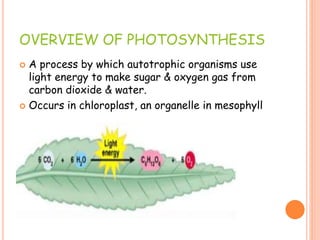
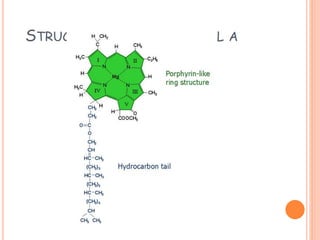
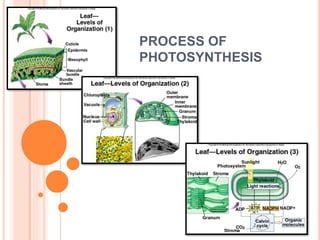
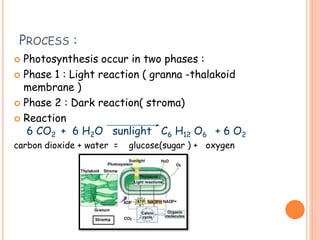
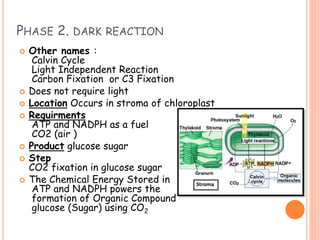
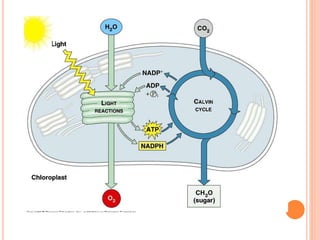
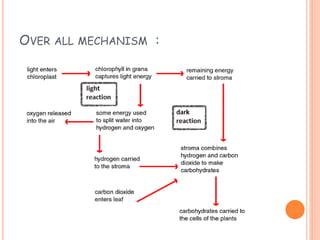
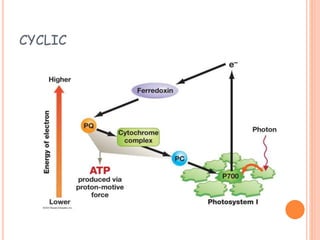
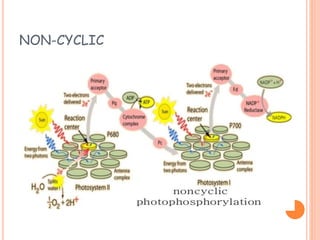
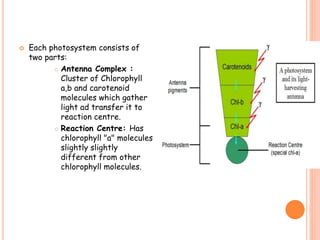
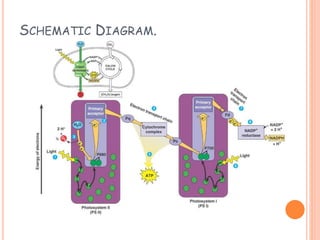
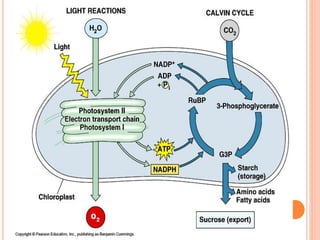
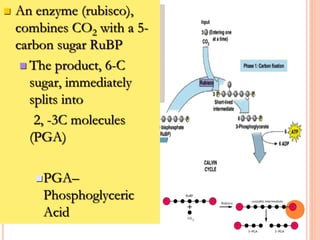
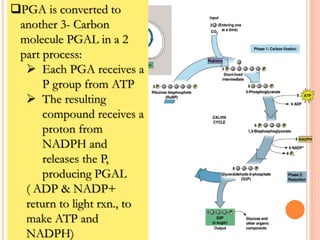
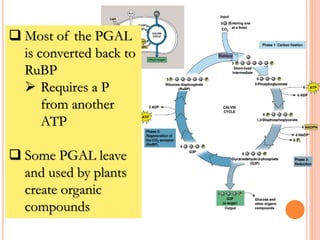
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. It occurs in two phases: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. The light reactions capture energy from sunlight and use it to make ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle uses these products to incorporate carbon from carbon dioxide into organic compounds to fuel the plant. Some plants use alternative pathways like C4 or CAM photosynthesis that help reduce photorespiration and increase water use efficiency.