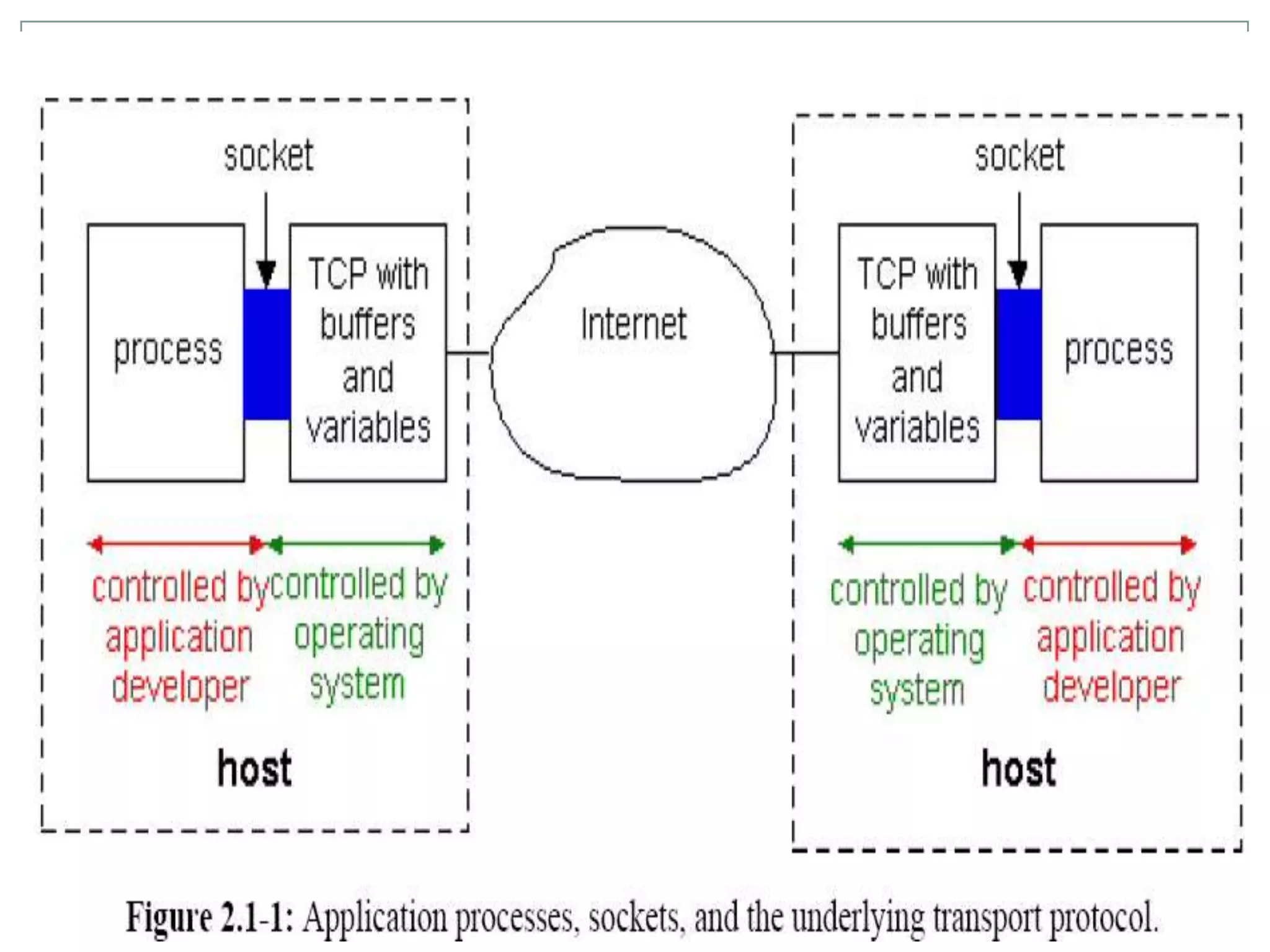
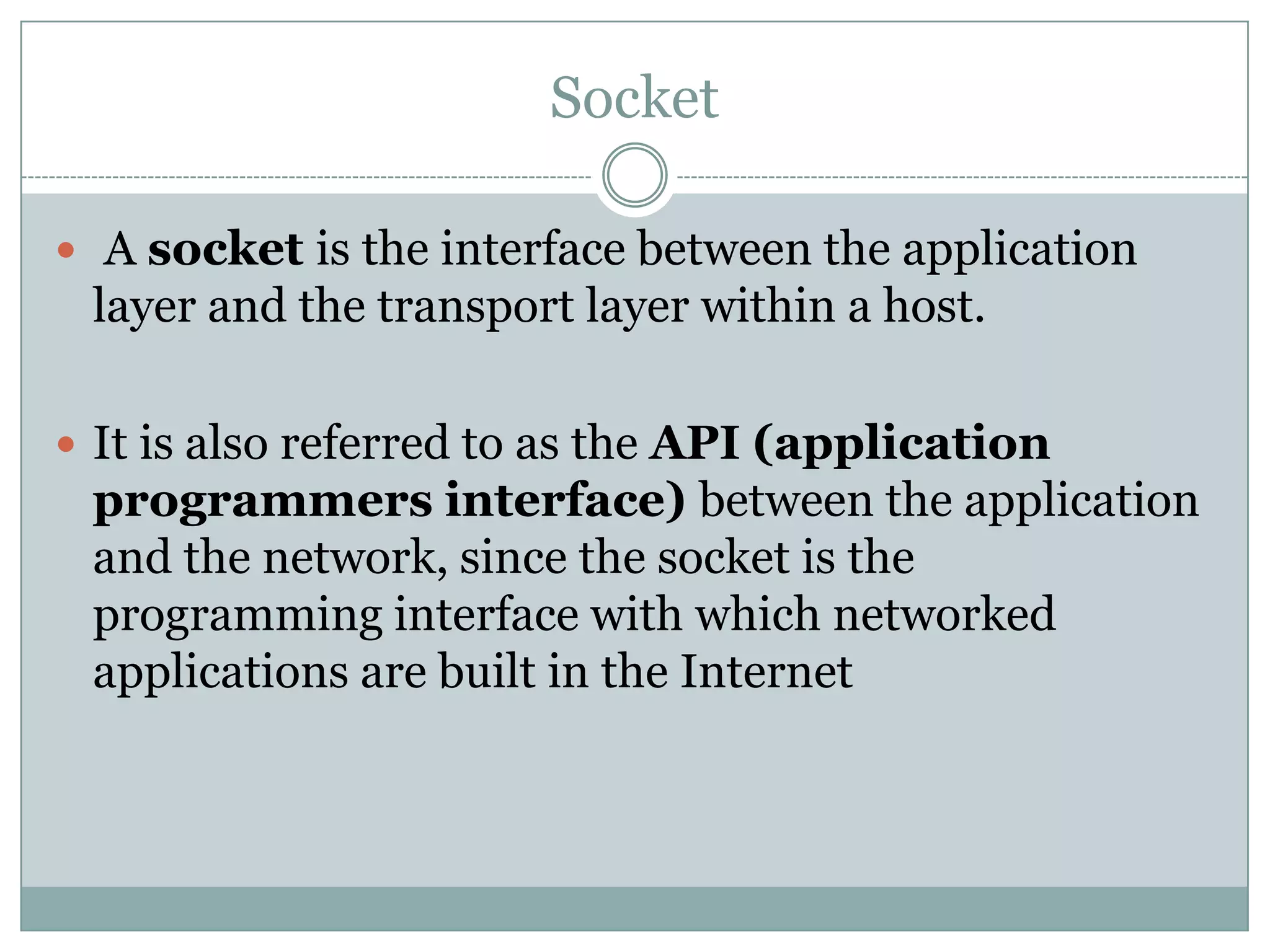
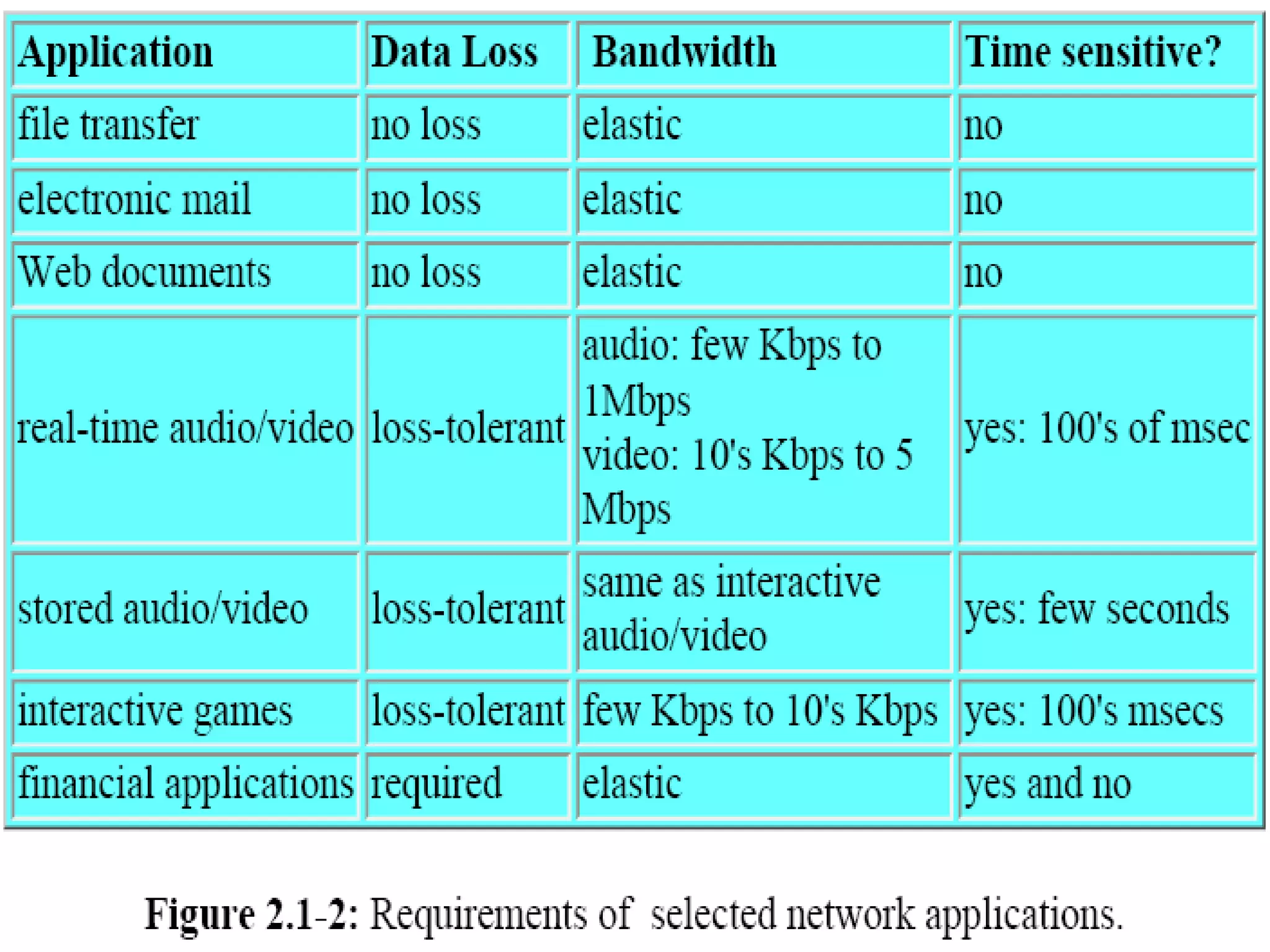
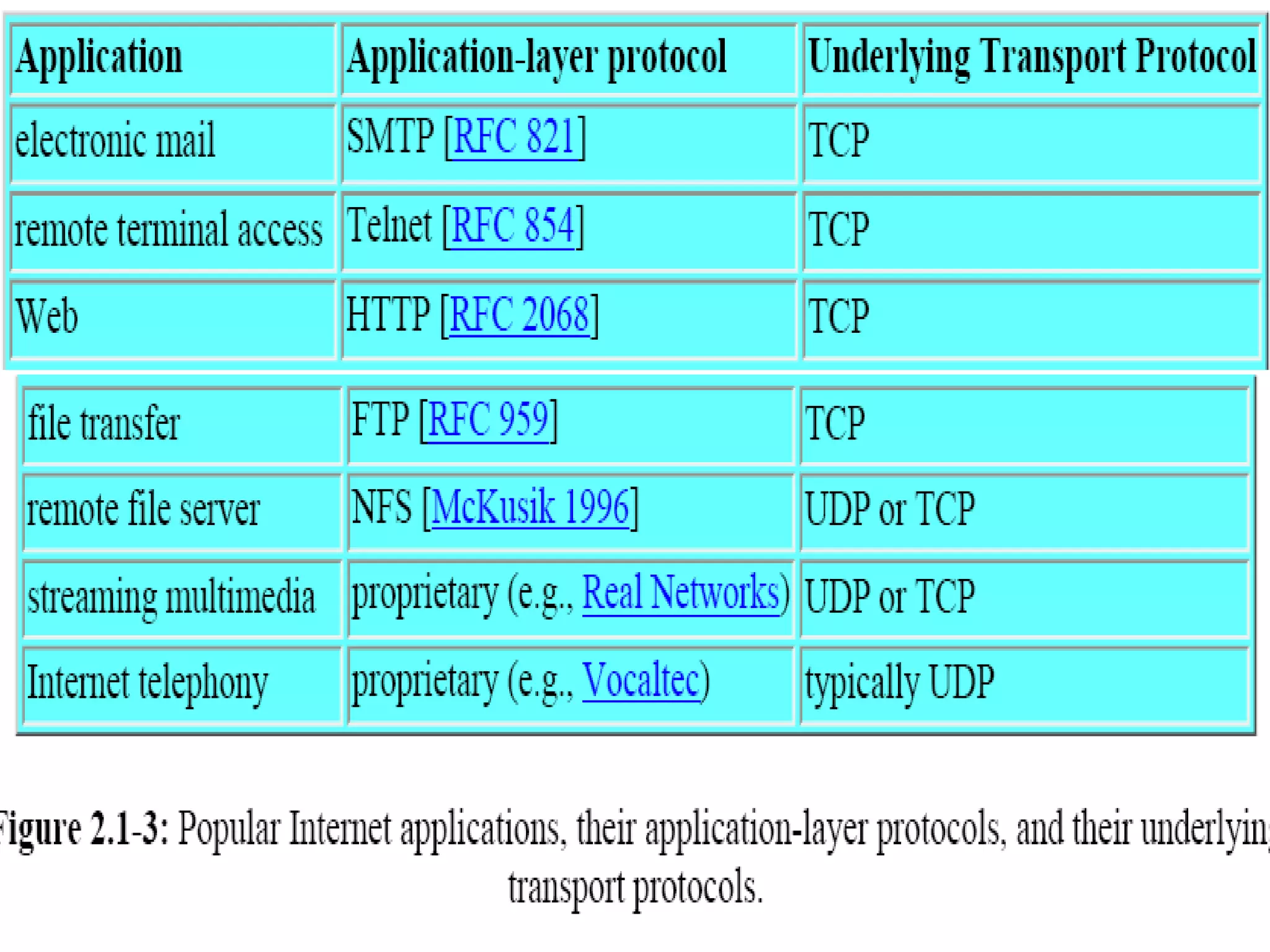
This document discusses application layer protocols and components of web applications. It explains that application layer protocols define how processes running on different systems communicate by exchanging messages. A key application layer protocol is HTTP, which specifies how browsers and web servers exchange request and response messages. The document also describes how processes are addressed to allow communication, including using IP addresses and port numbers. User agents like web browsers interface between users and the application layer.