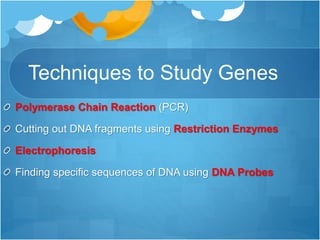
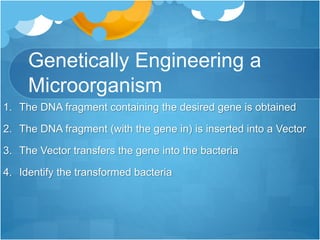
Techniques to study genes include polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify DNA fragments, using restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sequences, electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments by size, and DNA probes to find specific sequences. Genetic engineering techniques allow genes to be inserted into bacteria using vectors like plasmids. This allows production of proteins like human insulin. Golden rice has been genetically engineered to produce beta-carotene to reduce vitamin A deficiency in some countries. However, it has also raised ethical concerns about reducing biodiversity.