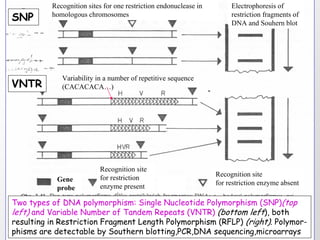
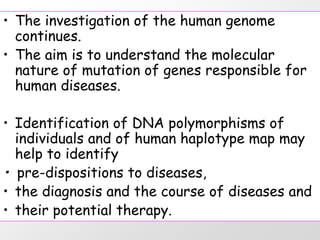
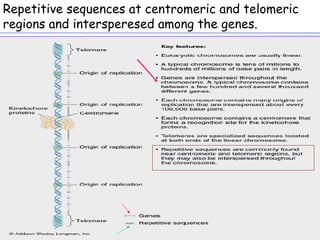
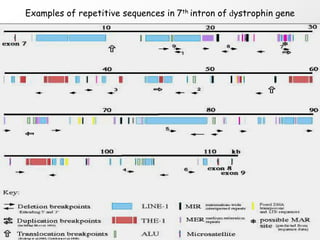
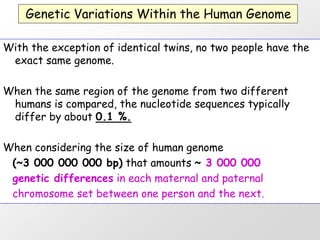
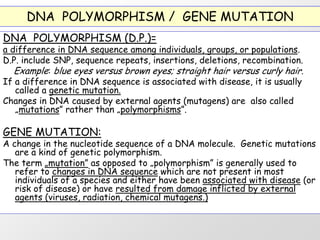
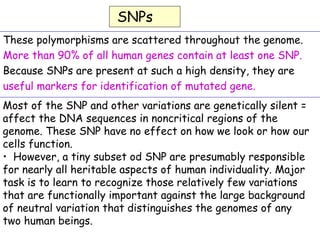
1. DNA polymorphisms, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), are natural variations in DNA sequences among individuals.
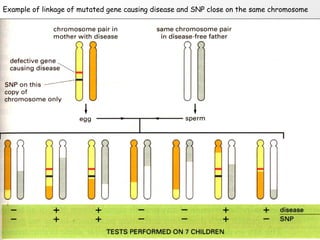
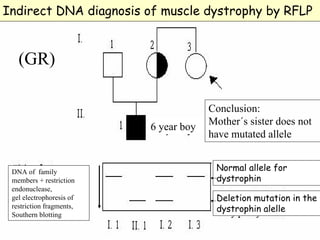
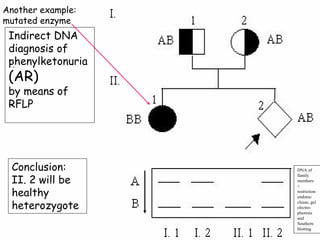
2. These polymorphisms can be used for indirect DNA diagnosis of genetic diseases through detection of restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) near mutated genes.
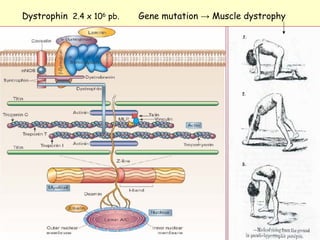
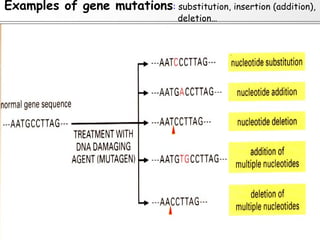
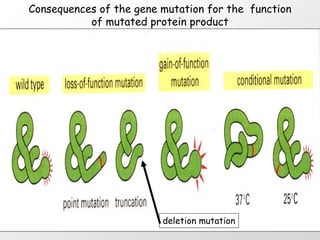
3. Examples of gene mutations include substitutions, insertions, and deletions that can alter protein products and cause disease if in coding regions. Indirect diagnosis uses linked polymorphisms to infer whether individuals carry disease-causing mutations.












![Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) [„SNiPS”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11dnapolymorphismsmutationsandgeneticdiseases4-110914045221-phpapp02/85/L11-dna__polymorphisms__mutations_and_genetic_diseases-19-320.jpg)