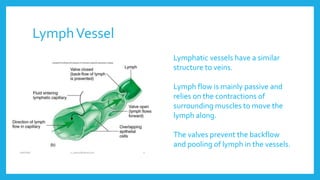
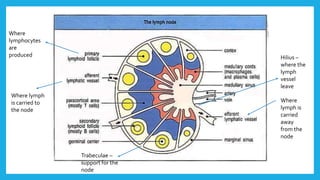
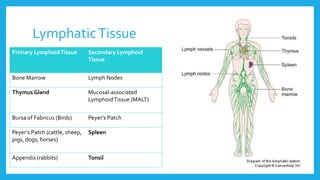
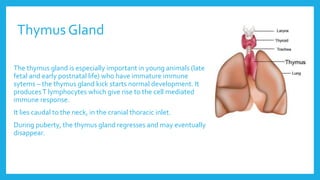
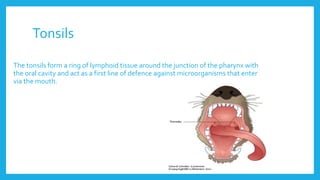
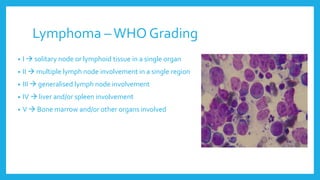
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes that plays a crucial role in returning excess tissue fluid to the blood, filtering lymph to remove foreign particles, transporting waste materials, and producing lymphocytes for immunity. It consists of various components, including lymphatic vessels that rely on muscle contractions for lymph flow and lymph nodes that filter lymph and produce immune cells. Disorders such as lymphangitis and lymphoma can affect the lymphatic system, with treatments ranging from antibiotics and management strategies to chemotherapy and surgery.