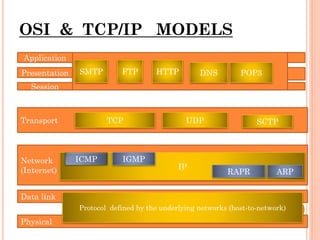
The document describes the TCP/IP model and its layers:
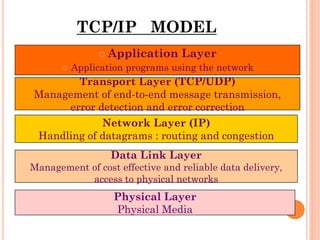
1. The application layer contains common protocols like FTP, SMTP, HTTP, and DNS.
2. The transport layer contains TCP and UDP which manage end-to-end message transmission and error handling.
3. The network layer is IP which handles routing and congestion of data packets.
4. The lower layers include the data link layer which manages reliable data delivery to physical networks, and the physical layer which defines the physical media.