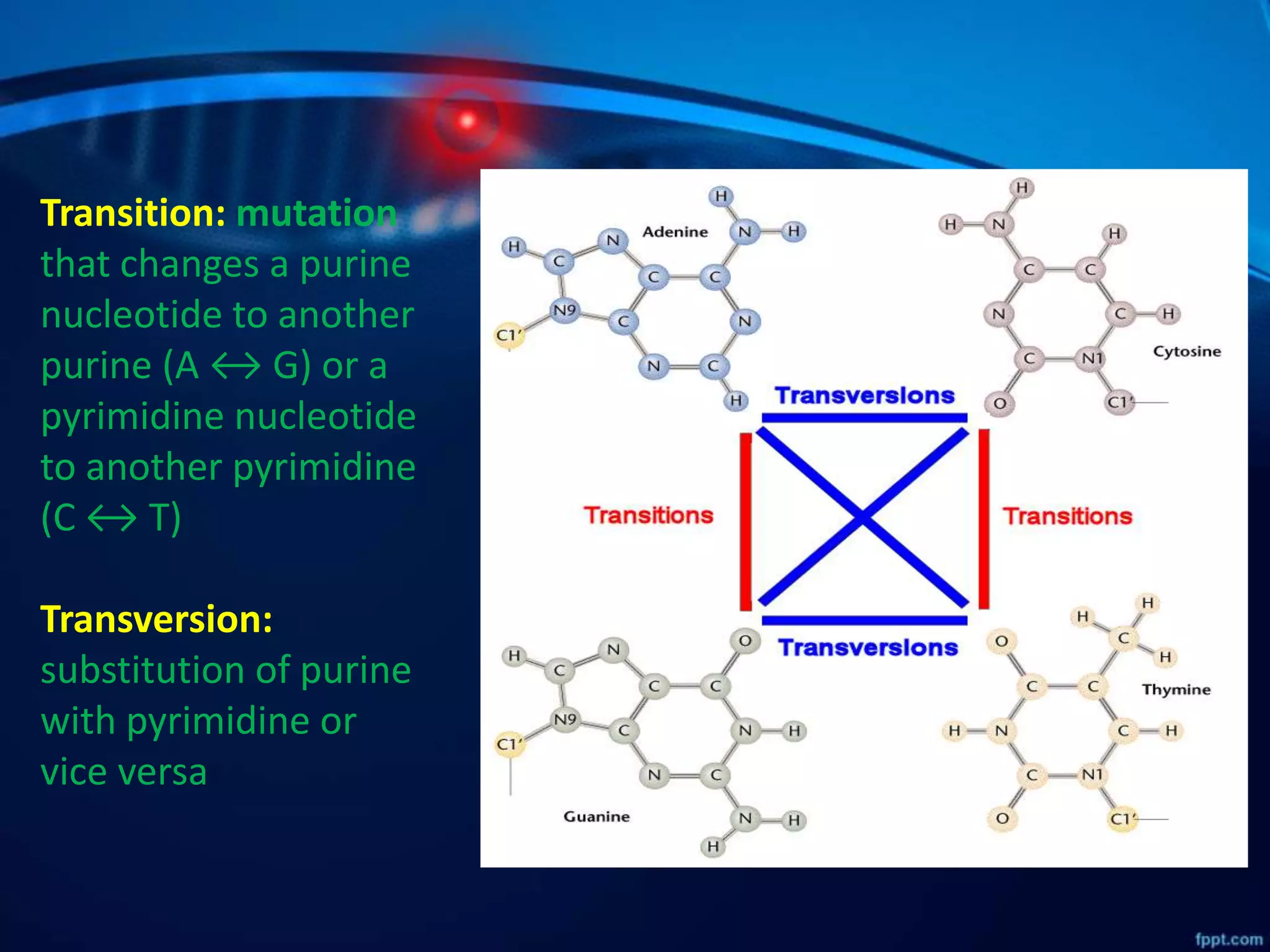
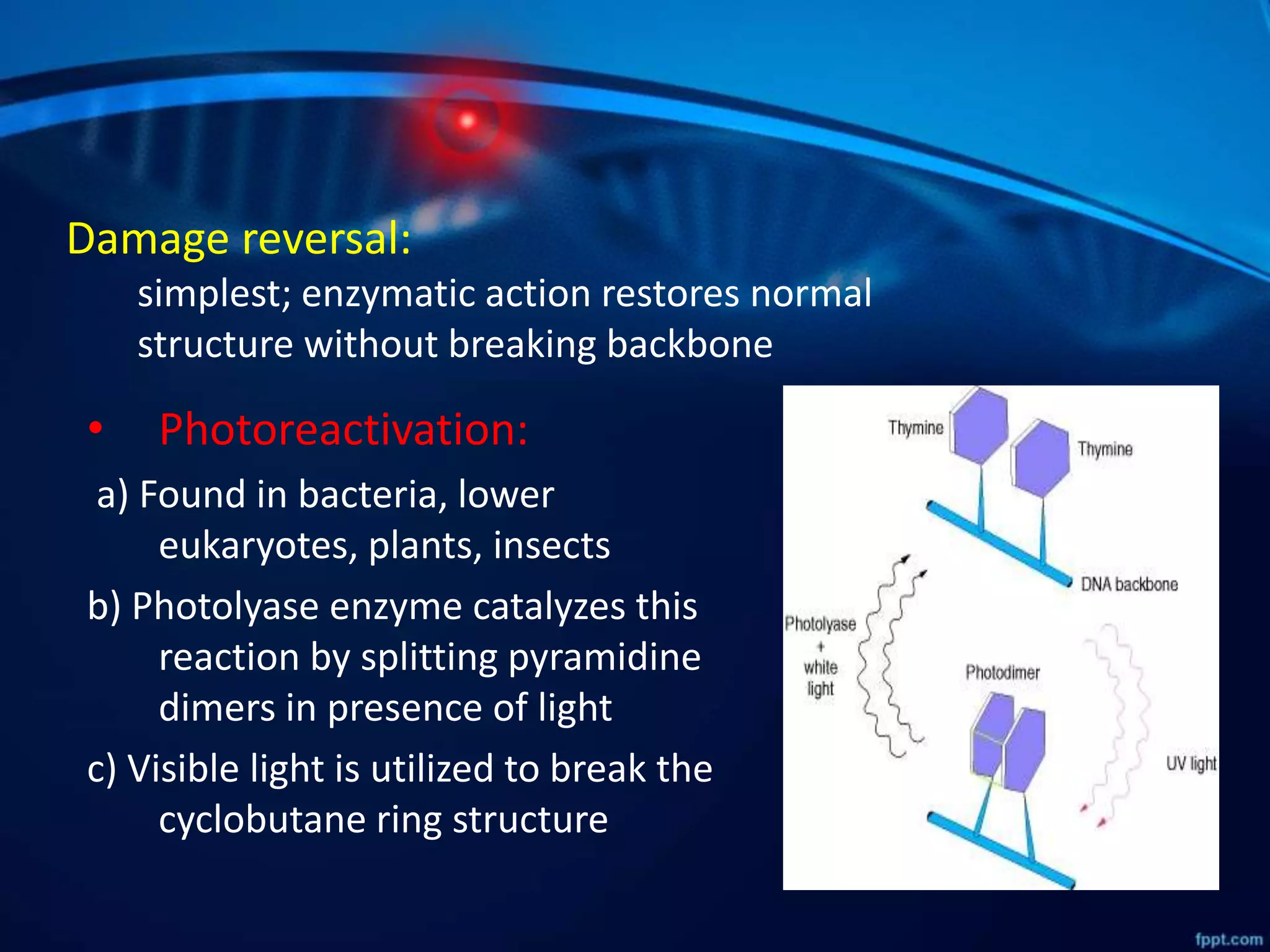
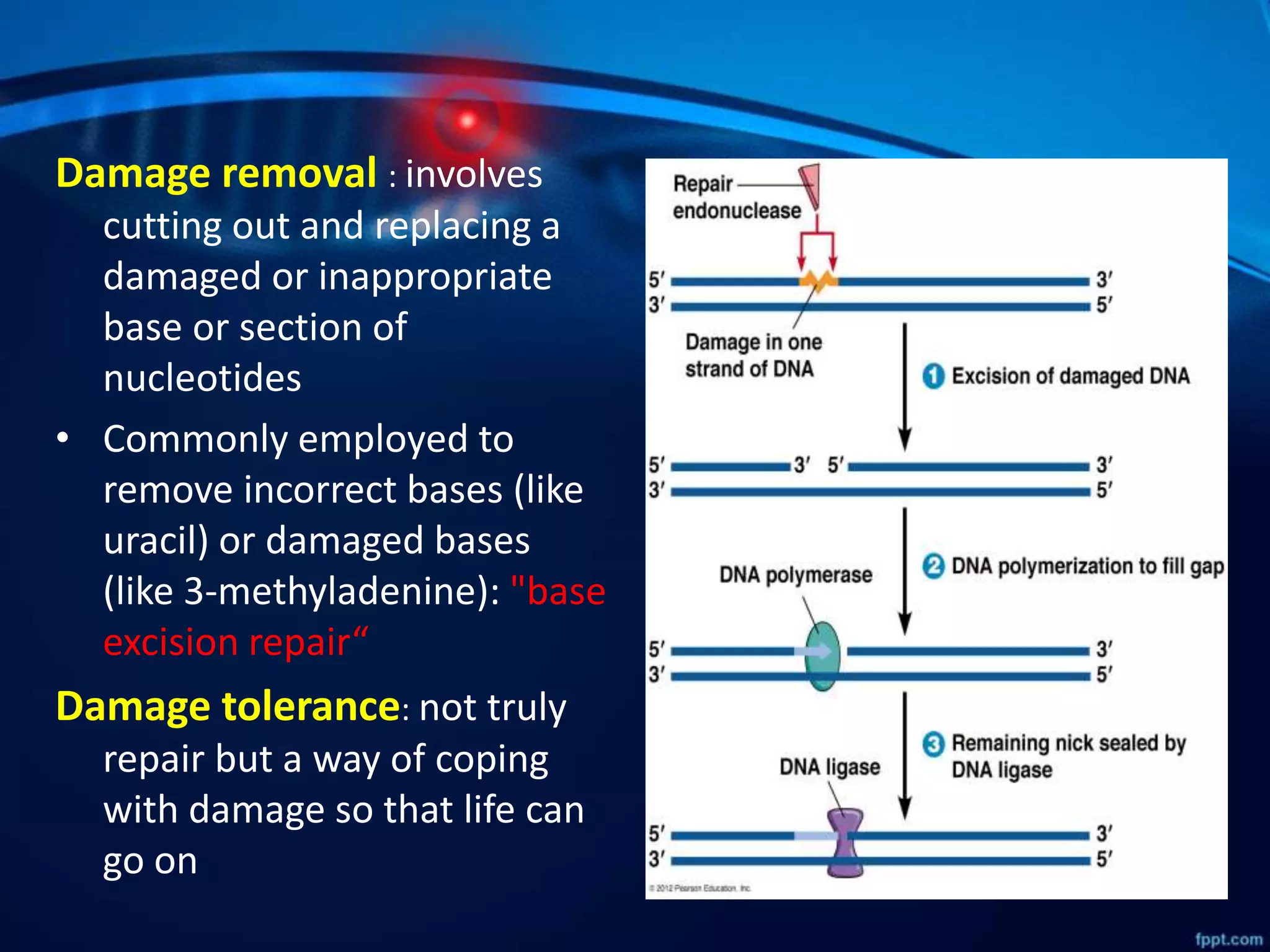
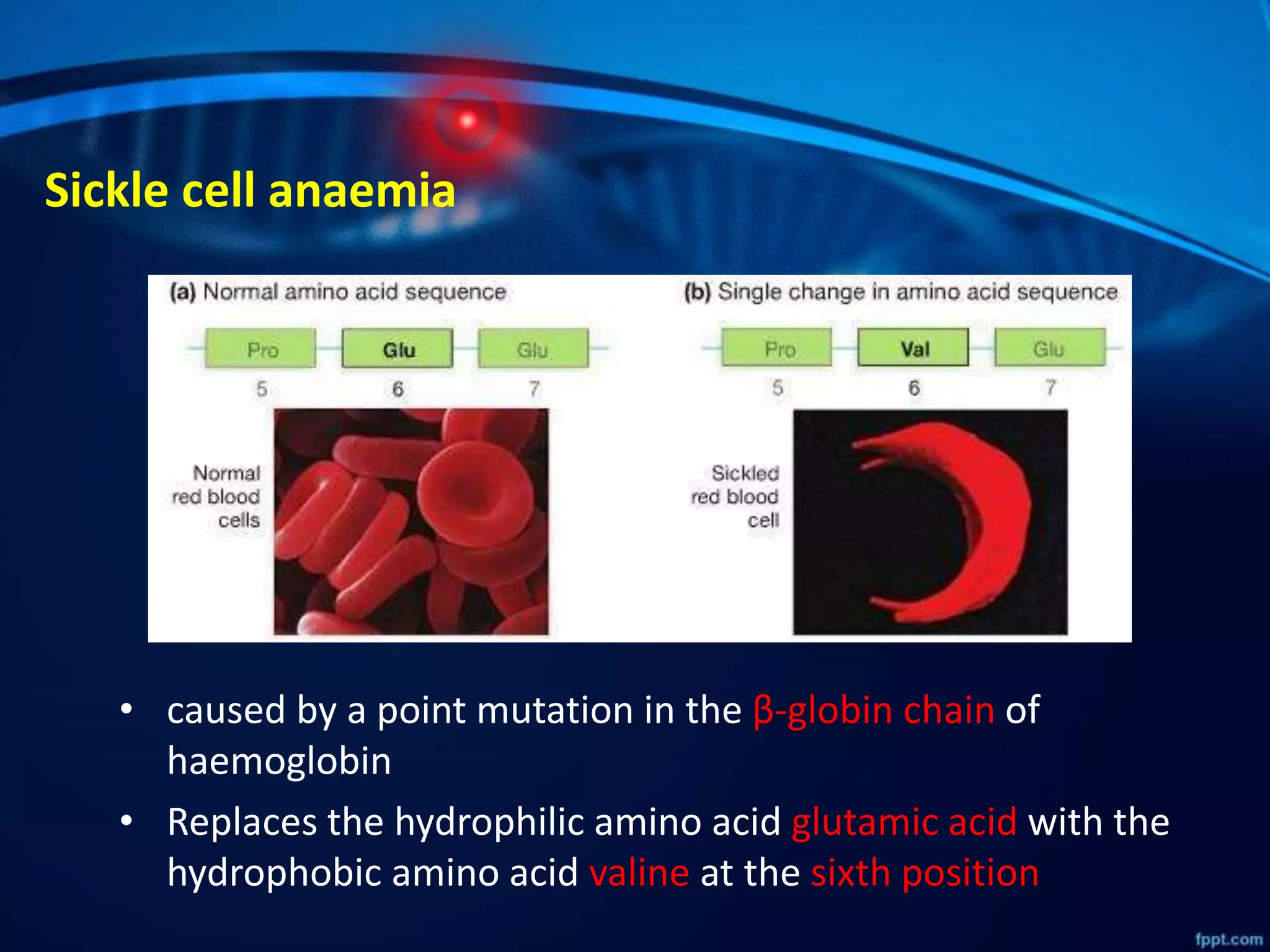
DNA mutations can occur through spontaneous errors in DNA replication or through exposure to mutagens like chemicals or radiation. There are several types of mutations that can occur at the single nucleotide level, including transitions, transversions, missense mutations, and nonsense mutations. The cell has DNA repair mechanisms to correct errors that occur, but unrepaired mutations can cause genetic disorders if they occur in germline cells. Common genetic disorders caused by single nucleotide mutations include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In some cases, mutations can provide benefits to organisms, such as resistance to diseases like malaria.