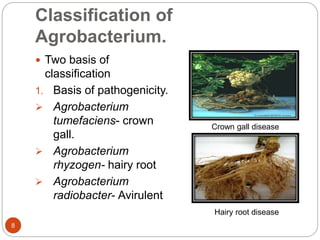
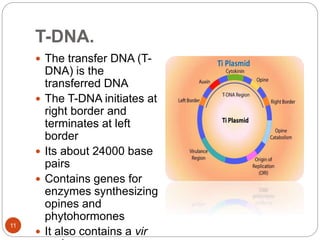
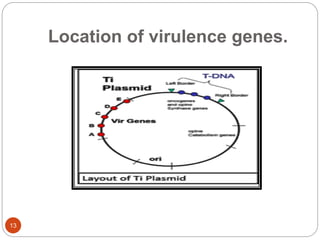
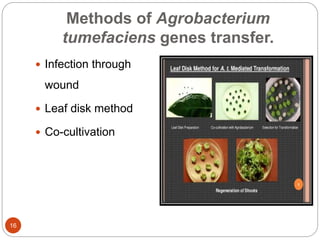
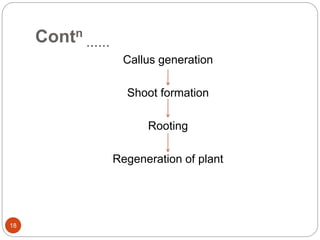
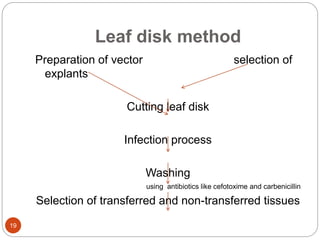
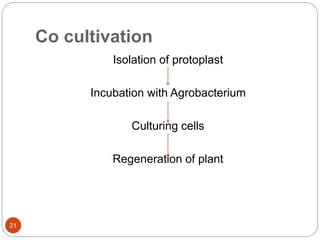
This document provides an overview of Agrobacterium-mediated gene transformation. It begins with an introduction to genetic transformation methods, including direct and indirect techniques. It then discusses Agrobacterium, including its classification, the history of using it for gene transformation, and features of its T-DNA and virulence genes. The document outlines the process of T-DNA transfer from Agrobacterium to plant cells. Finally, it describes some common methods for Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer, such as infection through wounds, leaf disk, and co-cultivation techniques.