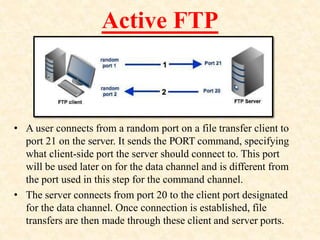
Protocols define rules for formatting and transmitting data across networks. Common protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, and SMTP. IP is the core Internet protocol that handles packet routing. TCP provides reliable data transmission and reassembles packets. HTTP is used for web pages, FTP for file transfer, and SMTP for email.