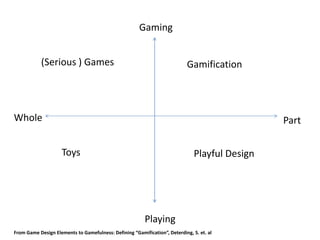
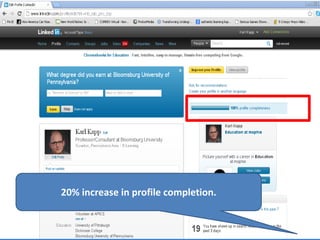
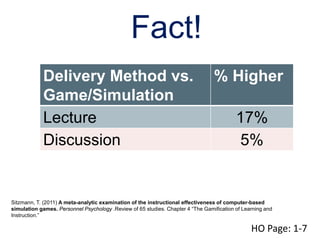
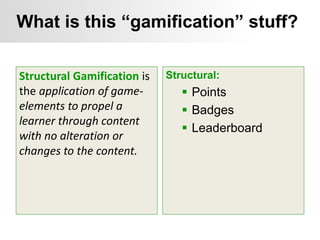
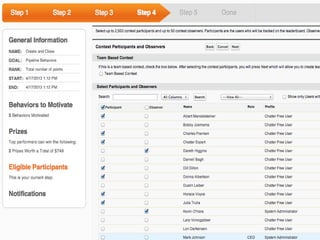
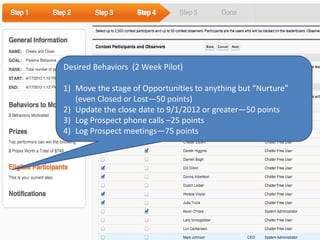
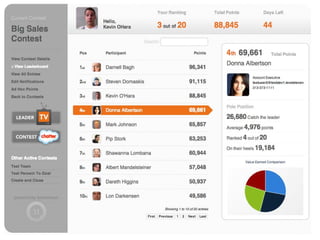
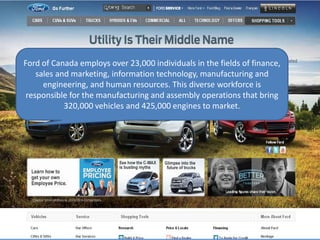
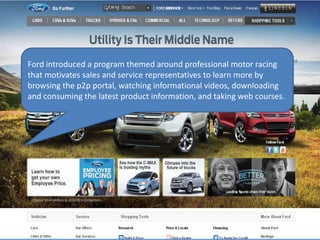
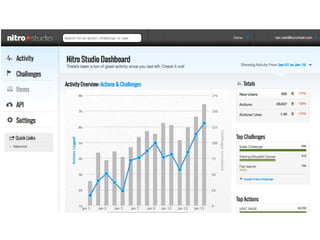
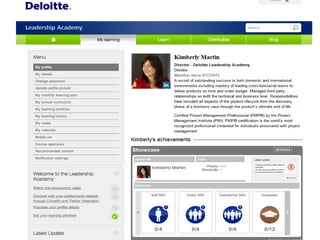
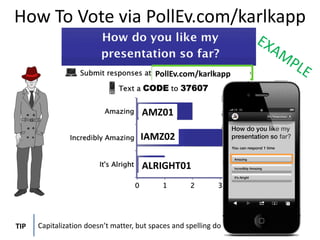
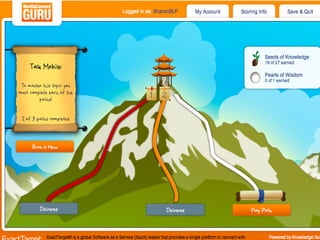
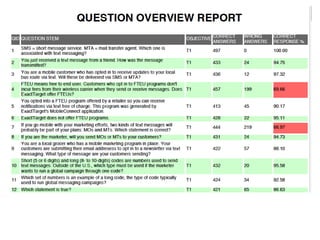
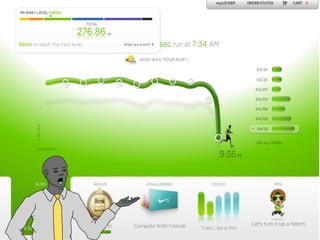
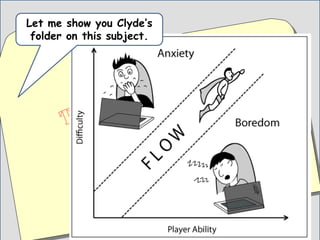
This document summarizes two case studies that used gamification to increase desired behaviors and learning outcomes. In the first case study, an insurance company used a gamified system to increase sales activity logging by over 250% and improve data in their salesforce system. The second case study discusses how a car company gamified an existing sales training program, which led to a 417% increase in site usage and exceeding the previous year's traffic volume within three months. Both cases illustrate how gamification can effectively promote learning and behavior change in organizational settings.