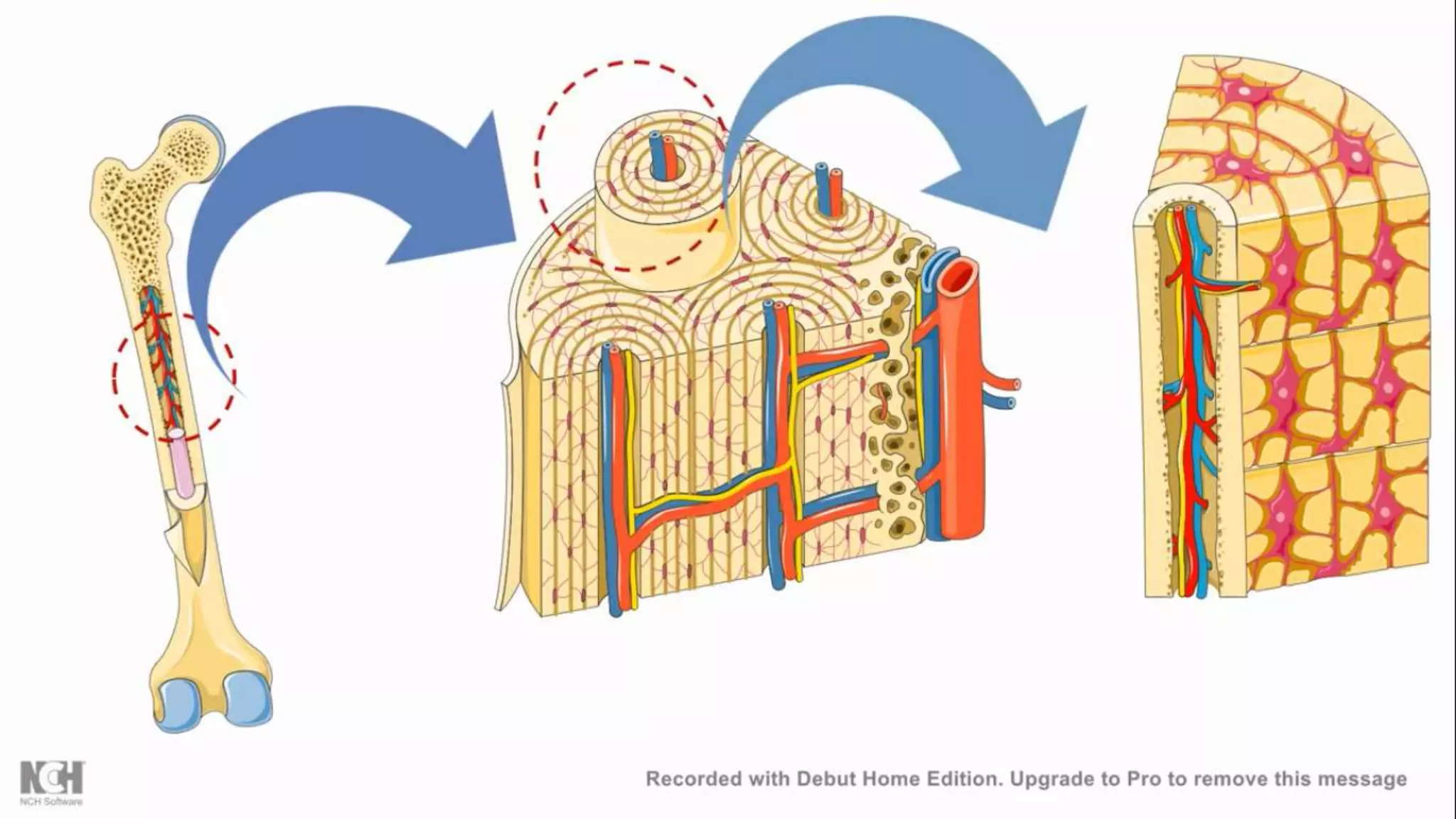
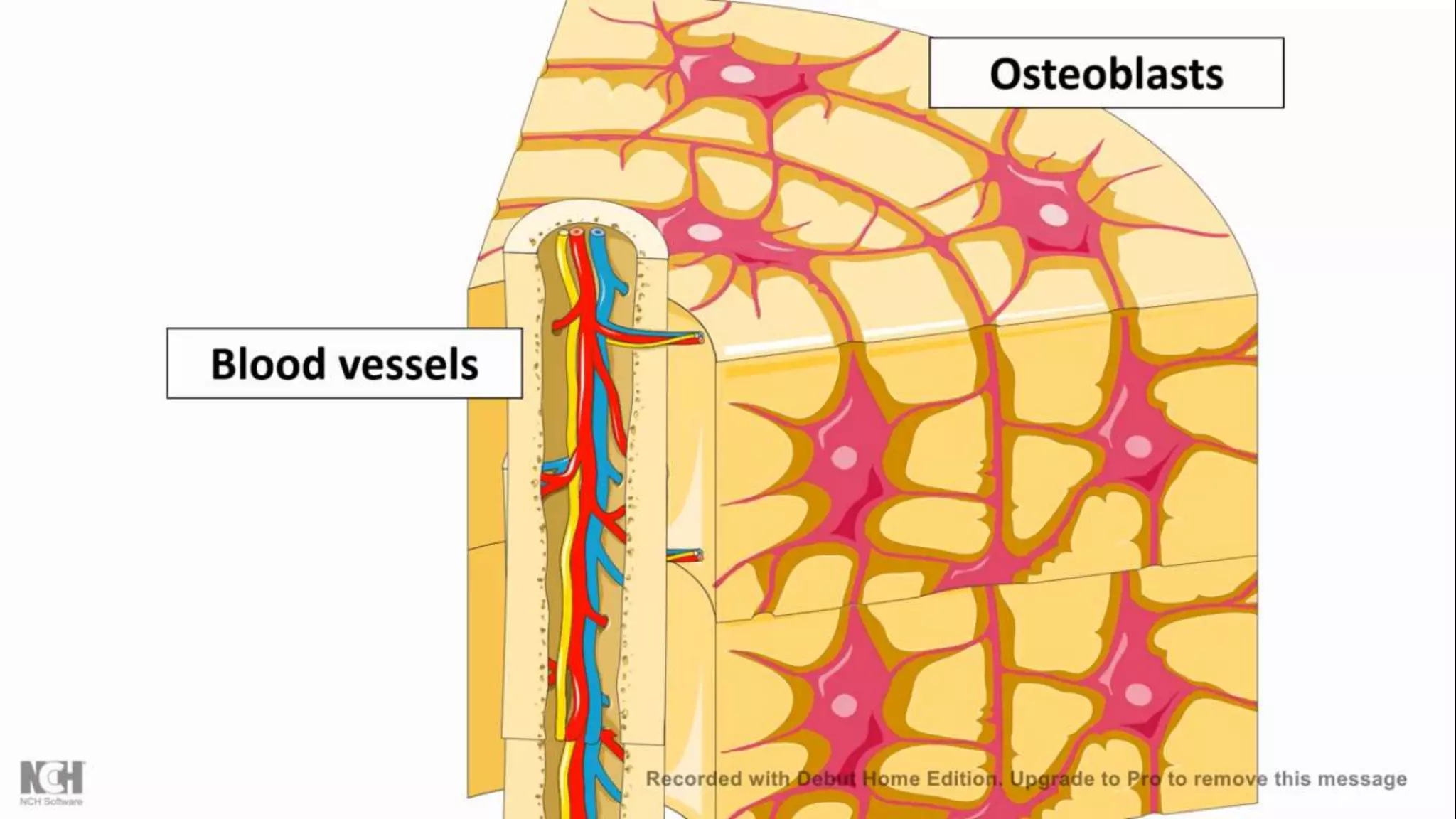
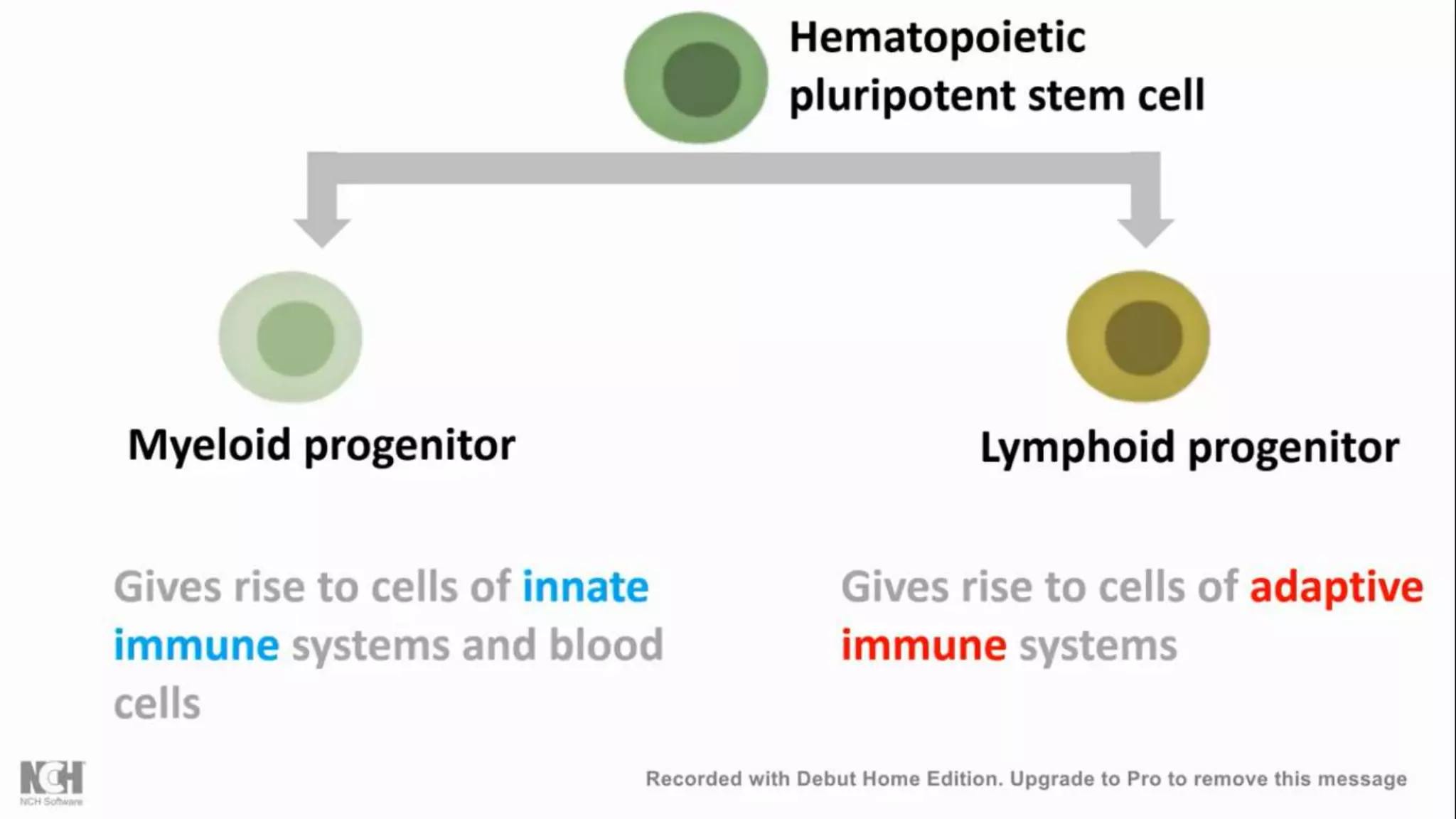
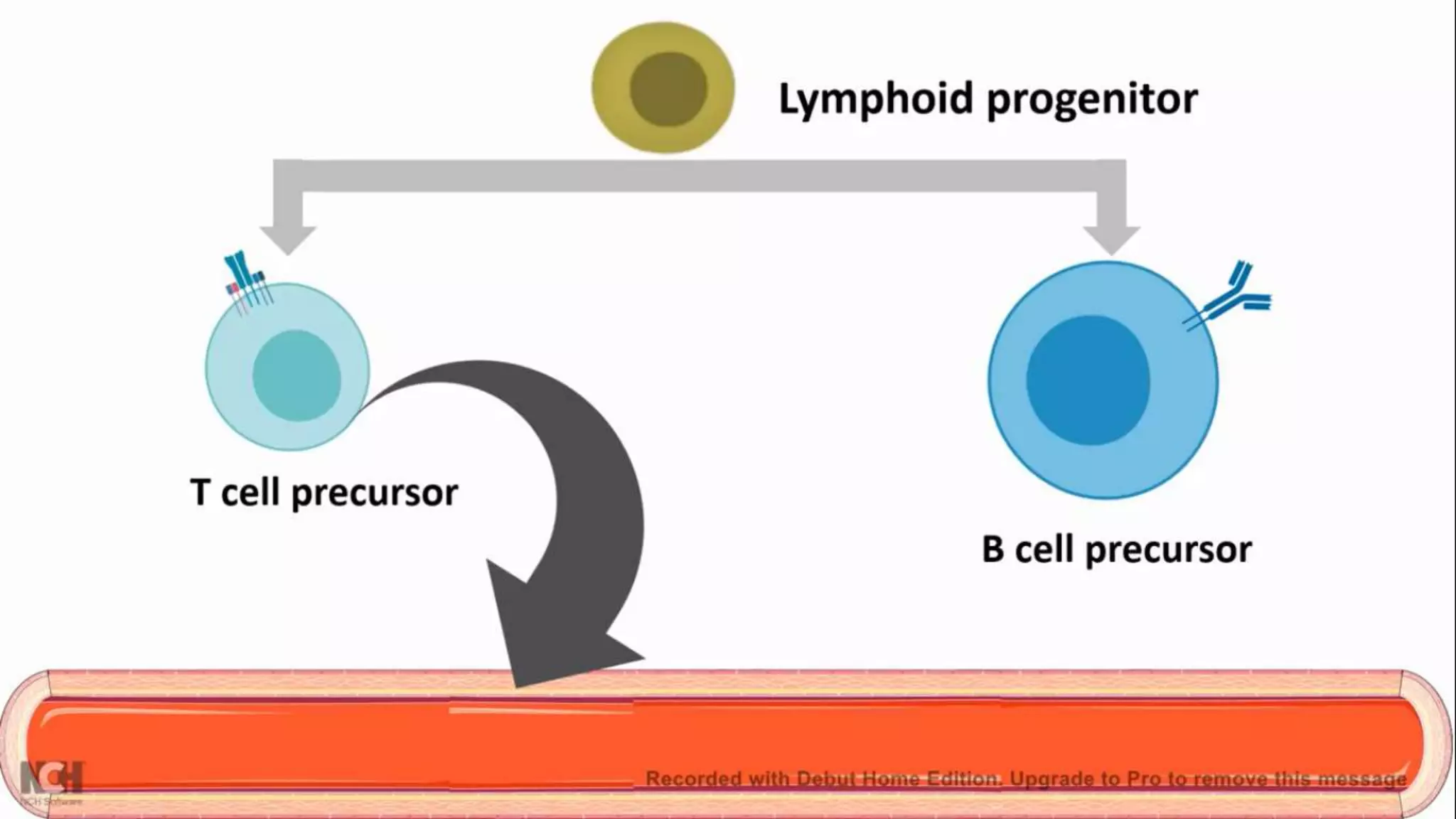
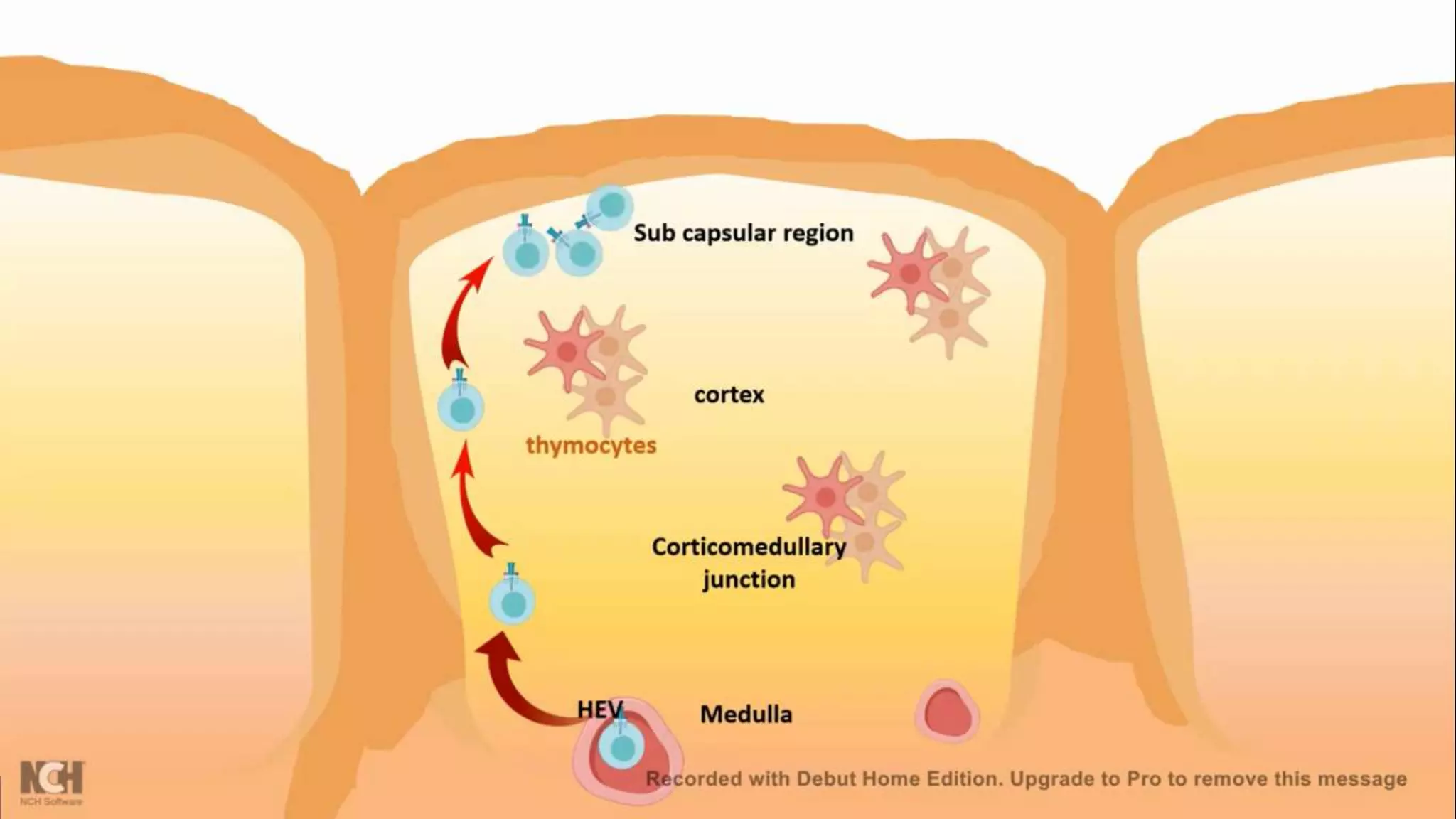
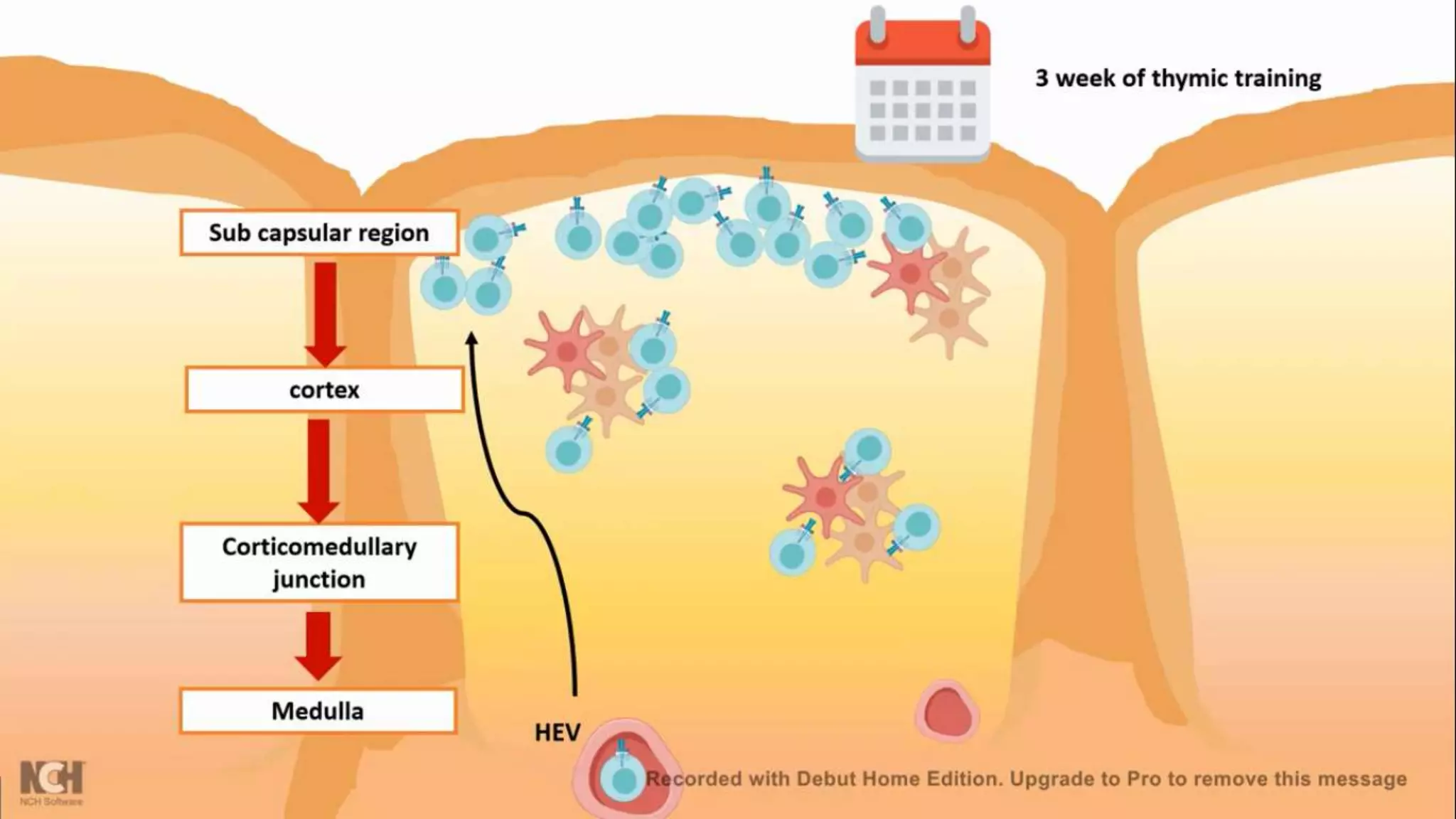
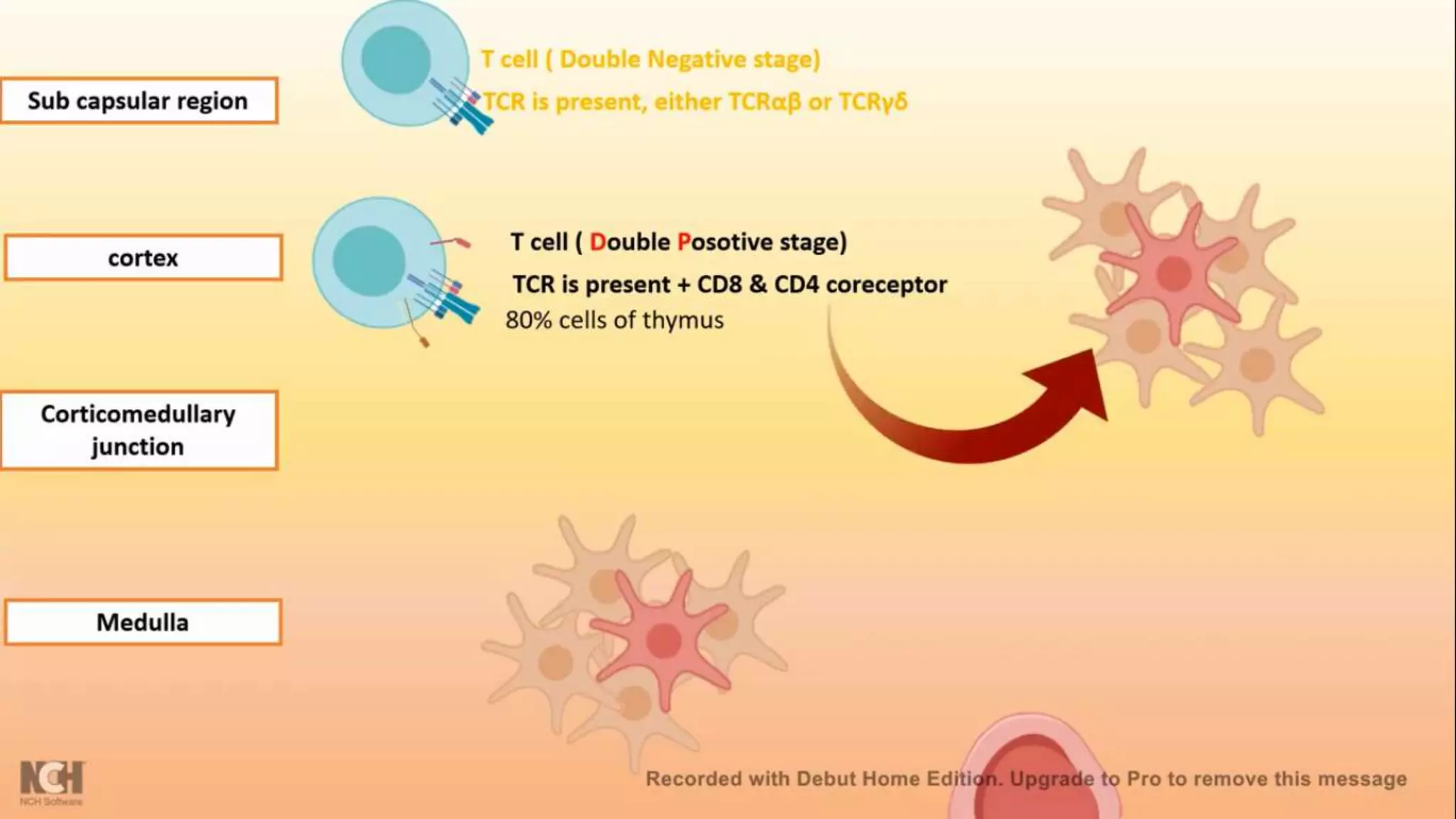
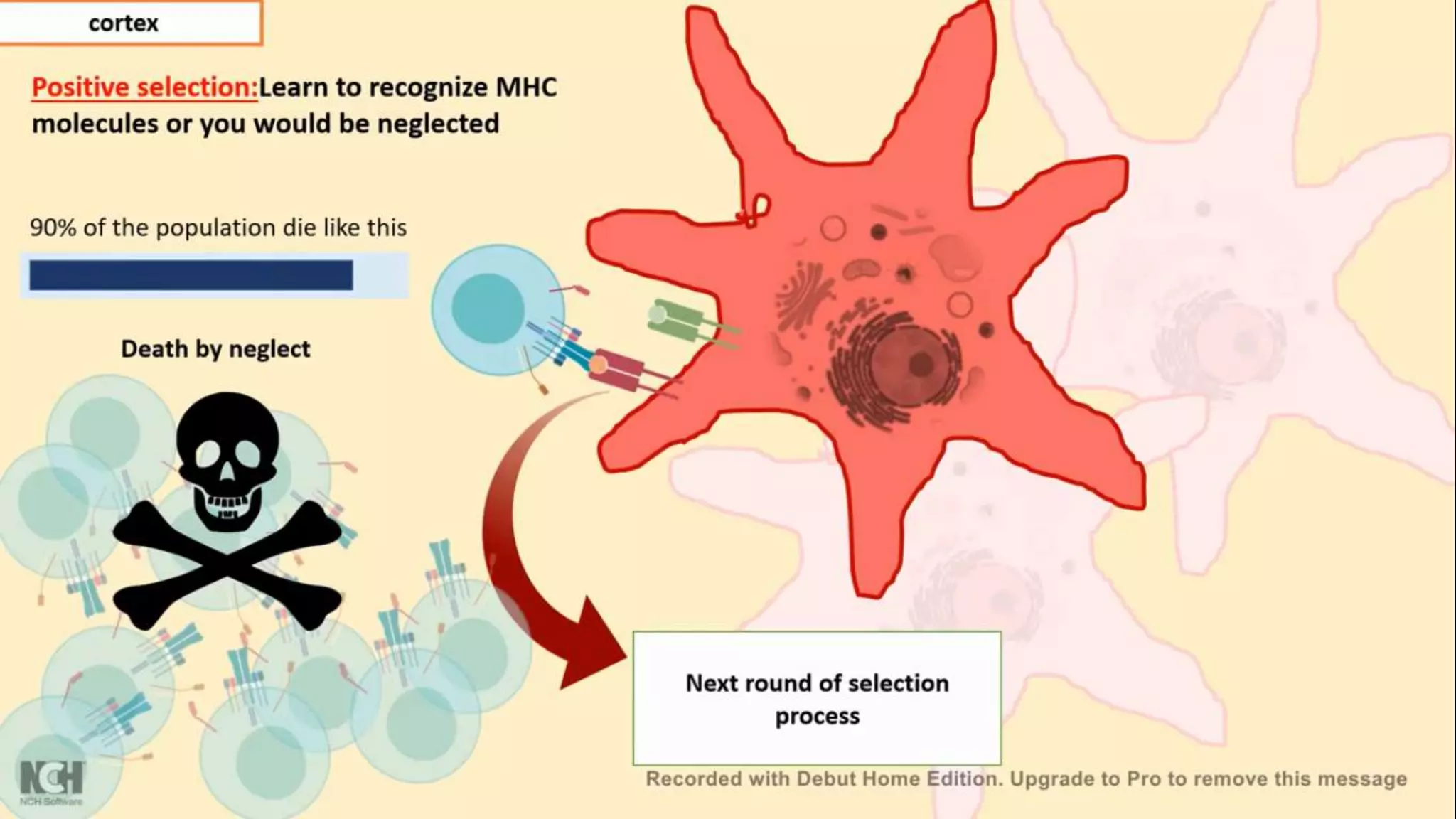
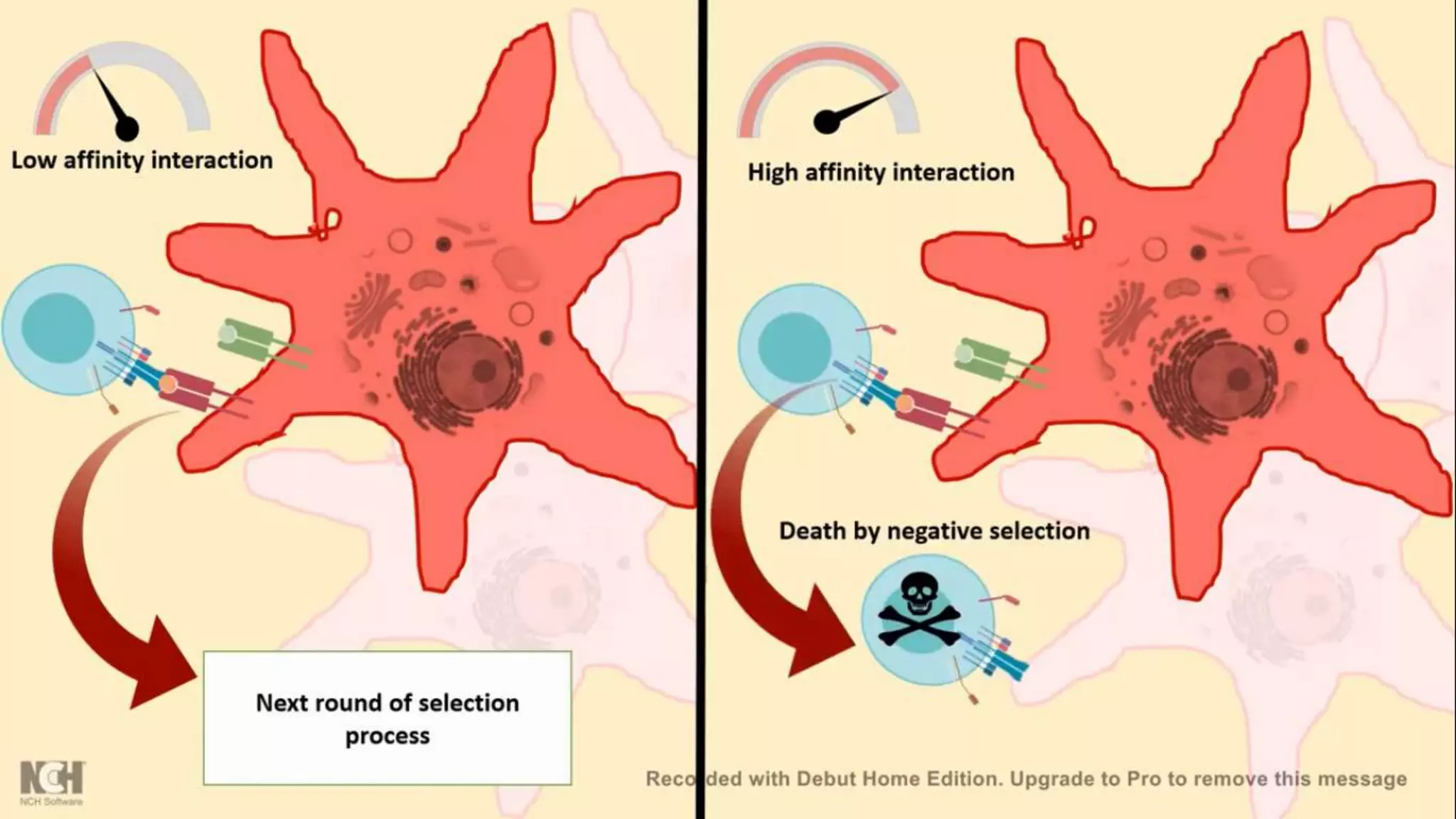
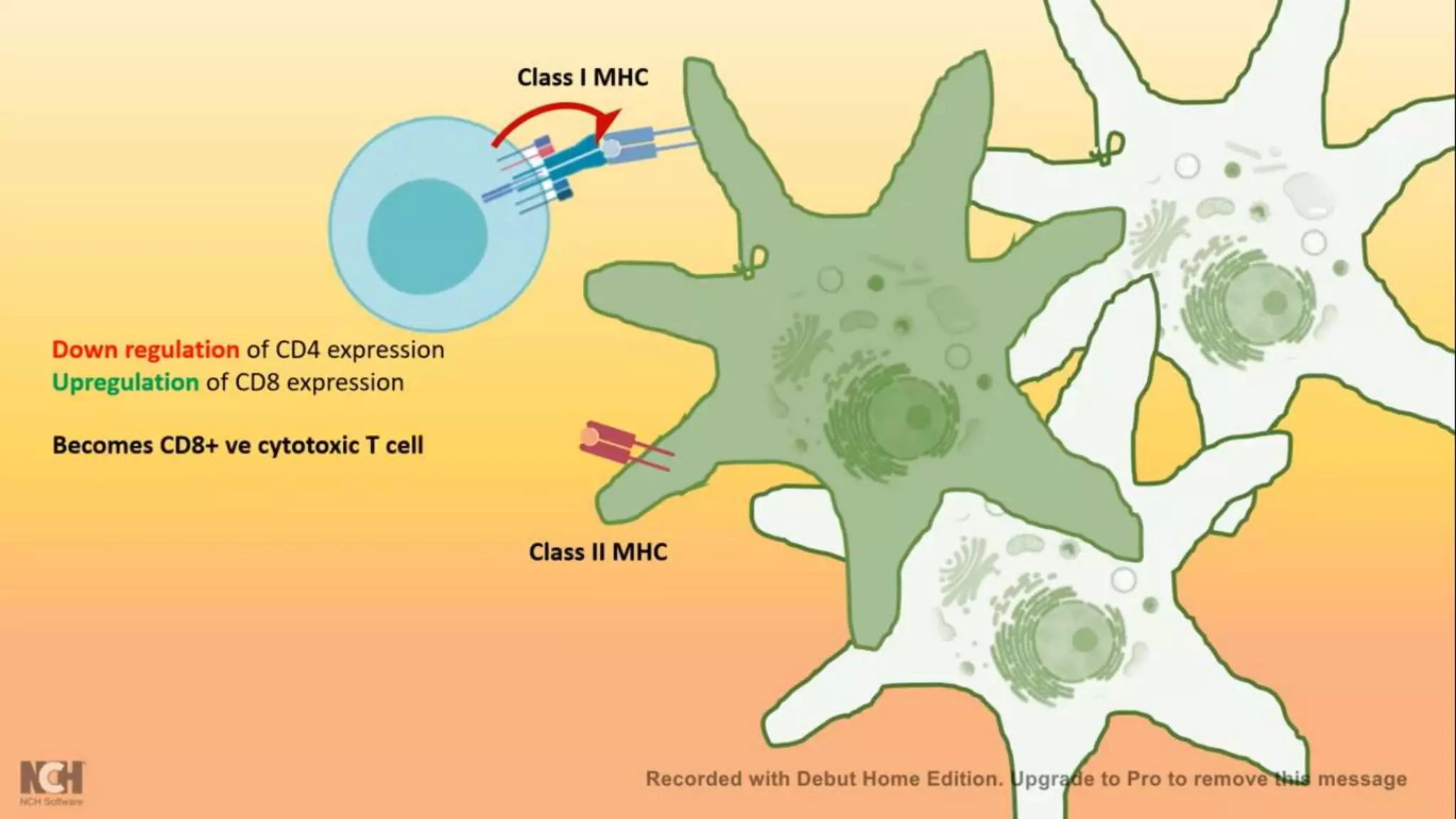
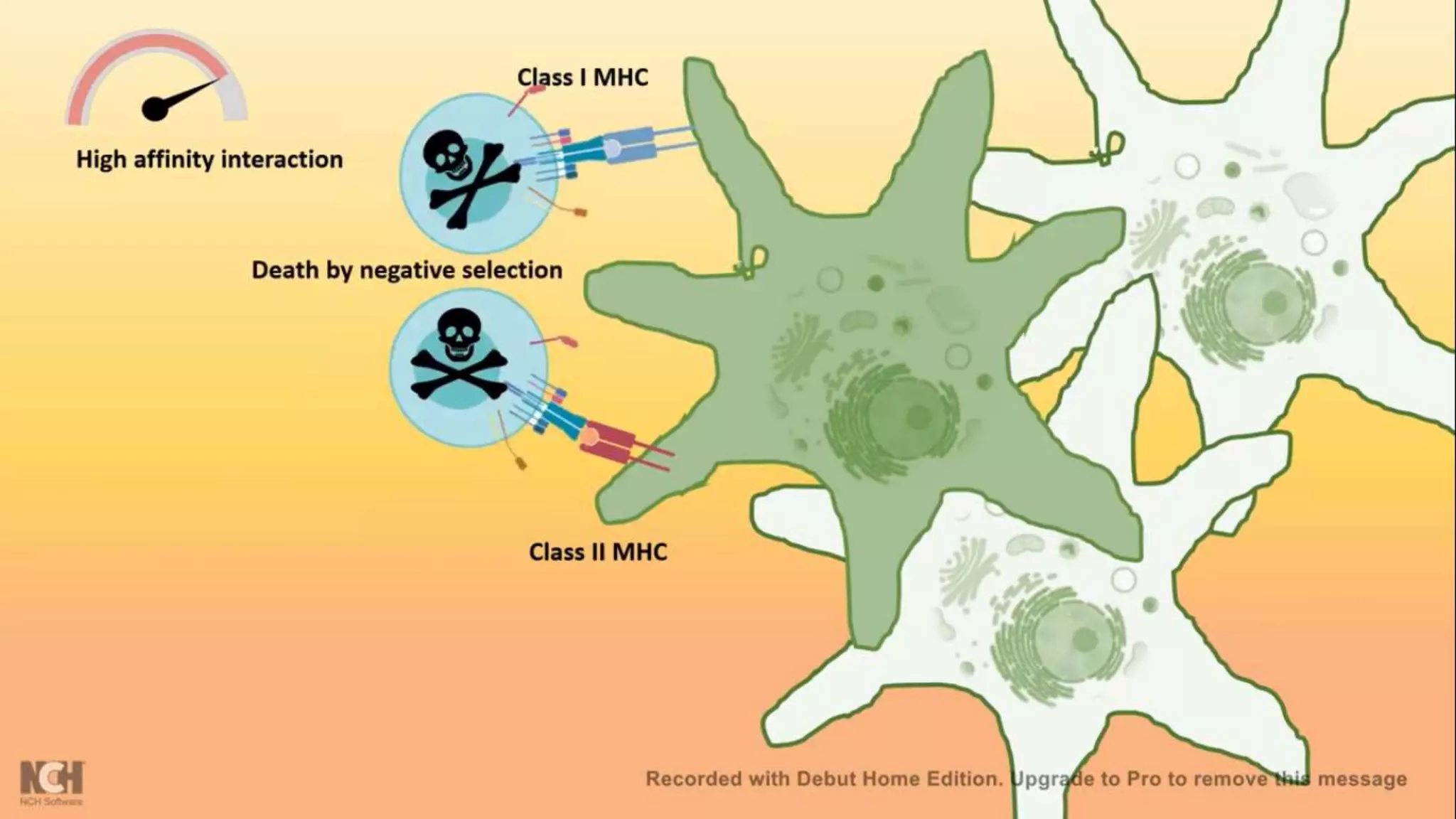
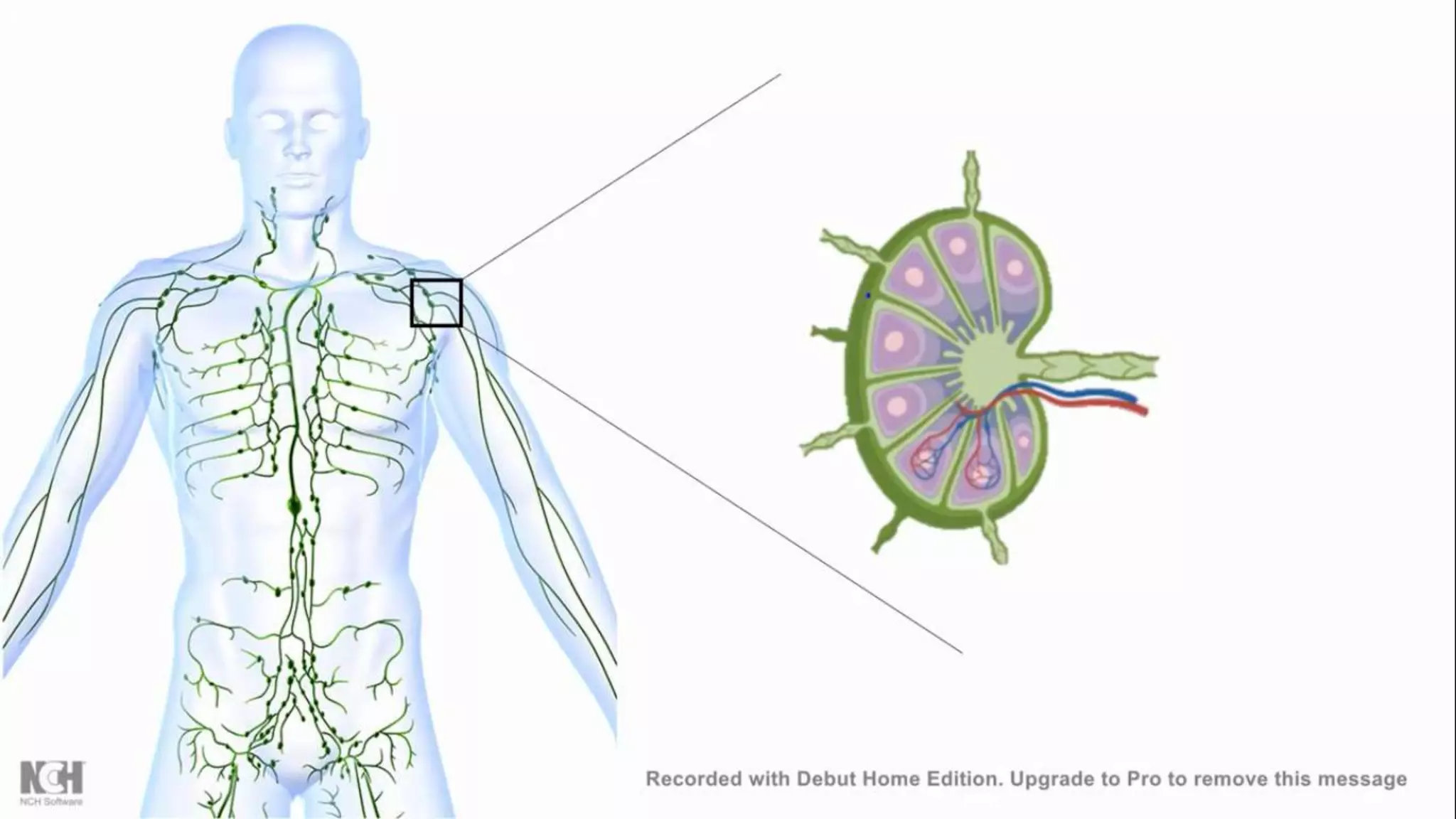
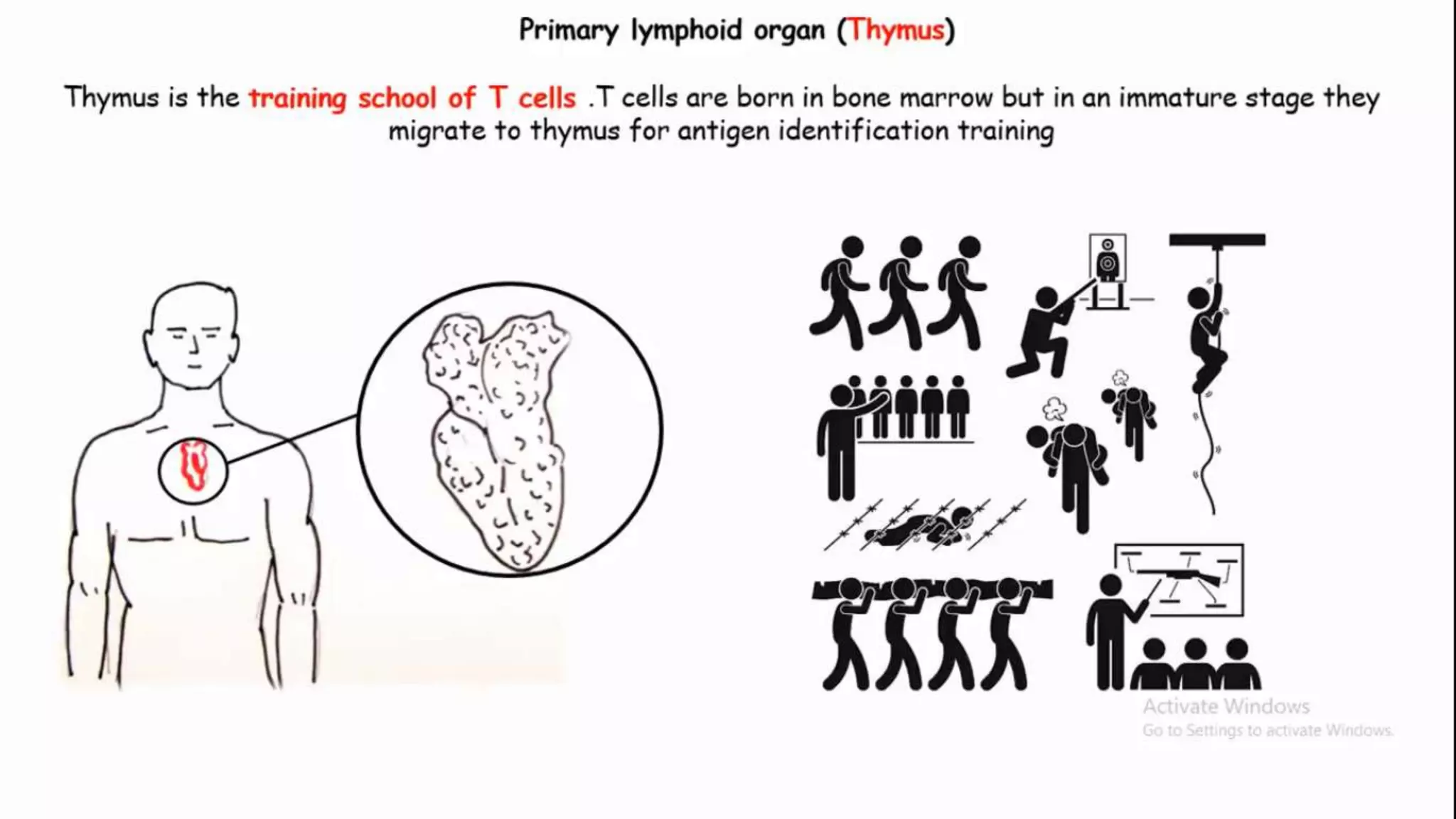
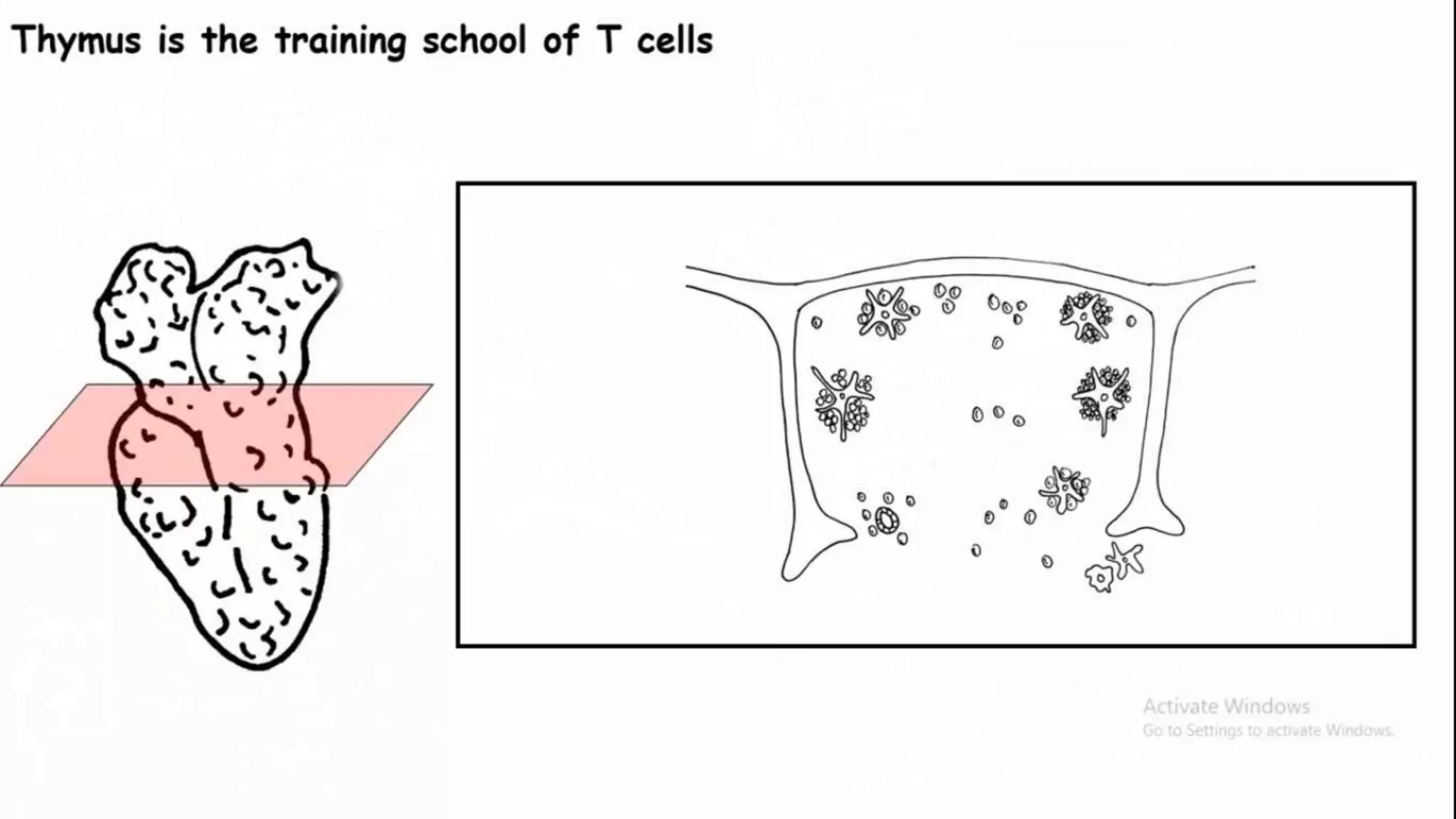
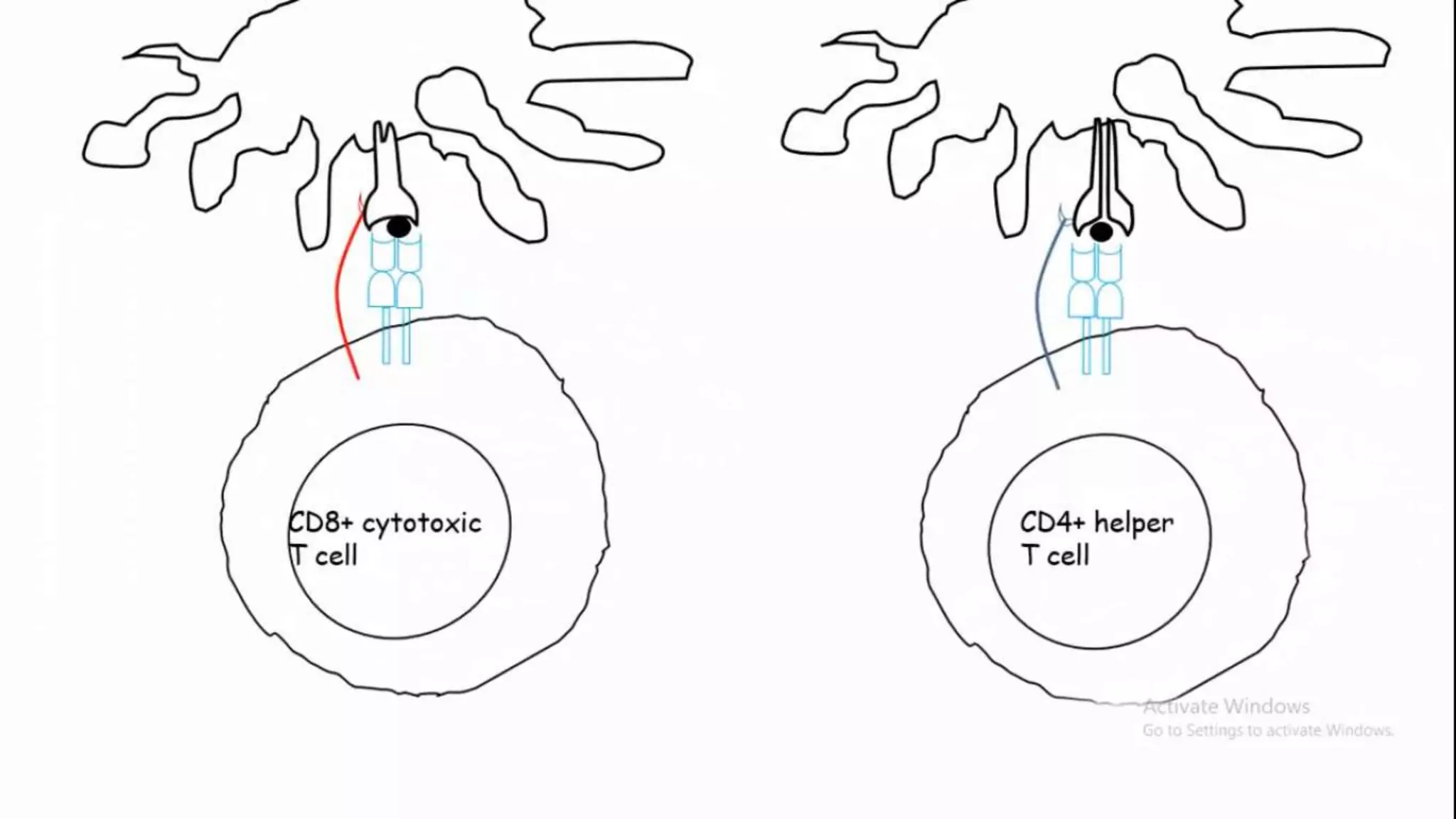
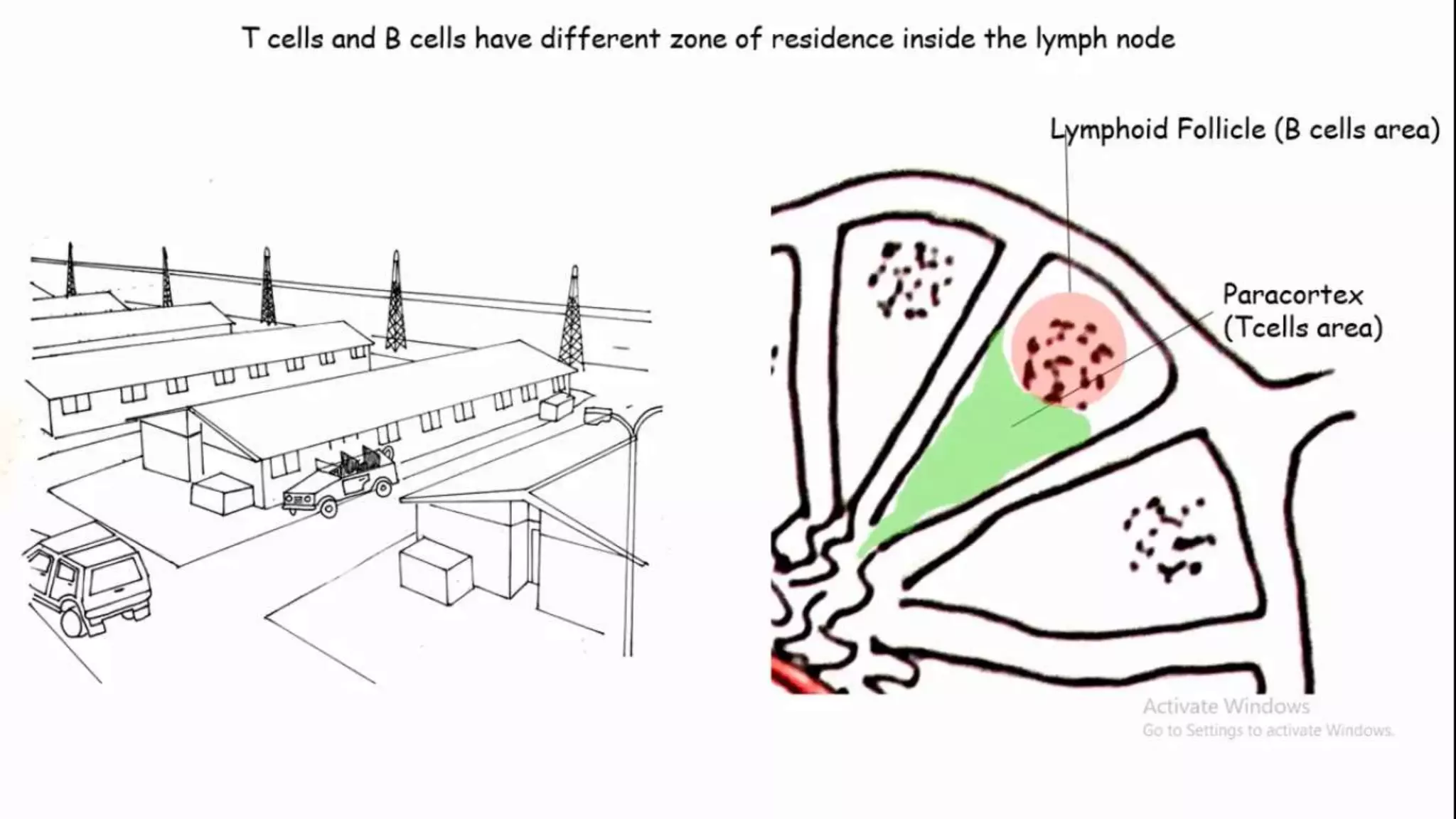
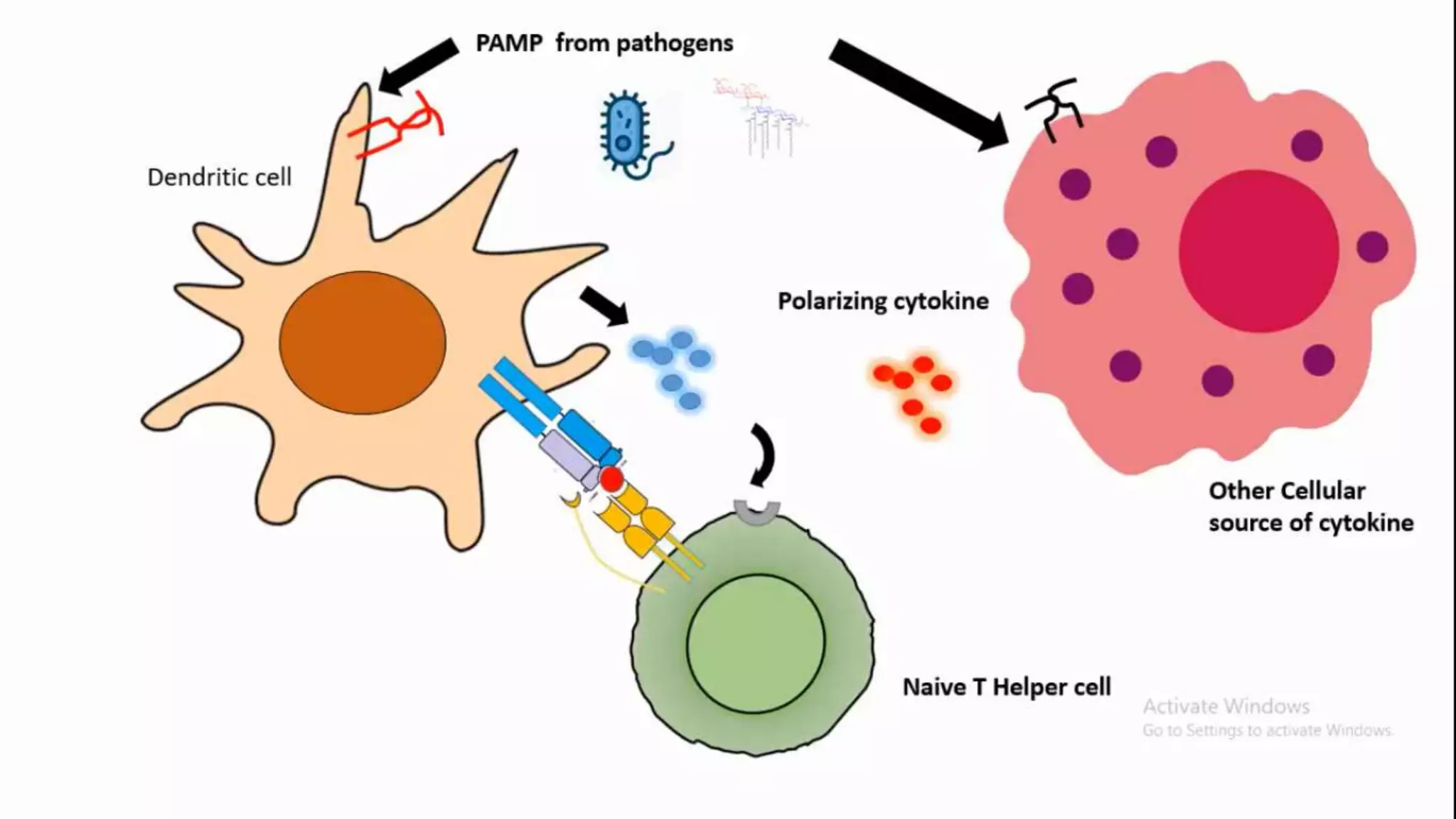
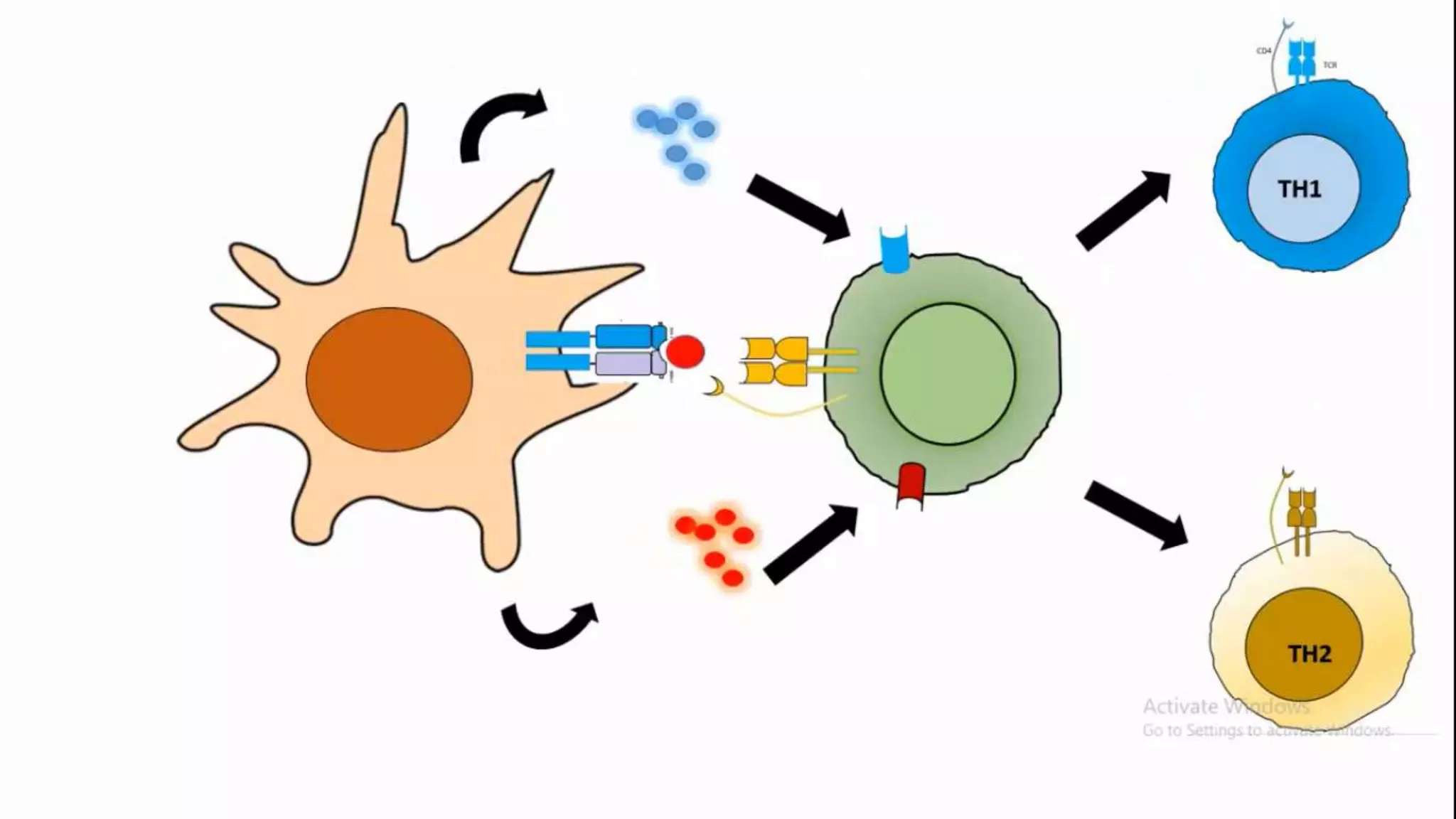
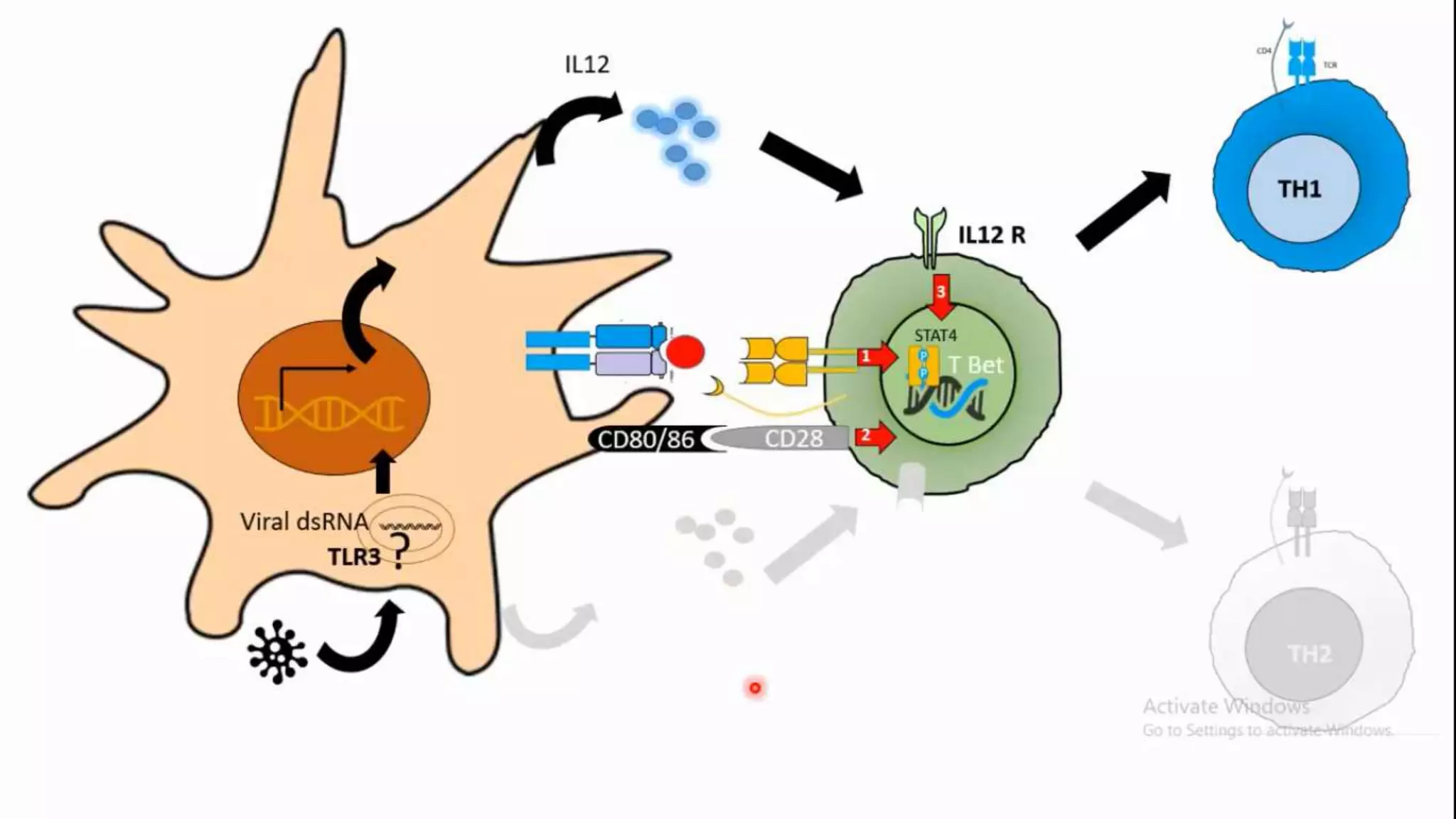
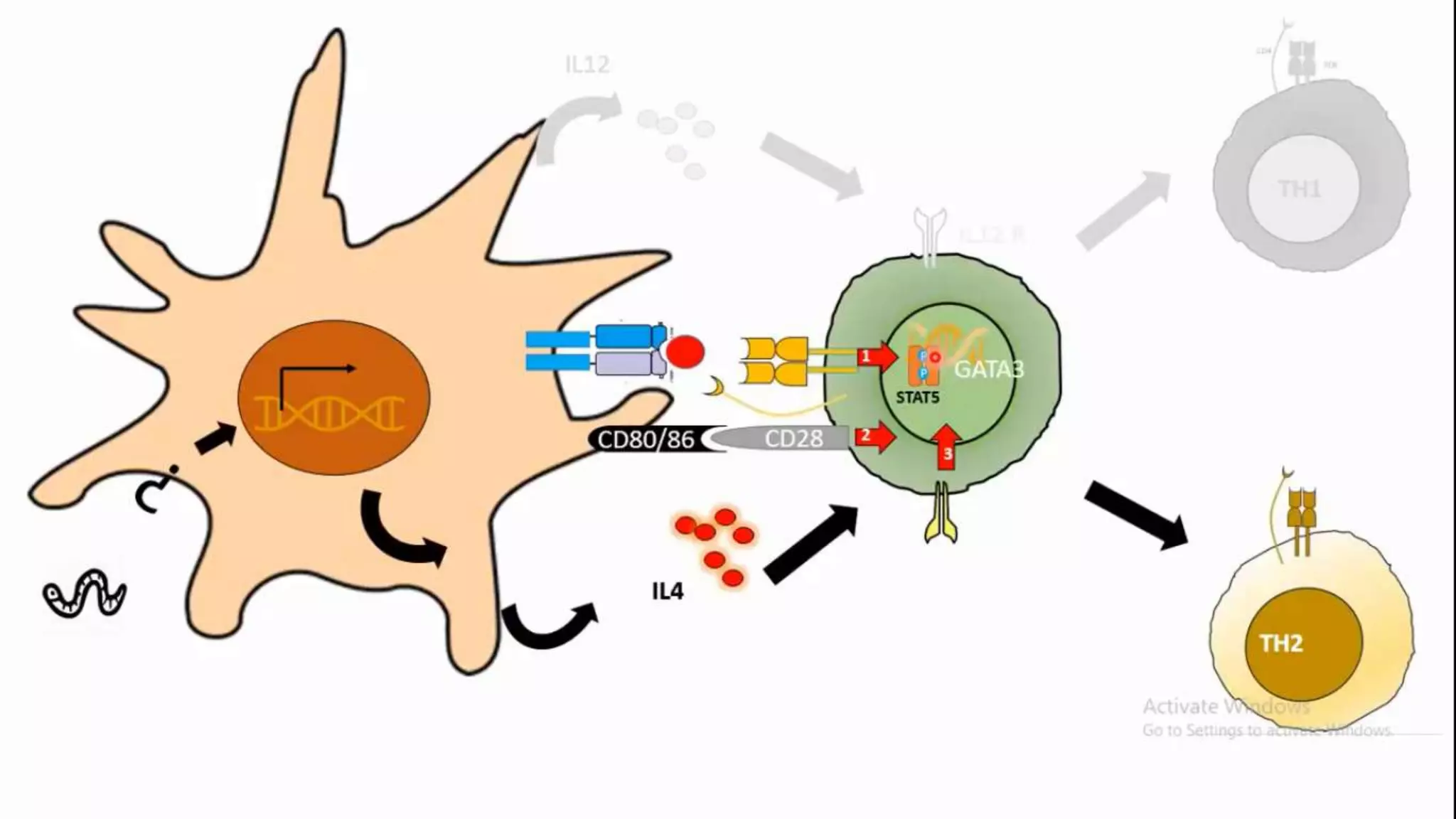
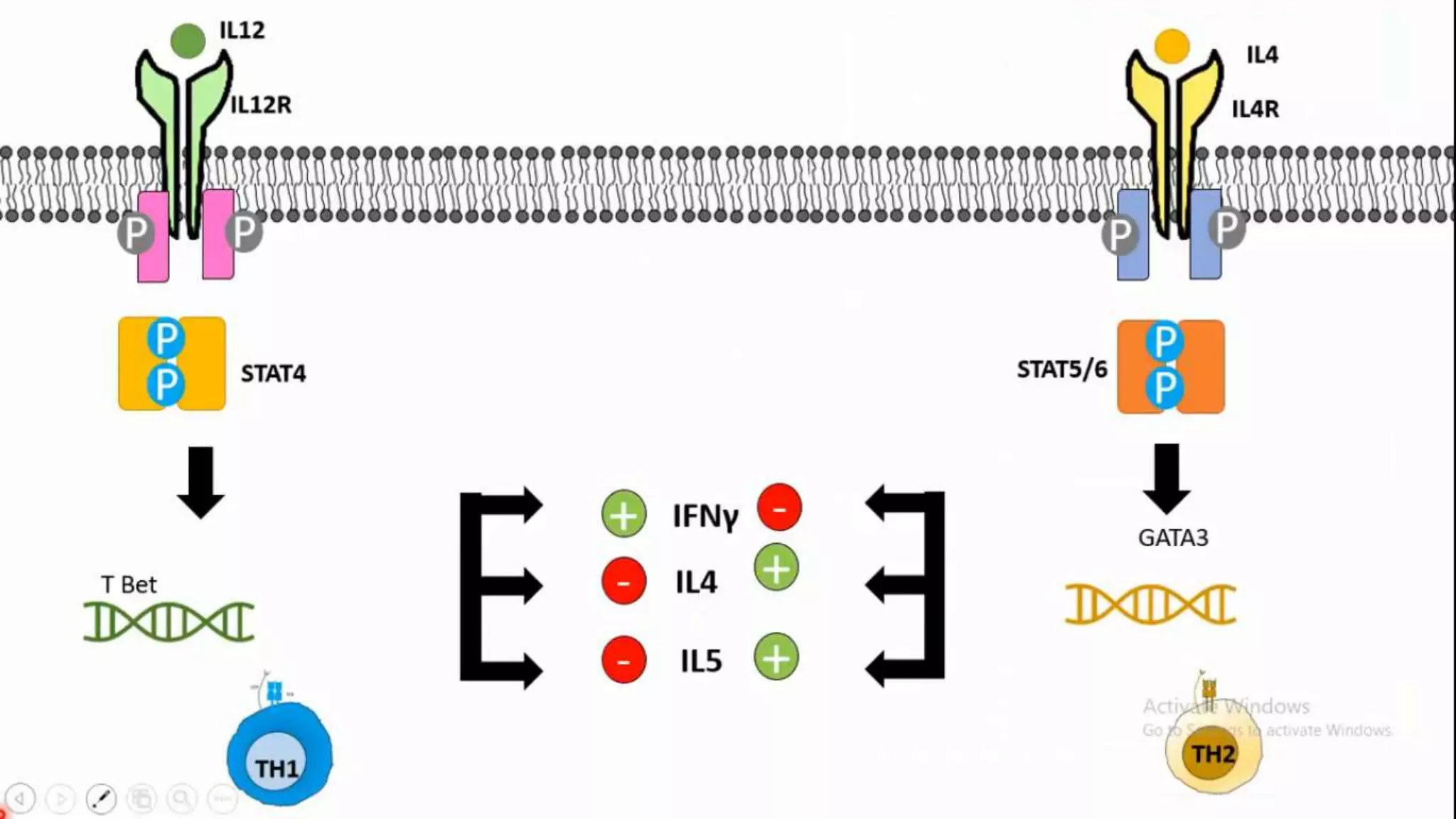
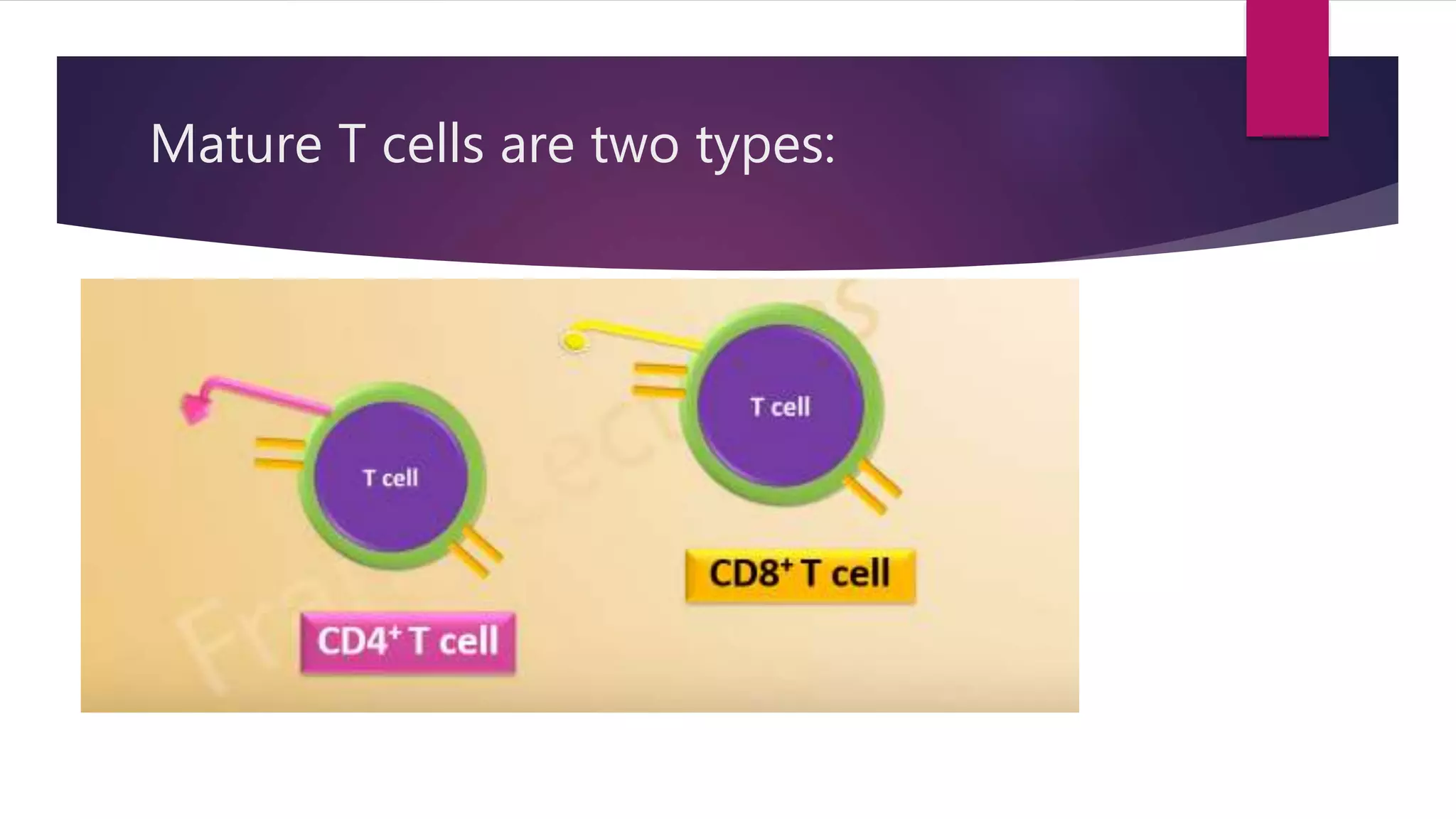
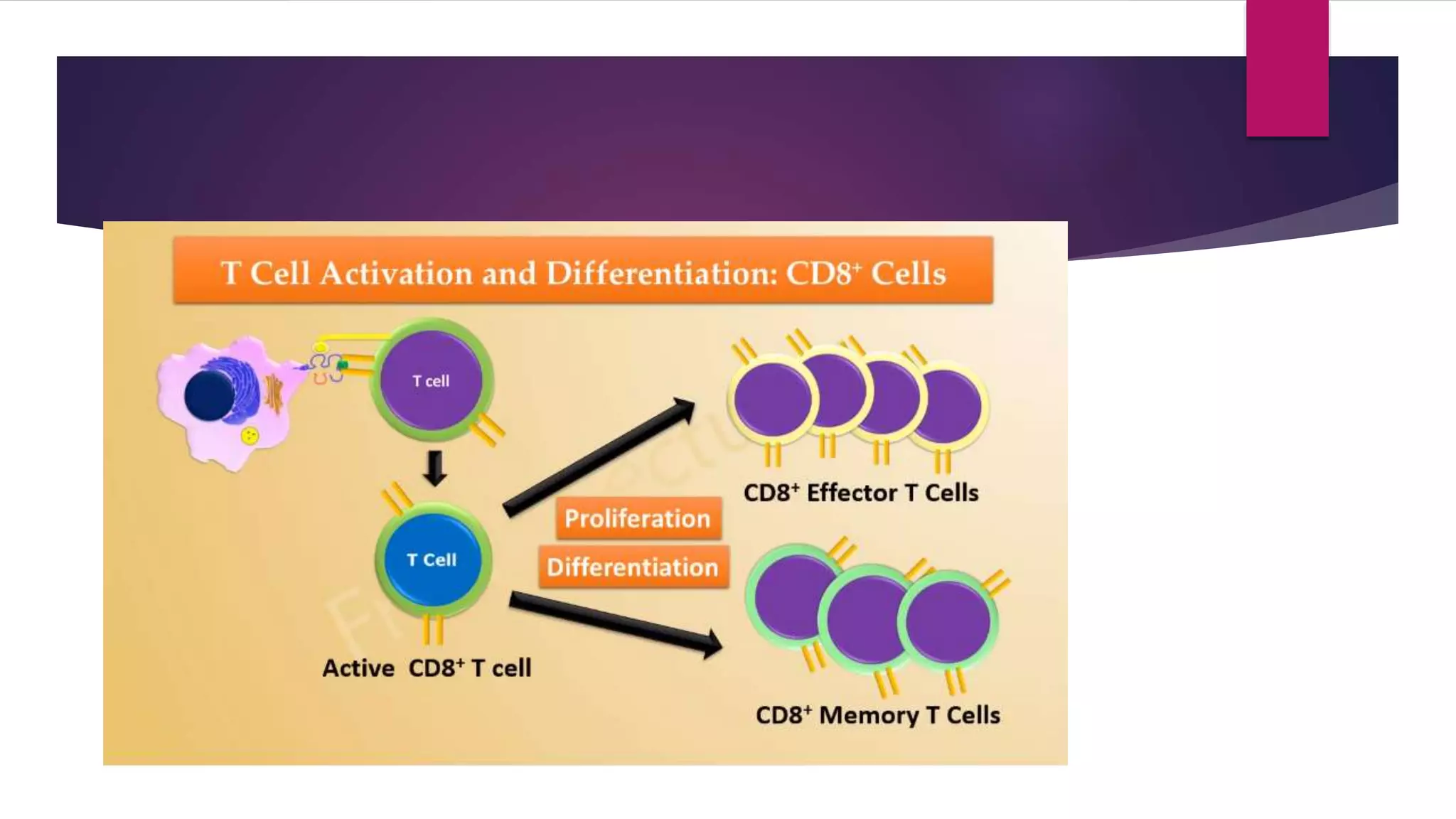
This document summarizes T cells and their activation process. It describes how T cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow then migrate to the thymus to mature. The main types of mature T cells are helper CD4+ T cells and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. Activation of T cells requires two signals: recognition of antigen by the T cell receptor, and a costimulatory signal such as CD28 binding. When activated, T cells proliferate and secrete cytokines like IL-2 that stimulate immune responses. Memory T cells provide long-lasting immunity upon pathogen reexposure.