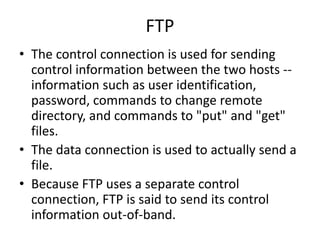
FTP uses two TCP connections - a control connection on port 21 for sending commands and a data connection on port 20 for transferring files. The control connection maintains state about the user and session and is used to open and close the data connection for individual file transfers. Common FTP commands are used to login with username and password, list directory contents, and get/put files between hosts.