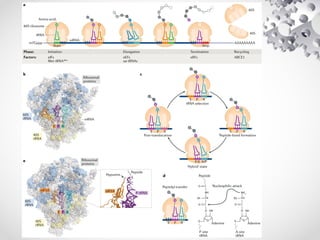
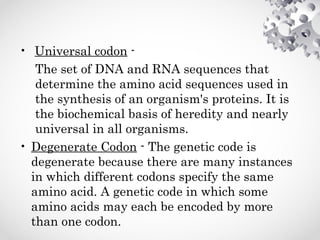
The document presents an overview of the translation process of the central dogma of molecular biology, detailing the three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. It explains the roles of various components including mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA, and translation factors, as well as definitions of key terminologies related to codons. The presentation concludes with references to video resources for further understanding of the translation mechanism.