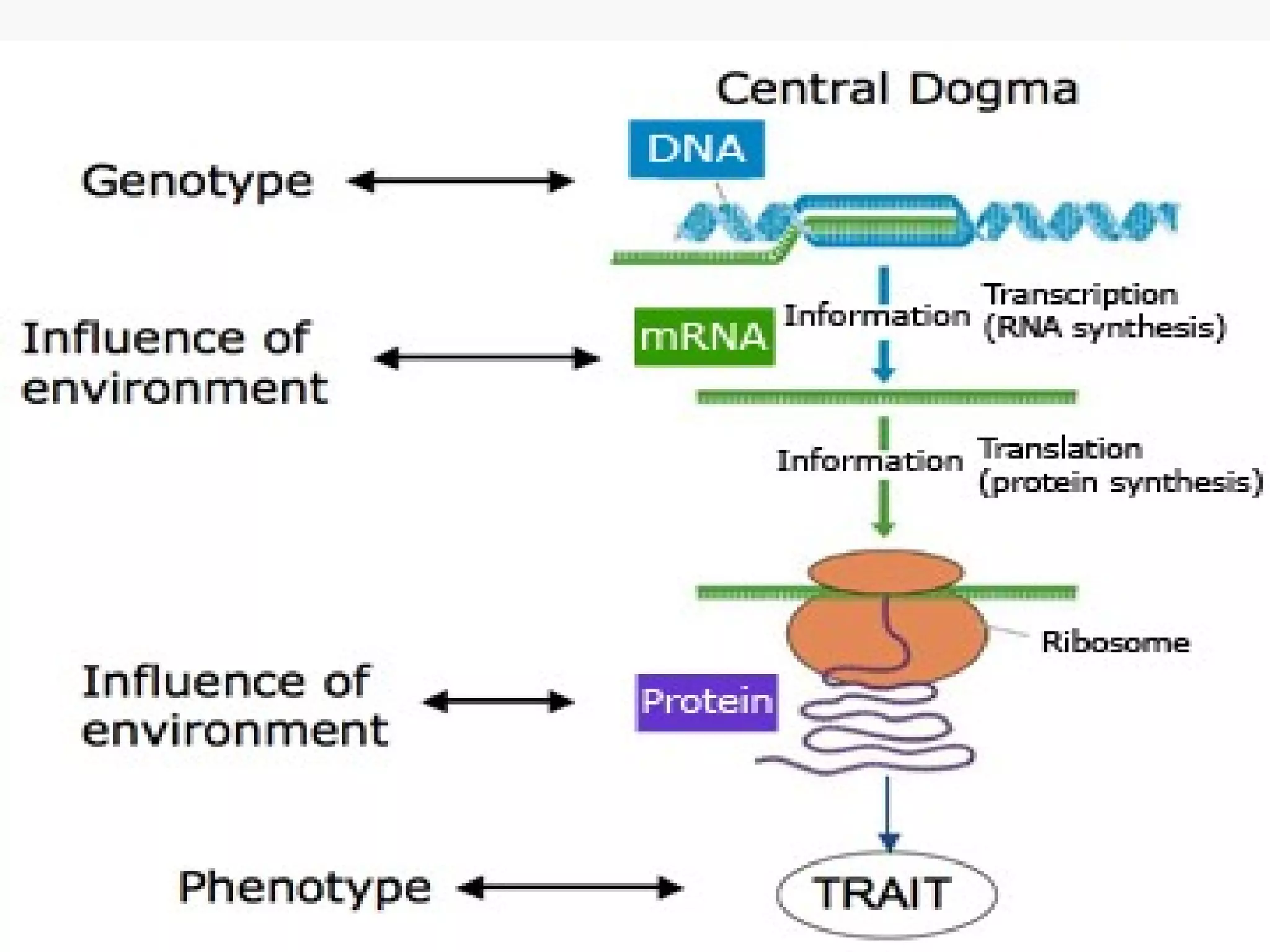
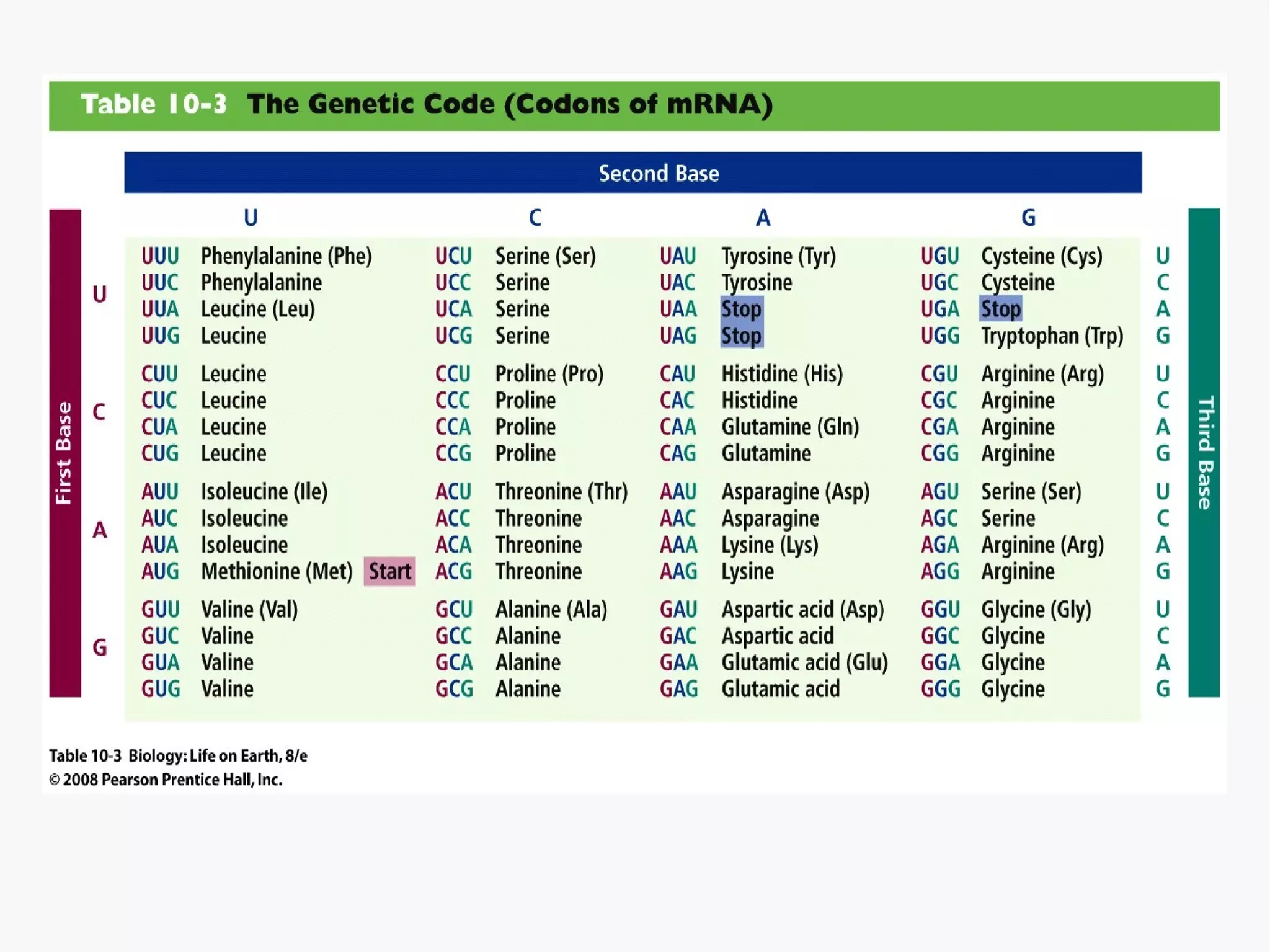
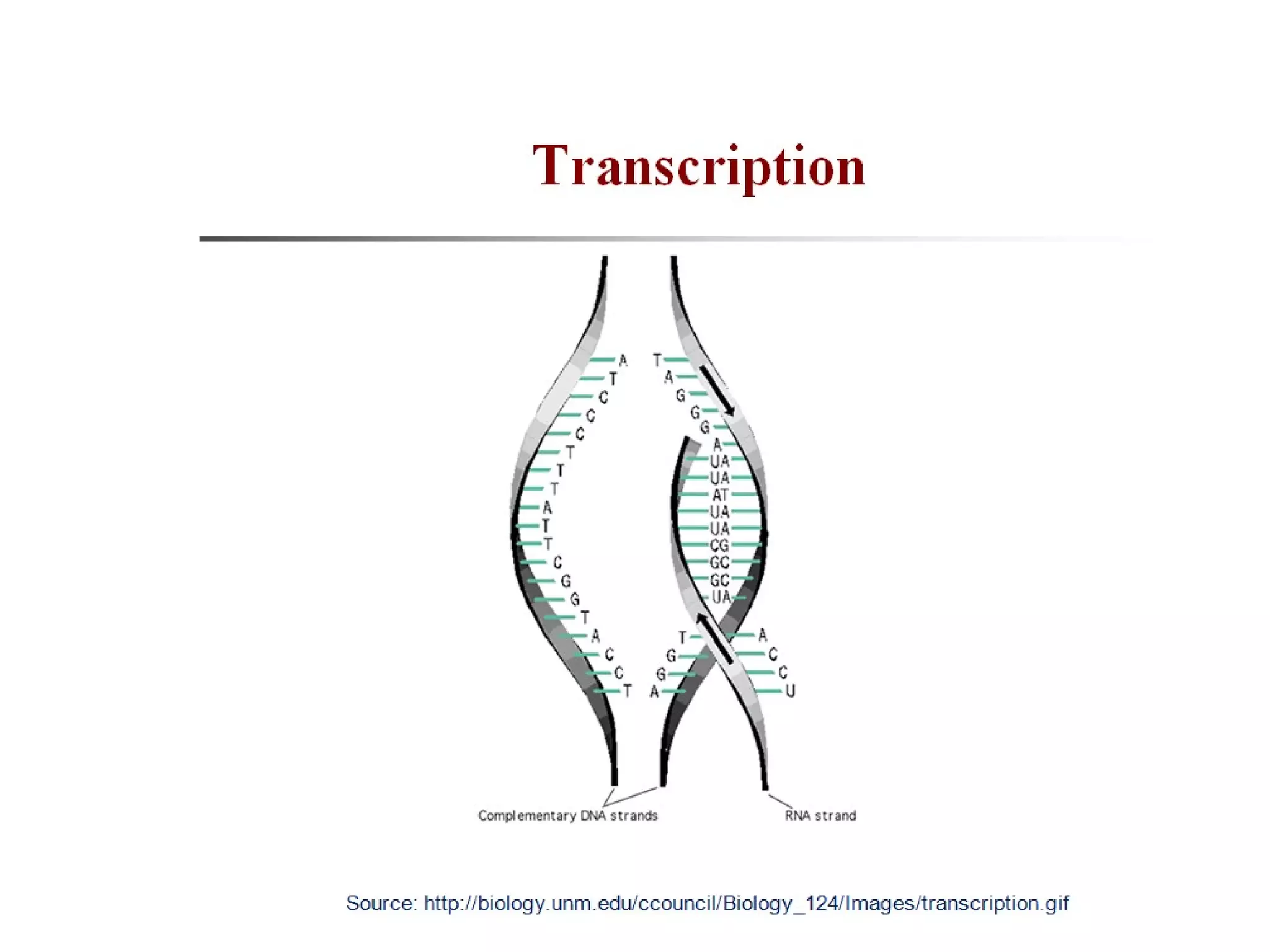
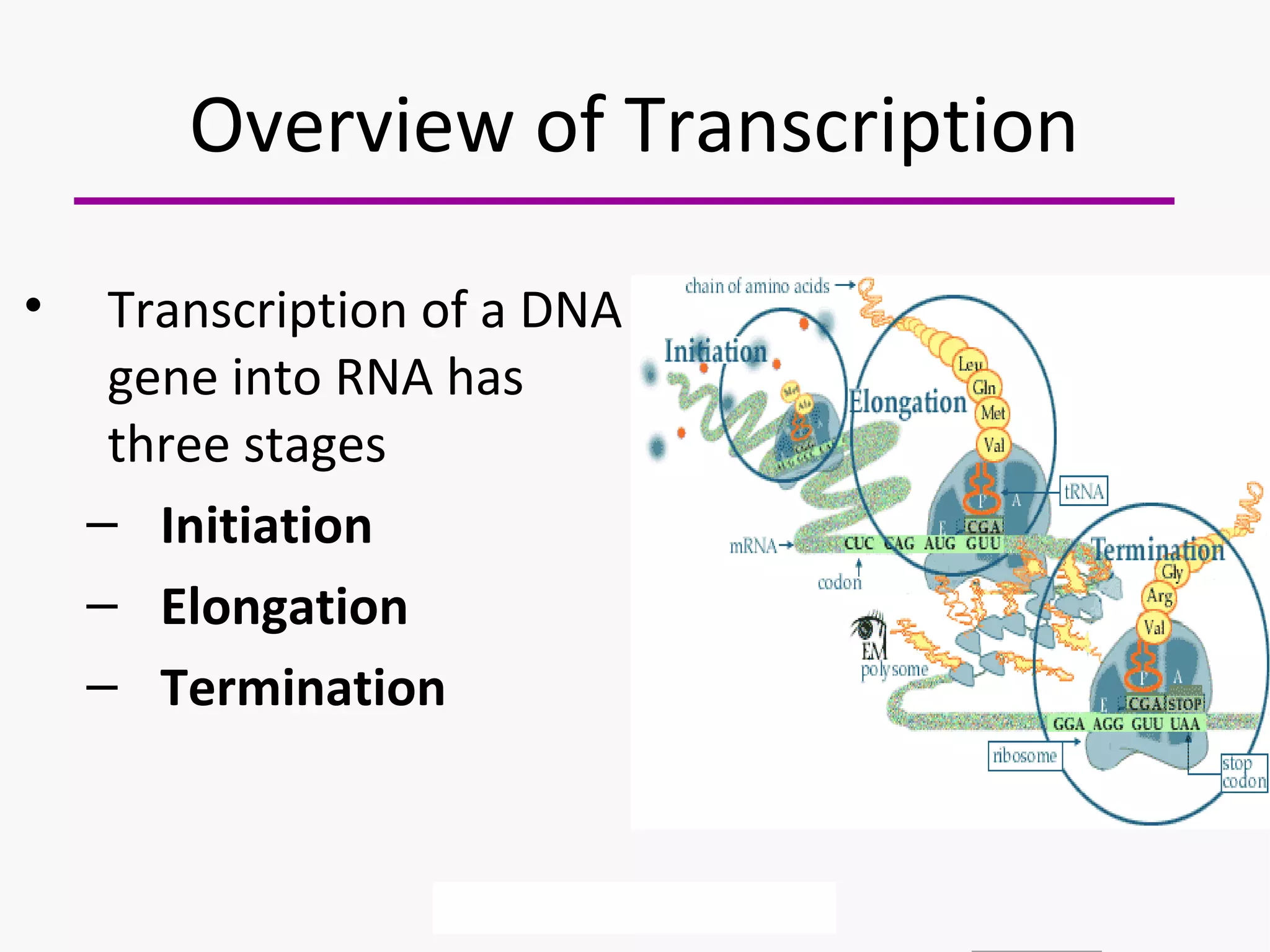
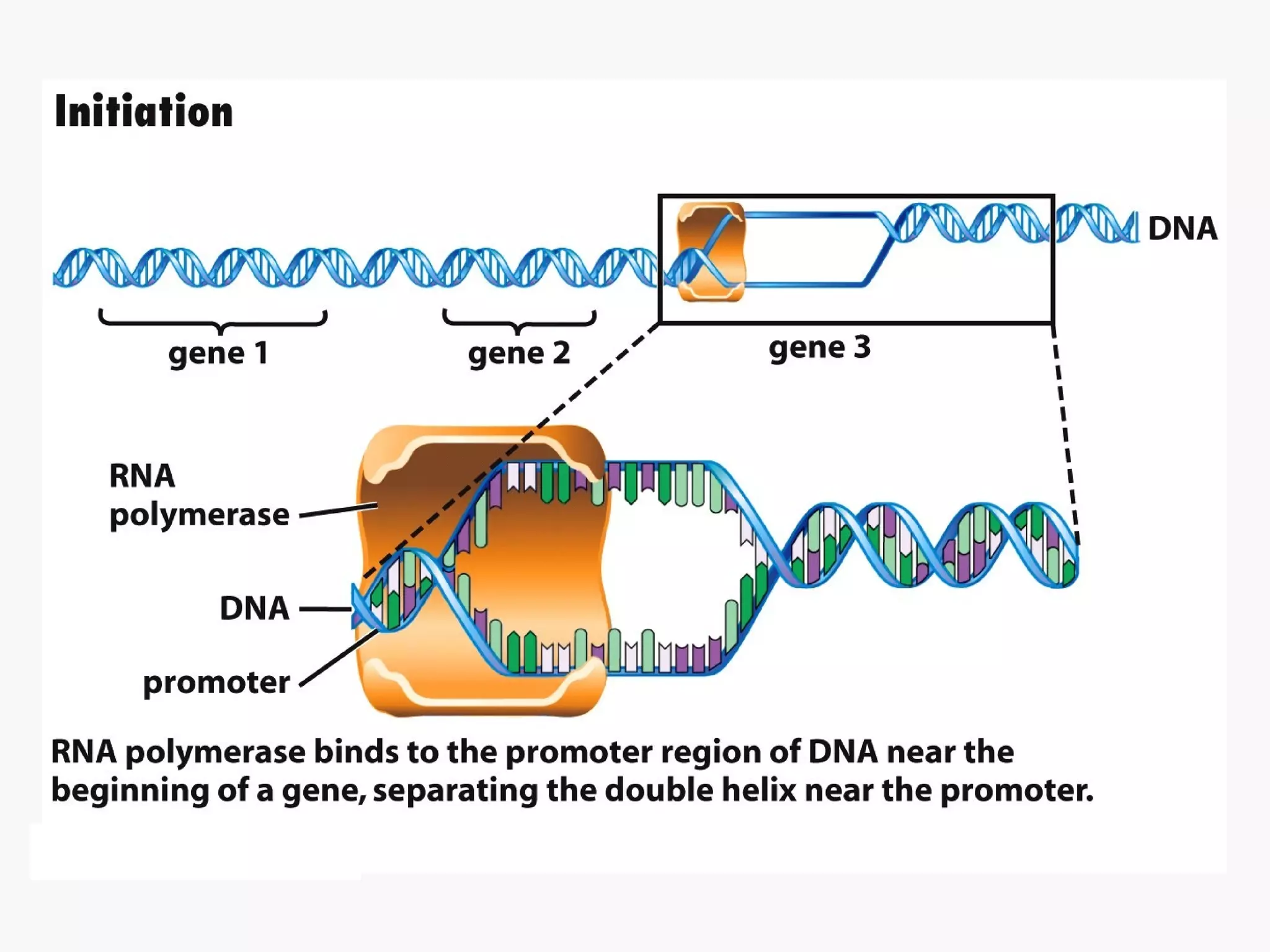
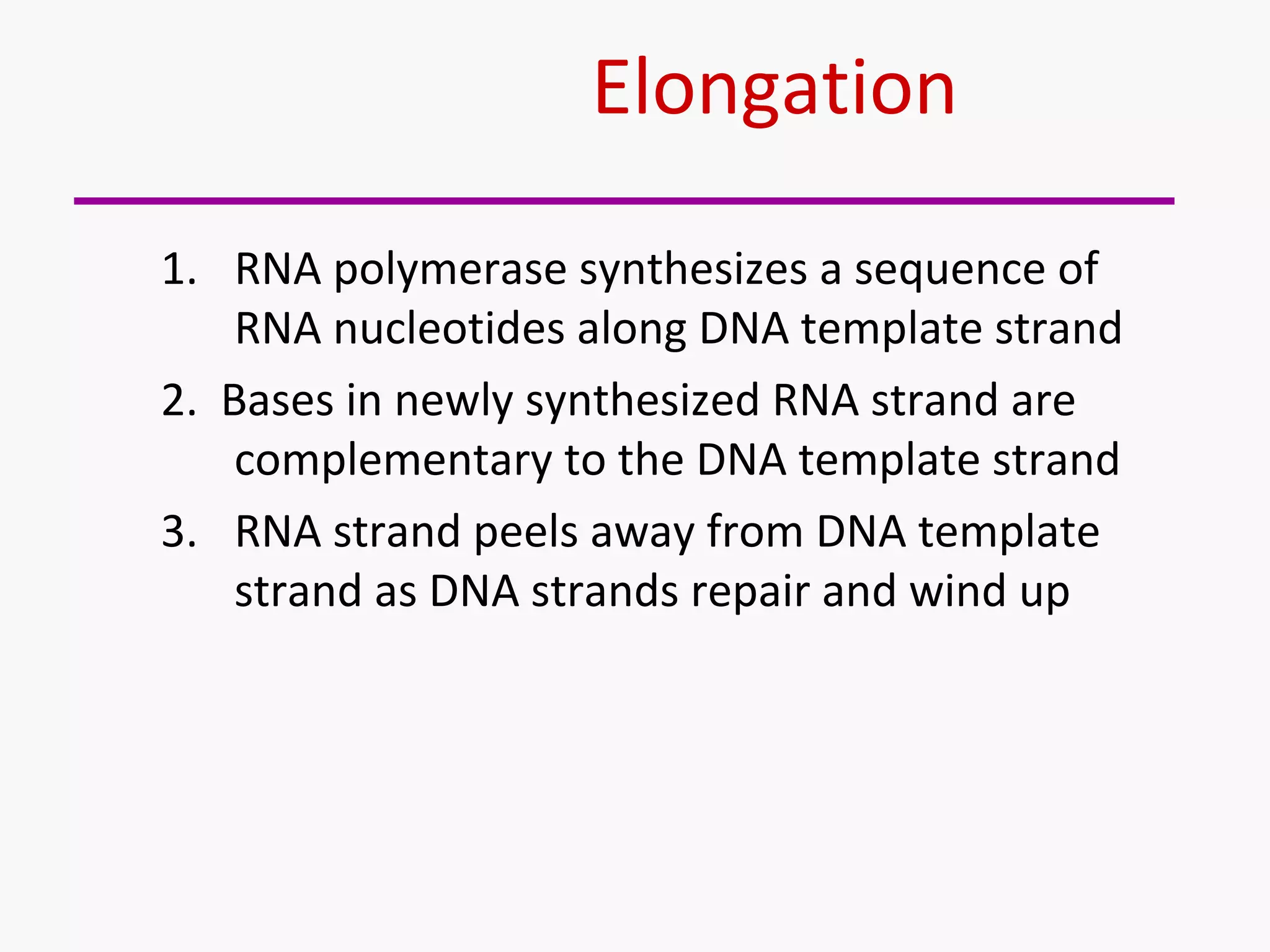
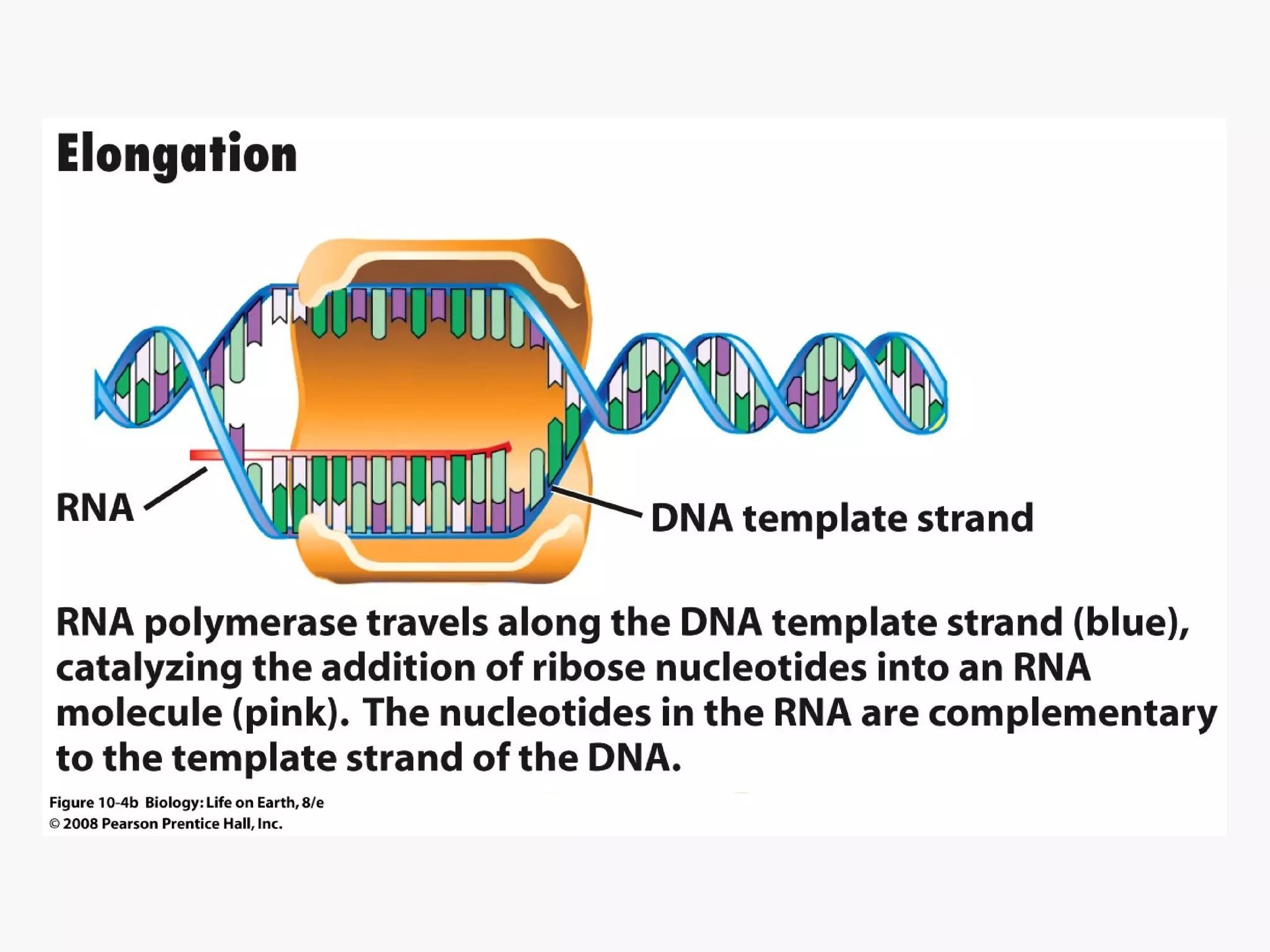
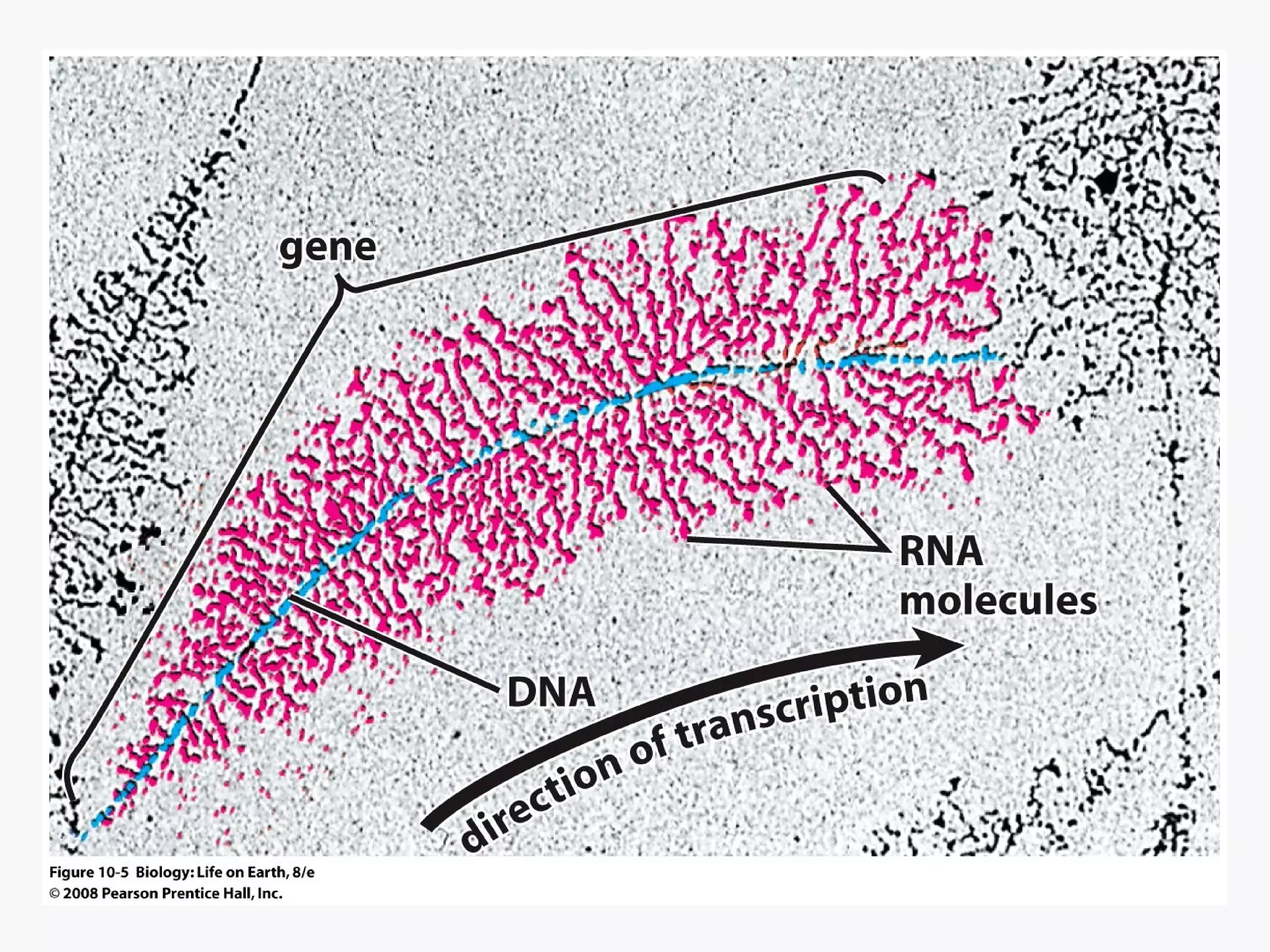
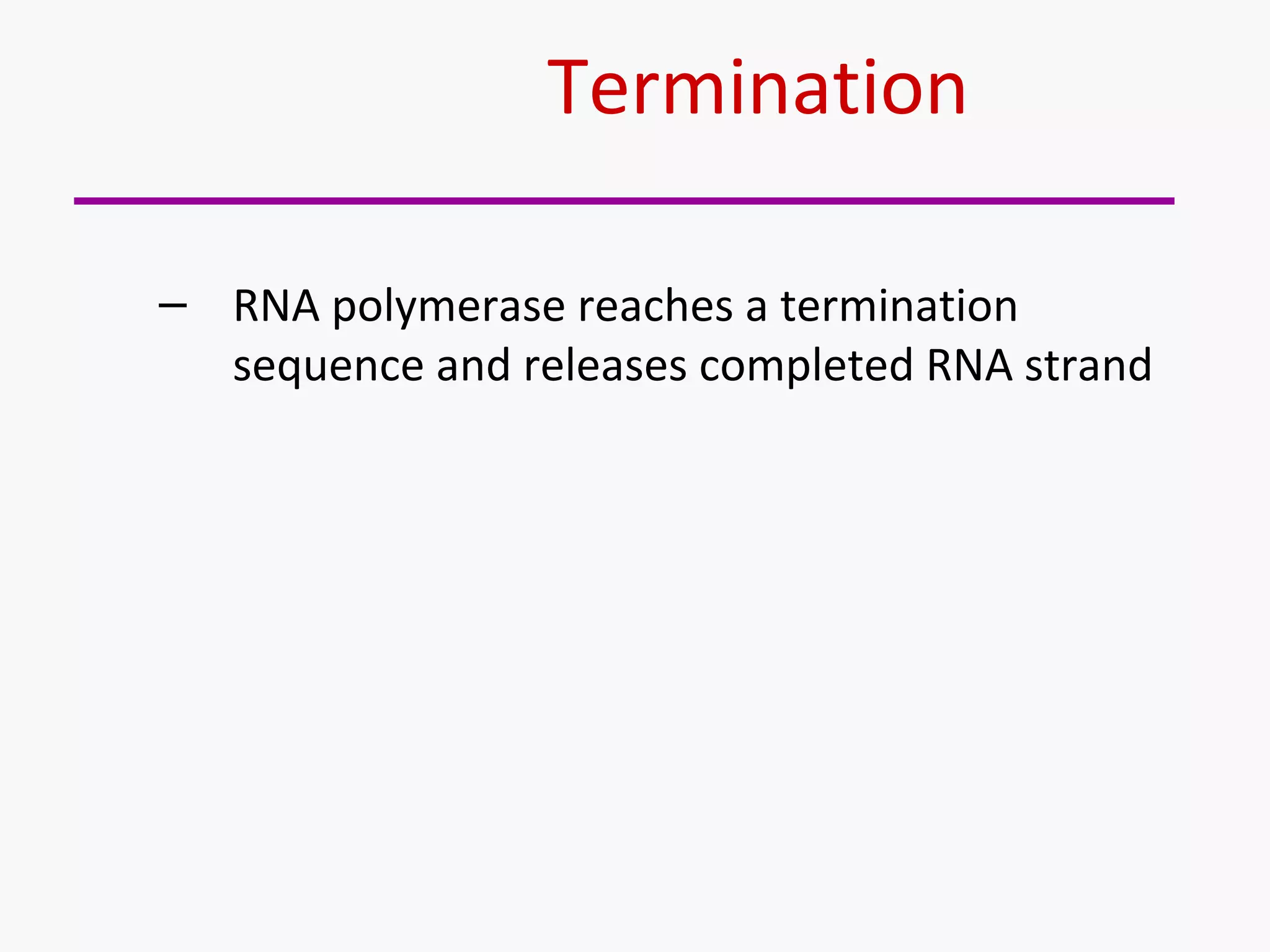
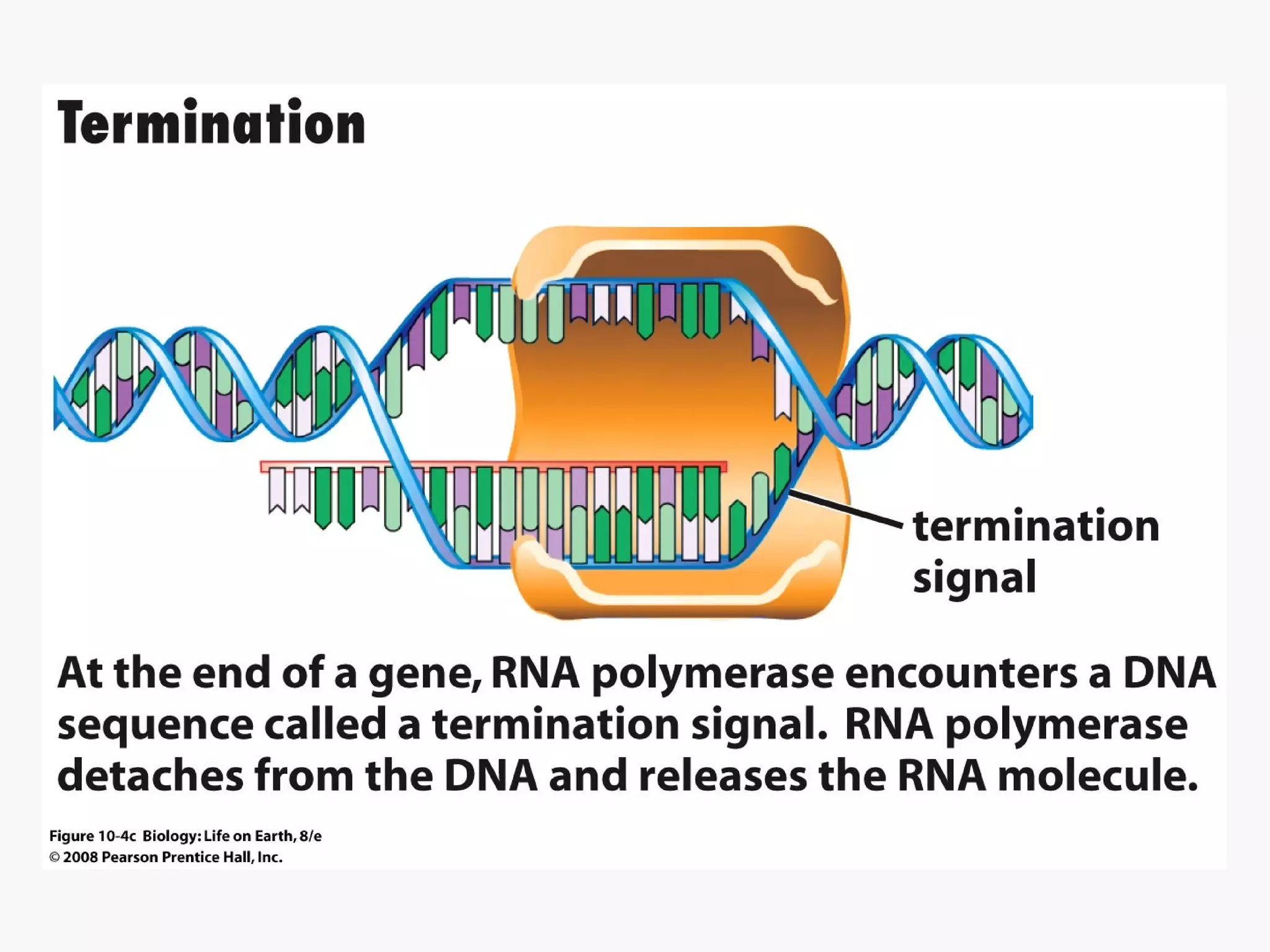
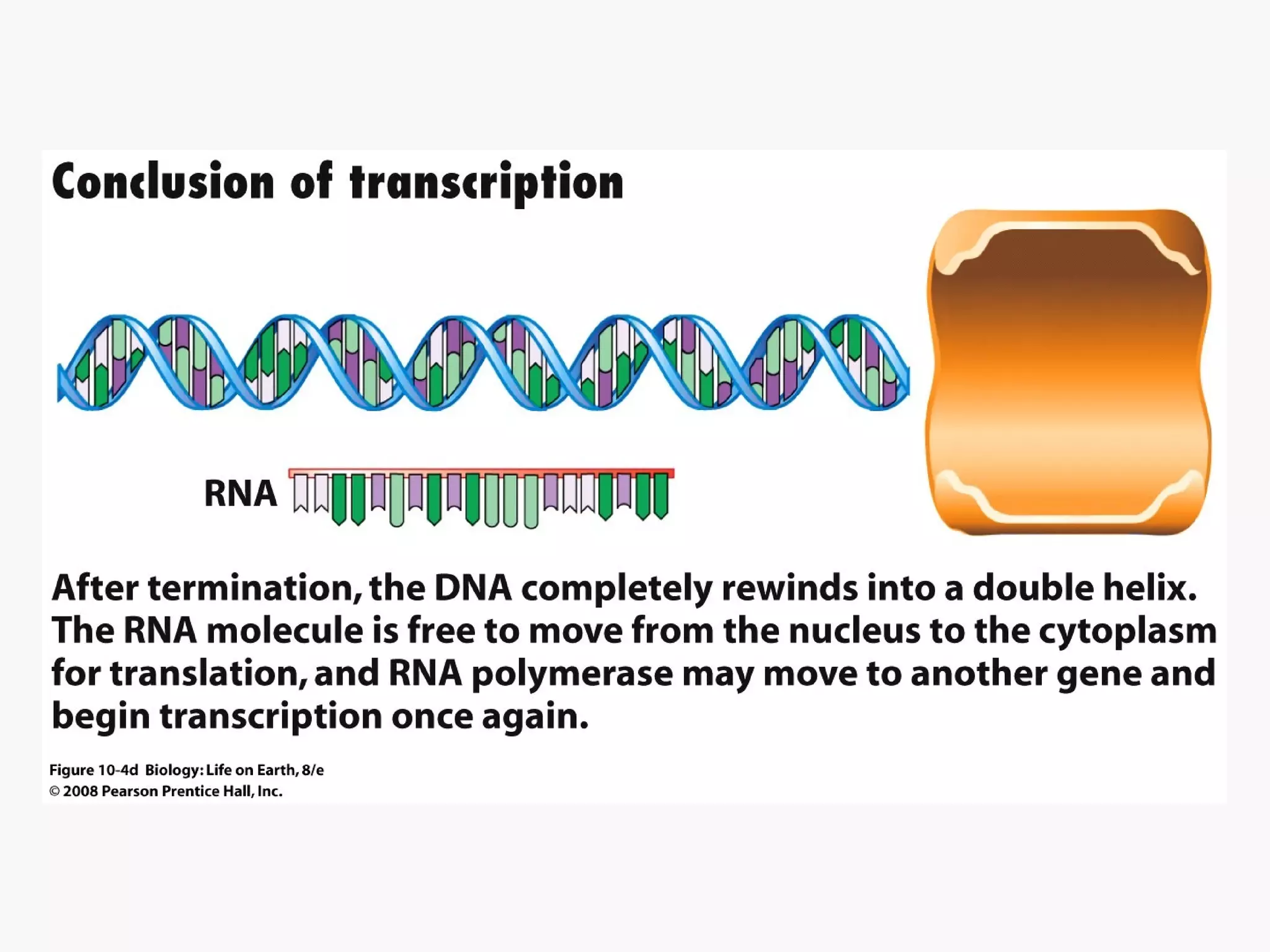
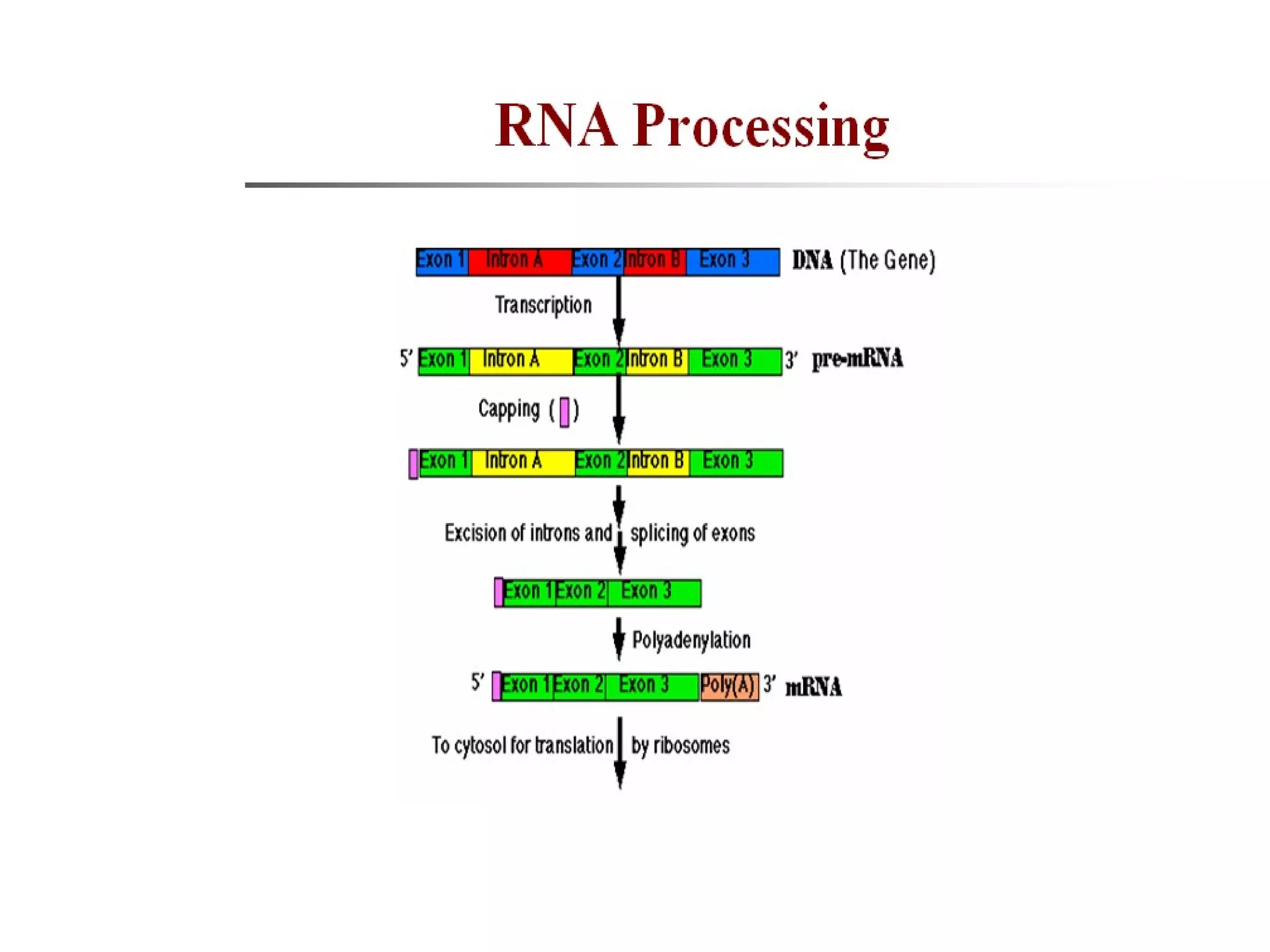
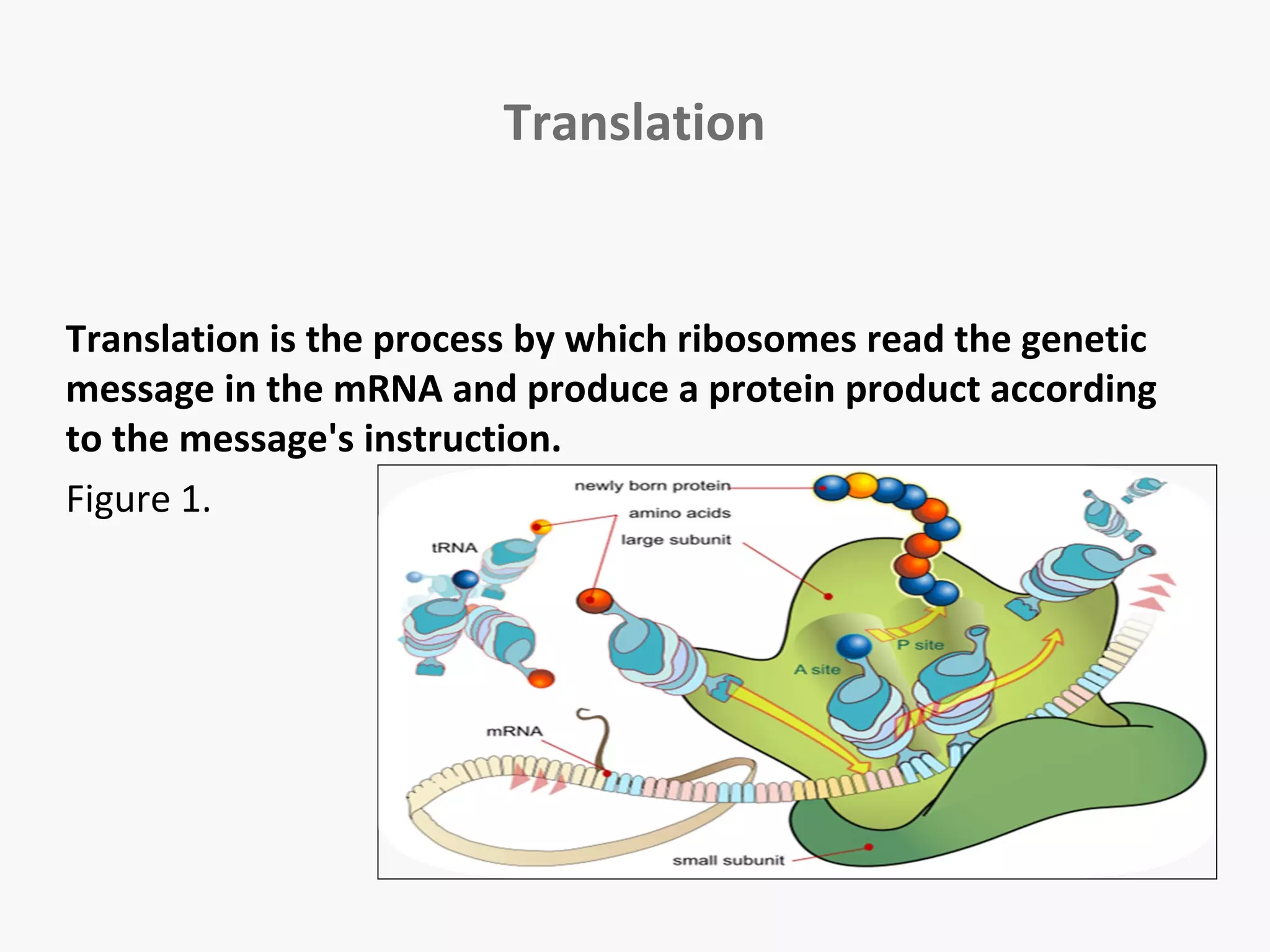
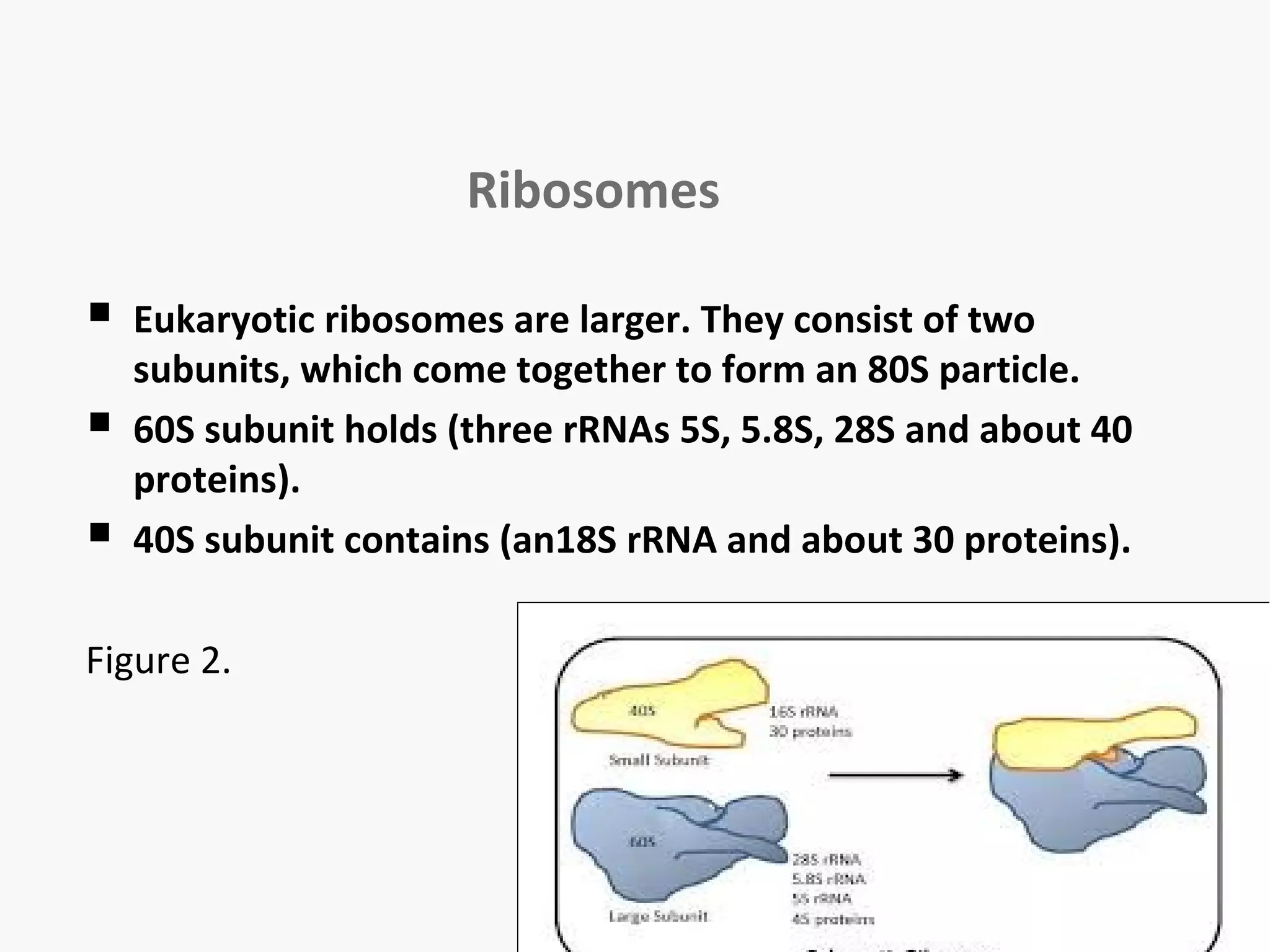
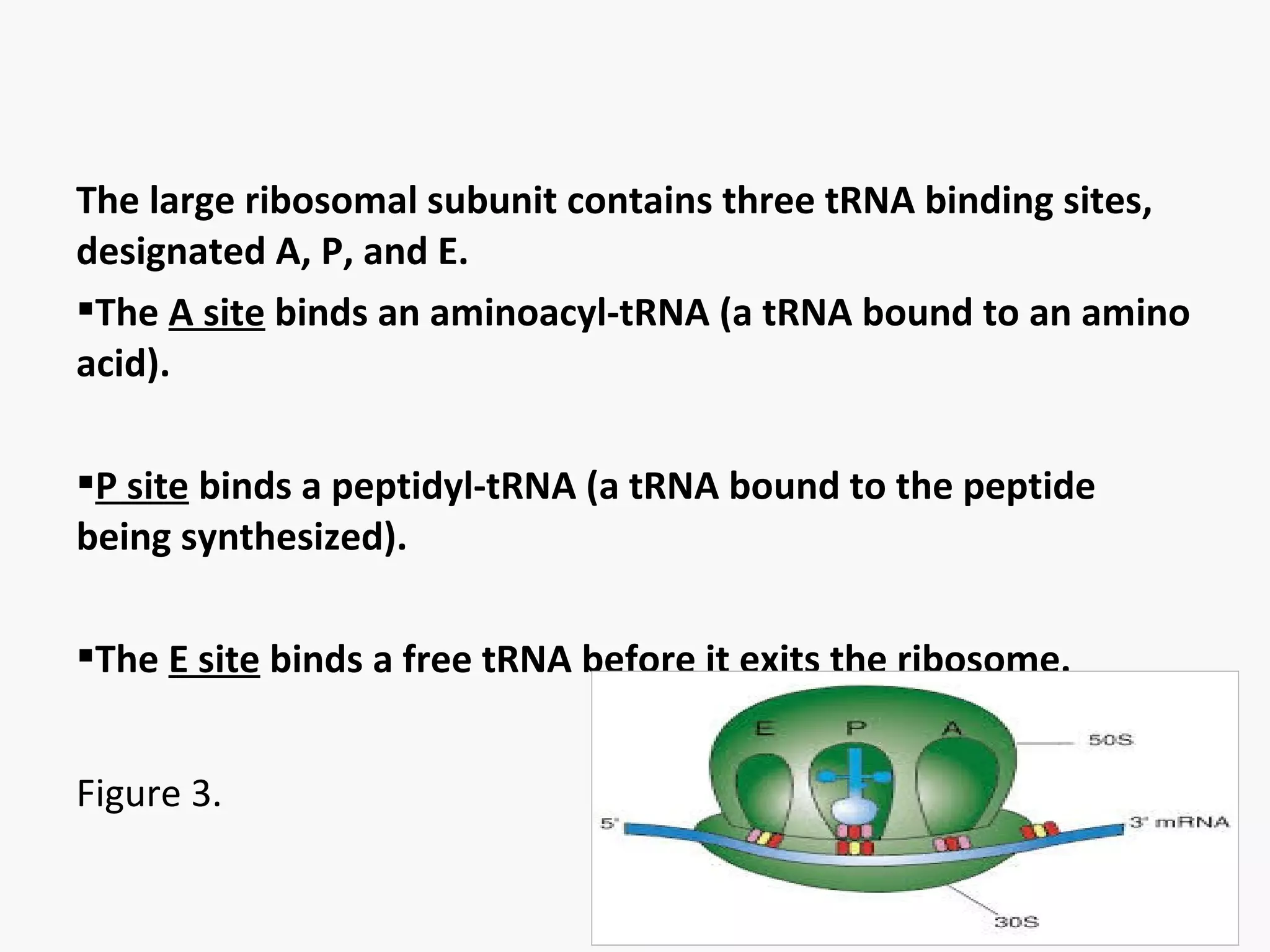
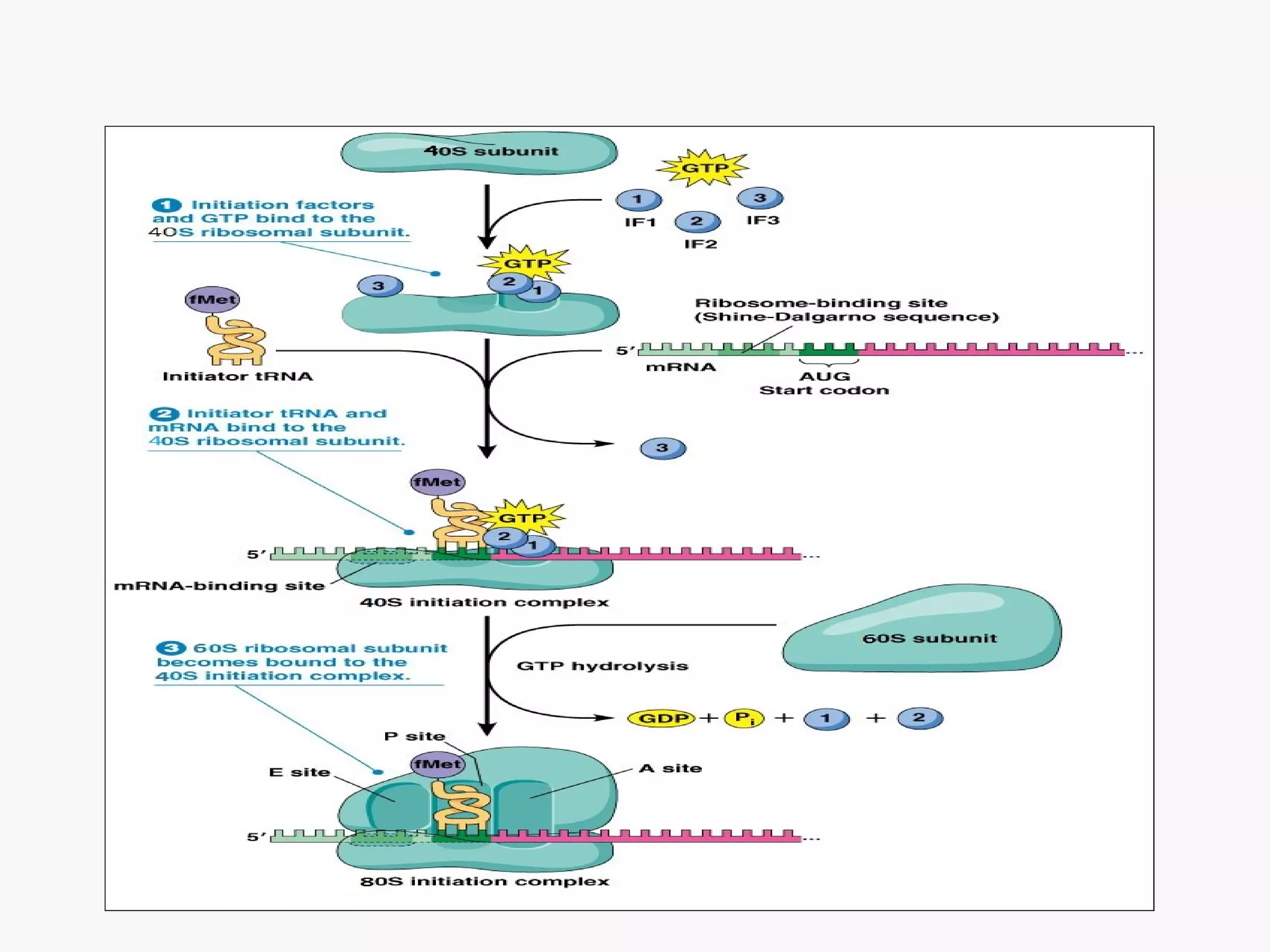
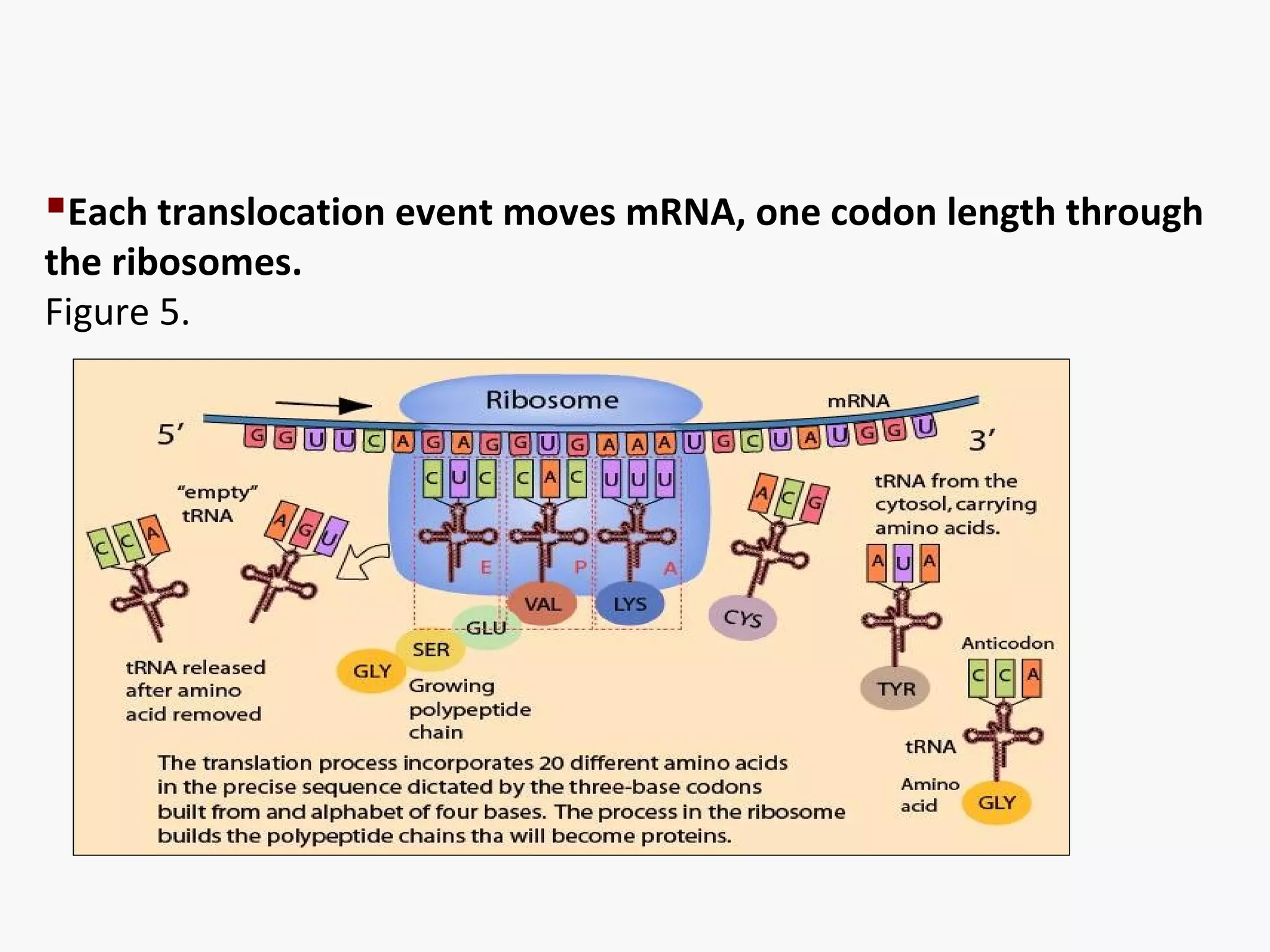
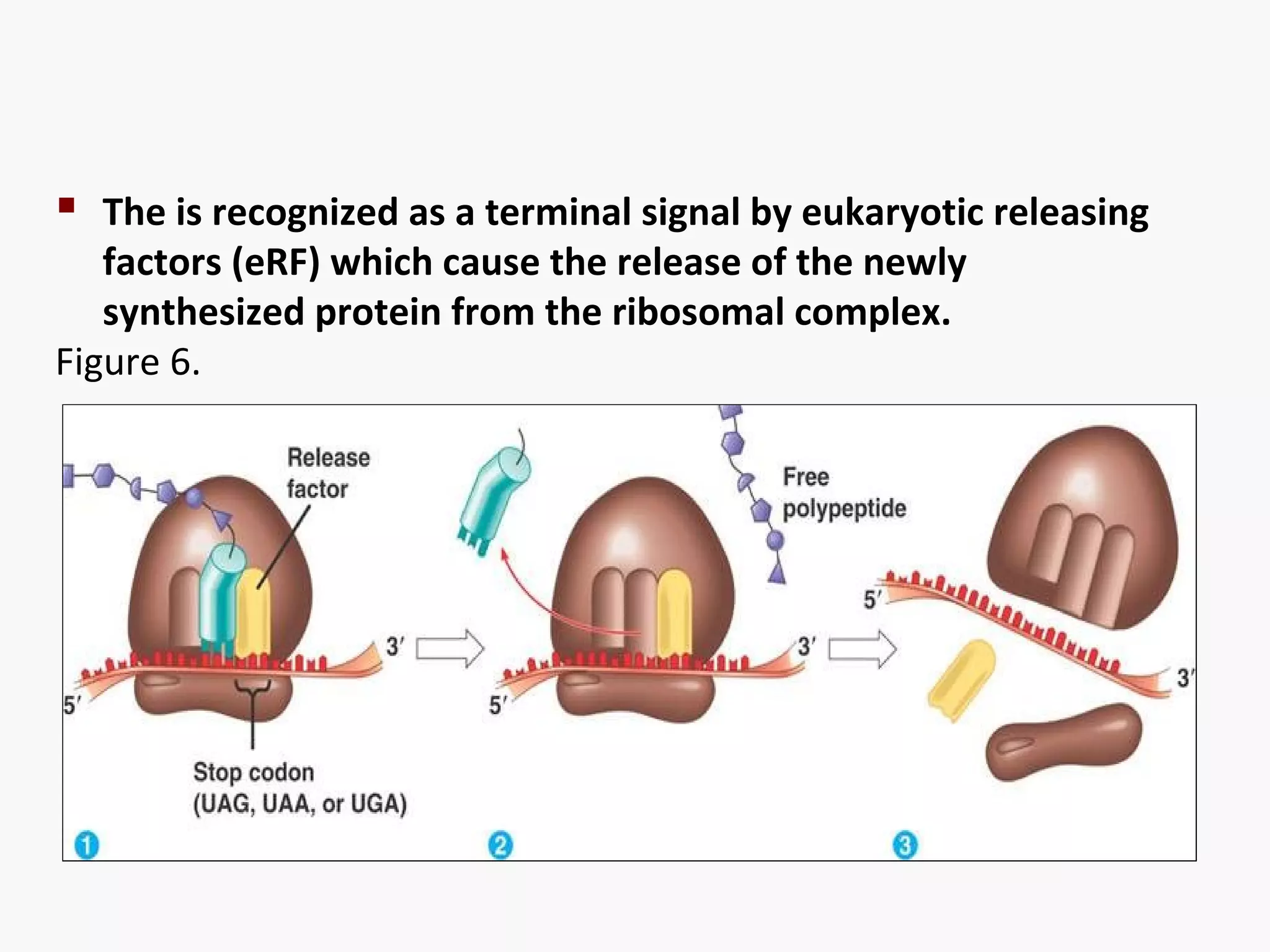
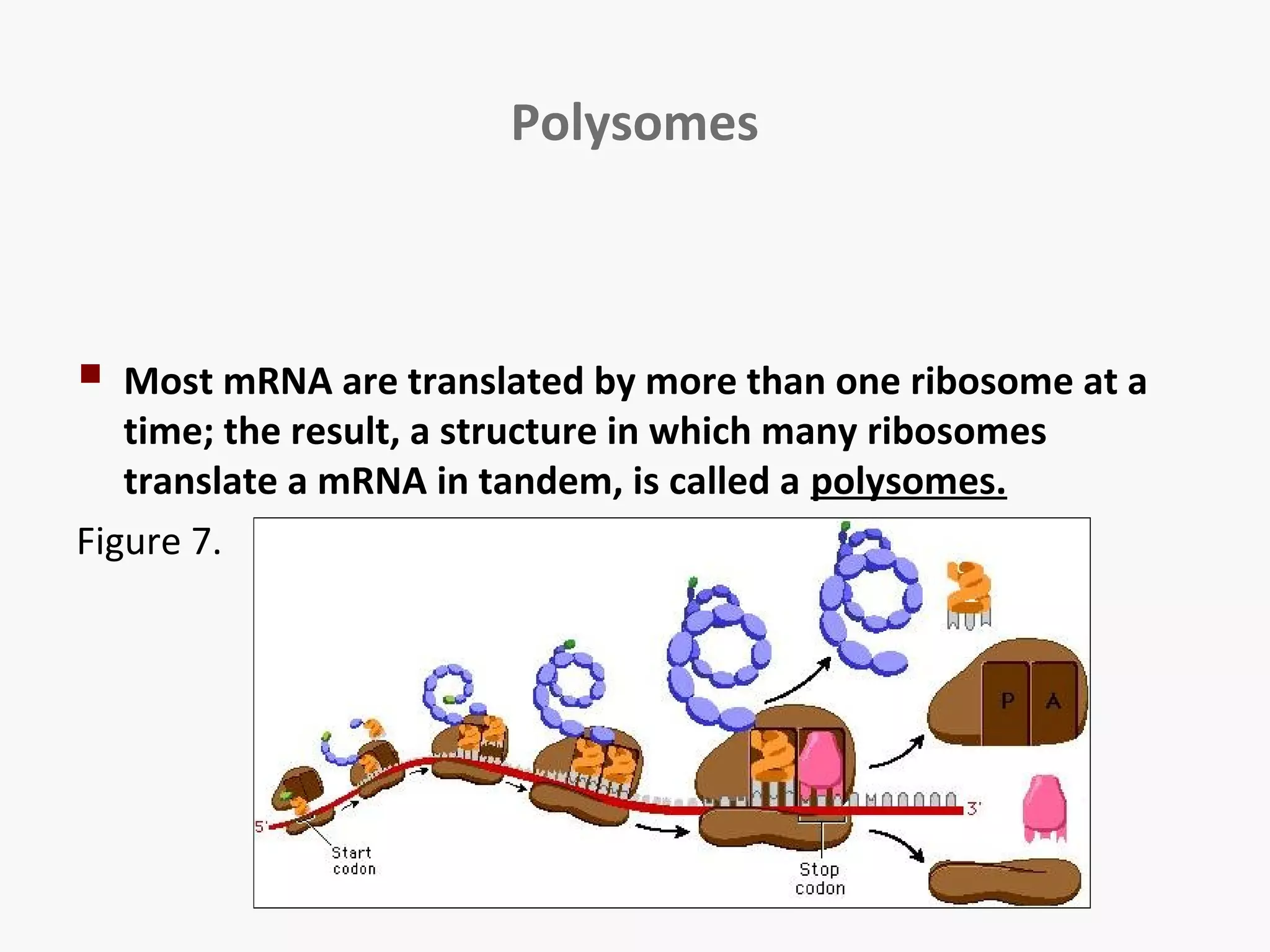
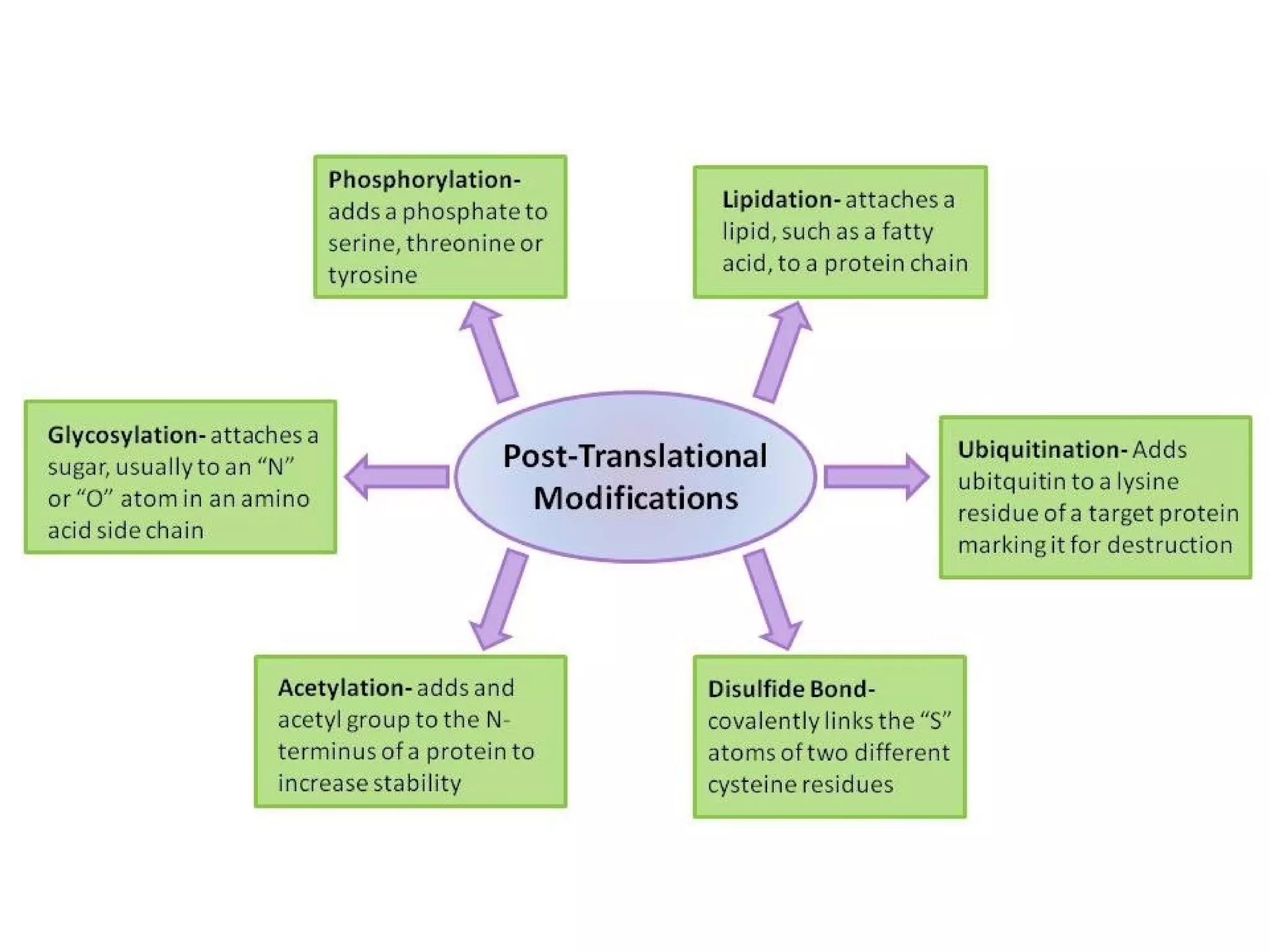
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used to produce a functional product like proteins or RNA. It involves two main steps: transcription of DNA into mRNA and translation of mRNA into proteins. Transcription involves unwinding the DNA and synthesizing mRNA complementary to the template strand. Translation uses ribosomes to read the mRNA codon by codon and add the corresponding amino acids to produce a protein according to the genetic code. It occurs through three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination.