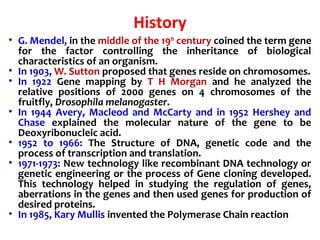
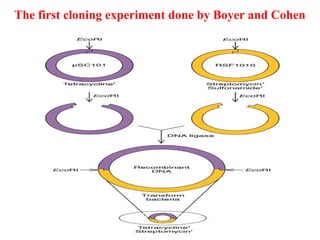
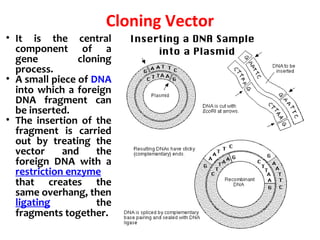
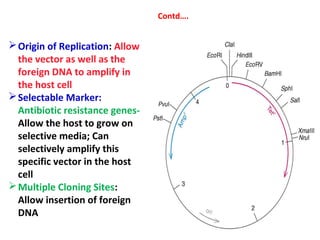
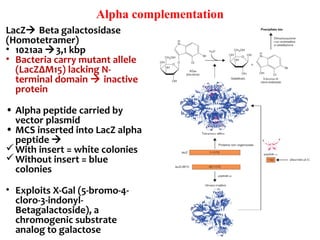
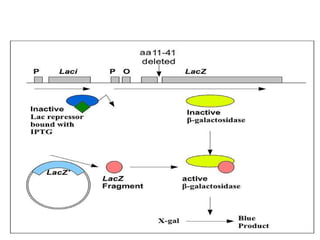
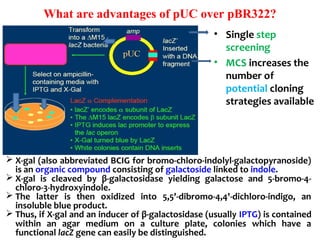
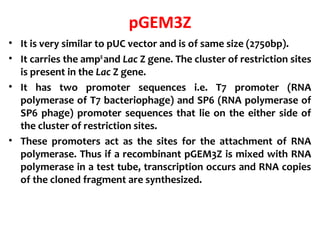
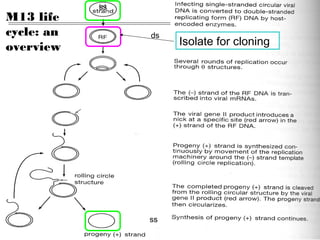
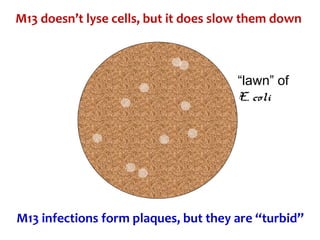
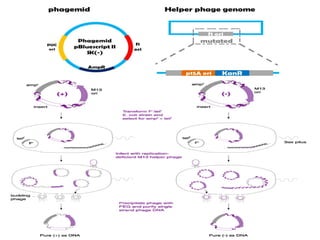
Gene cloning involves inserting DNA fragments into cloning vectors, which are then transferred into host cells. Some key points:
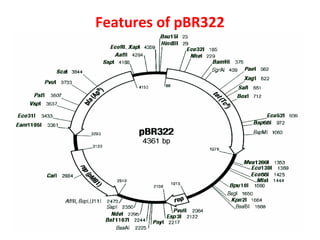
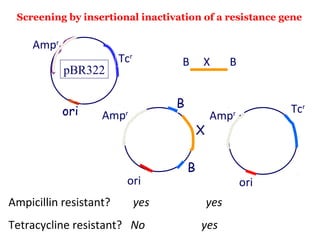
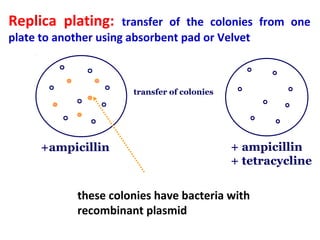
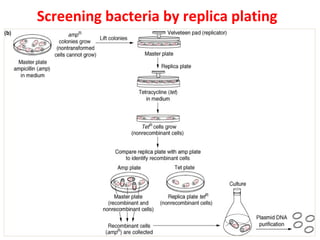
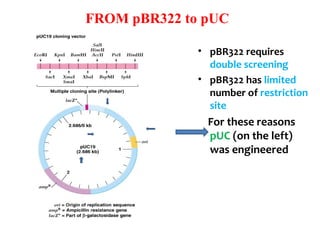
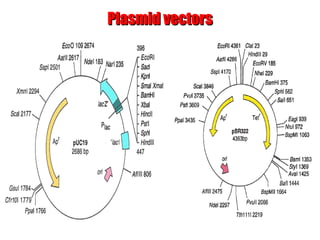
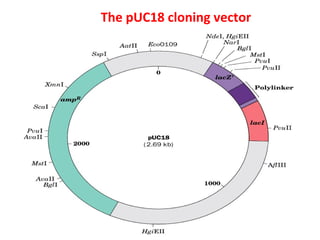
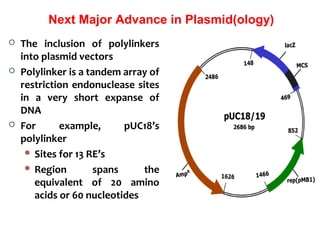
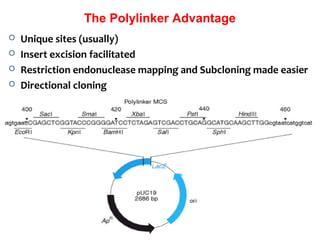
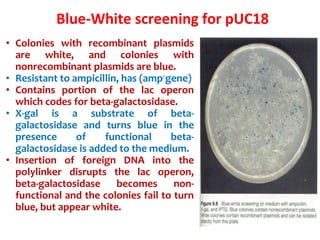
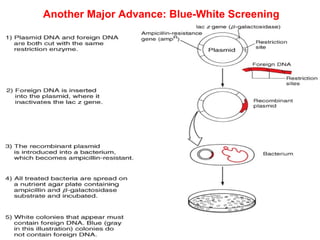
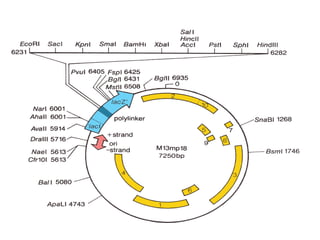
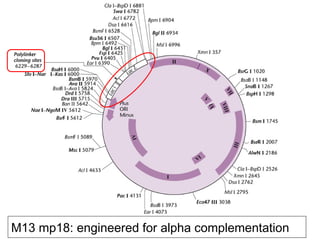
- Plasmid vectors like pBR322 were early cloning vectors but had limitations. Improved vectors like pUC18 addressed these with features like blue-white screening and expanded multiple cloning sites.
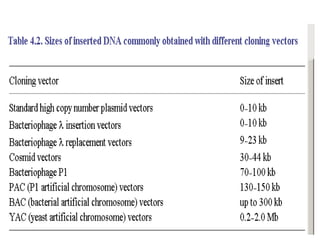
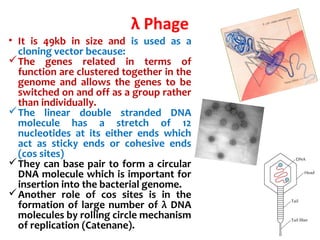
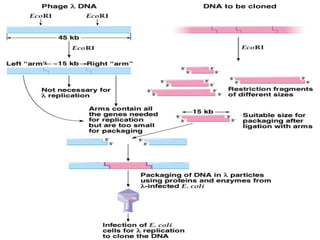
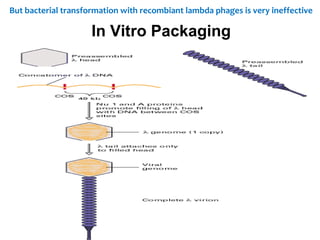
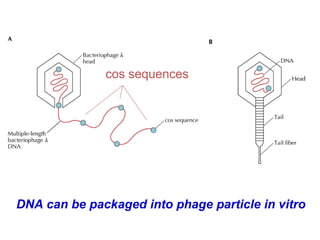
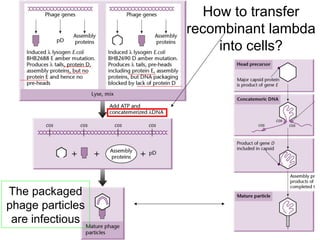
- Lambda phage vectors can clone larger DNA fragments of 5-25kb compared to plasmid vectors. The lambda phage genome is engineered to package recombinant DNA in vitro before infecting host cells.
- Different vector types are suited to different applications based on size of insert, host range, and other factors. Gene cloning allows isolation and analysis of genes and their regulation.












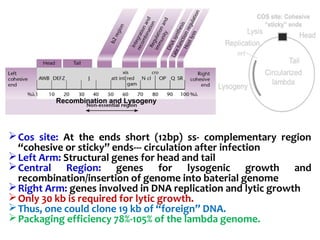








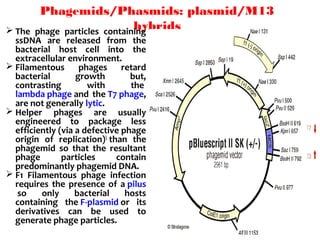
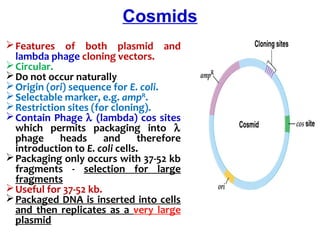
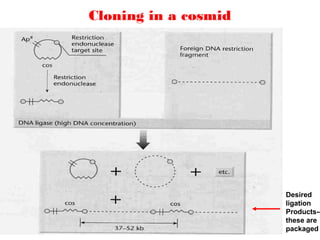
![ A cosmid is a type of hybrid plasmid that contains a Lambda phage
cos sequence.
Cosmids (cos sites + plasmid = cosmids) DNA sequences are originally from
the lambda phage.
They are often used as a cloning vector in genetic engineering.
Cosmids can be used to build genomic libraries.
They were first described by Collins and Hohn in 1978.
Cosmids can contain 37 to 52 (normally 45) kb of DNA, limits based on the
normal bacteriophage packaging size.
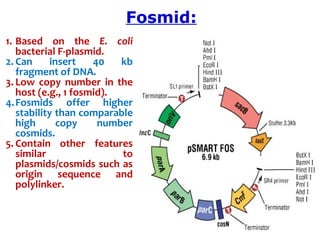
They can replicate as plasmids if they have a suitable origin of replication: for
example SV40 ori in mammalian cells, ColE1 ori for double-stranded DNA
replication or f1 ori for single-stranded DNA replication in prokaryotes.
They frequently also contain a gene for selection such as antibiotic resistance
, so that the transformed cells can be identified by plating on a medium
containing the antibiotic. Those cells which did not take up the cosmid would
be unable to grow.[3]
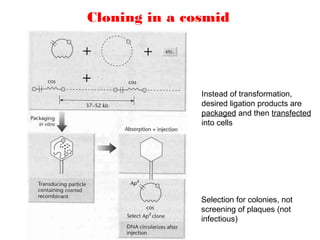
Unlike plasmids, they can also be packaged in phage capsids, which allows
the foreign genes to be transferred into or between cells by transduction.
Plasmids become unstable after a certain amount of DNA has been inserted
into them, because their increased size is more conducive to recombination.
To circumvent this, phage transduction is used instead. This is made possible
by the cohesive ends, also known as cos sites. In this way, they are similar to
using the lambda phage as a vector, except all the lambda genes have been
deleted with the exception of the cos sequence.
Cosmids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloningvectors-180609195846/85/Cloning-vectors-59-320.jpg)