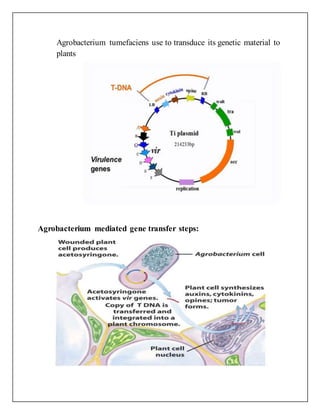
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium that can transfer DNA fragments called T-DNA into plant cells. It causes crown gall disease in susceptible plants like tomatoes and sunflowers by integrating T-DNA into the plant cell's genome. During Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer, wounded plant cells produce signal molecules that activate virulence genes in Agrobacterium, causing it to synthesize single-stranded T-DNA. The T-DNA is then transferred into the plant cell nucleus where it integrates and expresses genes that promote tumor formation. This natural process allows for stable transformation of plant cells and regeneration of whole transgenic plants.