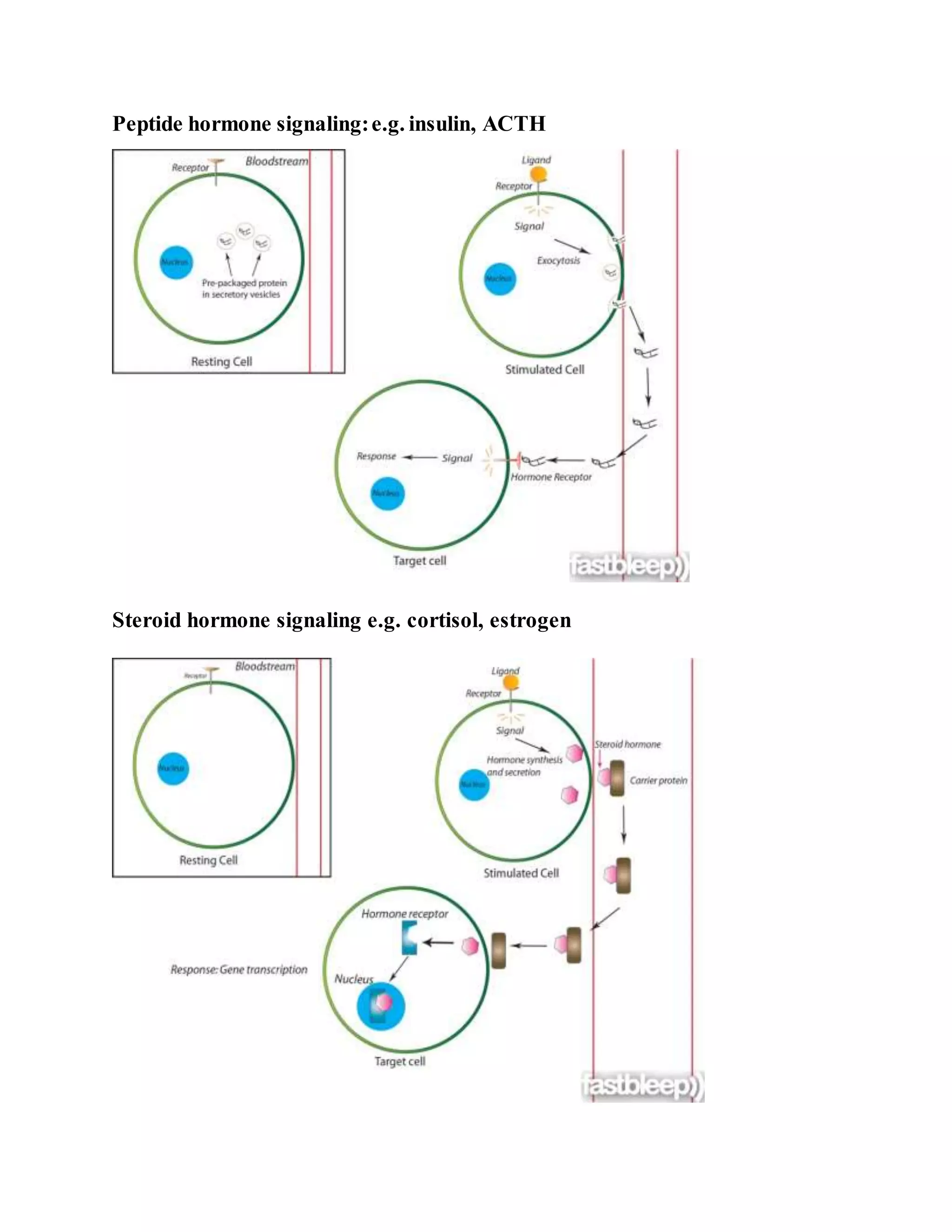
Endocrine signaling occurs when endocrine cells in ductless glands release hormones into the bloodstream to act on distant target cells. The major glands involved include the thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries/testes, parathyroids, thymus and pineal gland. Hormones can be peptides like insulin which bind cell surface receptors, or steroids like cortisol which enter cells and affect gene expression. Many pathways operate in a negative feedback loop controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.