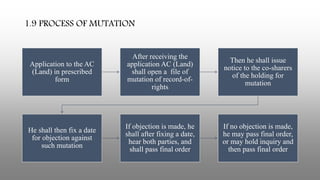
A man can acquire land through various means such as inheritance, sale, will, mortgage, etc. When land changes ownership, the new owner must apply for mutation to update the land records. Mutation involves inserting the new owner's name in the record-of-rights (khatiyan). Registration transfers ownership legally, while mutation updates the government land records. Mutation is required for both agricultural and non-agricultural land, though failure to mutate does not affect title for non-agricultural land. The legal basis for mutation is found in the State Acquisition and Tenancy Act of 1950.




![1.3 DISTINCTION BETWEEN REGISTRATION & MUTATION
• Registration is the process of documentation to the records in any
office either public or private. Registration of land is a full and final
agreement signed between two parties. Once a land is registered will
become the lawful owner of the property and is fully responsible for it
in all aspects.
• Once the land is registered in sub-registrar office, the buyer of the land
has to get the title of the land updated in his/her name in the local
revenue office [Assistant Commissioner (Land) Office]. This is
knowns as mutation.
• Thus, registration of land and mutation of land are two different
things. Mutation of land happens after the registration of land.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutationofland-170109163029/85/Mutation-of-land-5-320.jpg)


![1.5 GROUNDS FOR MUTATION APPLICATION
Mutation and updating land records are required in the following cases:
If the land owner dies and his/her successors want to update the
records. [sec. 143 (a) of State Acquisition and Tenancy Act, 1950]
Leading Case: Idris Ali vs. State, 38 DLR 270
If the ownership of land is transferred through sale, gift, will,
waqf, trust etc., by registered deed. [sec. 143(a) of the State
Acquisition and Tenancy Act, 1950]
If a person becomes owner of a land by the decree of a land by the
decree of a civil court.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutationofland-170109163029/85/Mutation-of-land-8-320.jpg)
![Continued…..
If the ownership of land is transferred through sale, gift, will,
waqf, trust etc., by registered deed. [sec. 143(a) of the State
Acquisition and Tenancy Act, 1950]
If a person becomes owner of a land by the decree of a land by the
decree of a civil court.
For abandonment or diluvion or acquisition of land. [Sec. 143 (d)
of the SAT Act, 1950]
If land ownership is dissolved for alluvion or under sections 90,
91, 92 and 93 of the State Acquisition and Tenancy Act, 1950.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutationofland-170109163029/85/Mutation-of-land-9-320.jpg)















![1.14 MUTATION AND TITLE OF THE LAND
• Record-of-rights itself is not a document of title. It is an evidence of
present possession [32 DLR 252].
• Mere mutation and payment of rents do not confer any title on any
person [Shahani Bibi vs. Nur Islam 4 BLC 195].
• However, when supported by other evidence, mutation would be a
valuable evidence. Rent paid after mutation will also become piece of
evidence.
• Rent receipts though not documents of title, are important items of
evidence of possession.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutationofland-170109163029/85/Mutation-of-land-26-320.jpg)


