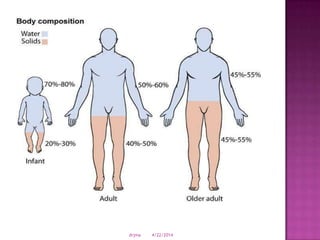
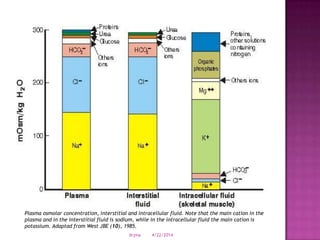
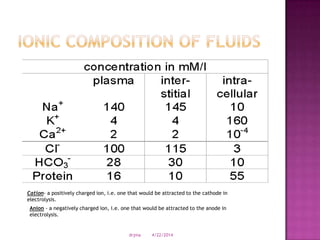
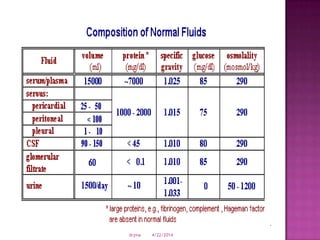
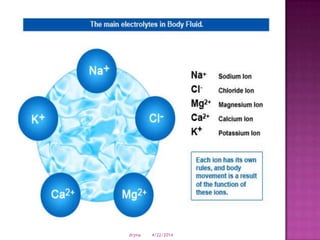
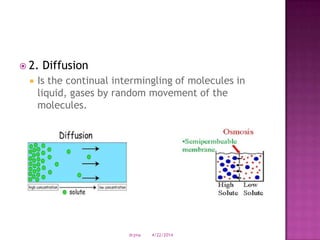
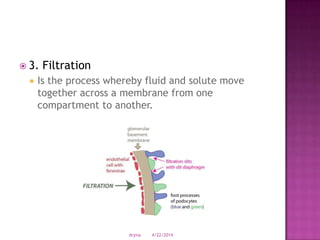
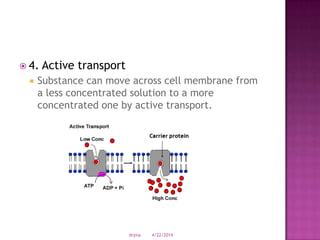
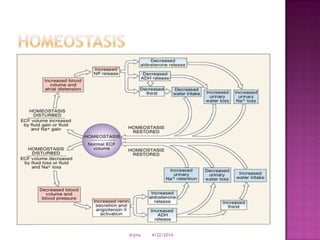
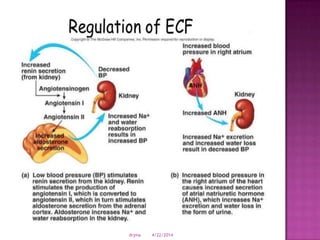
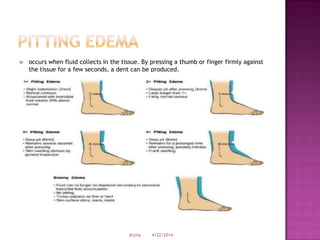
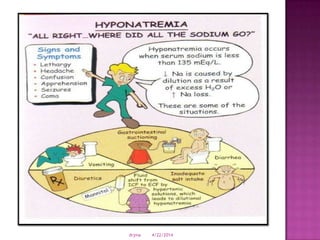
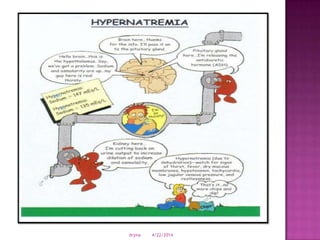
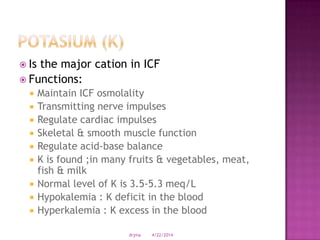
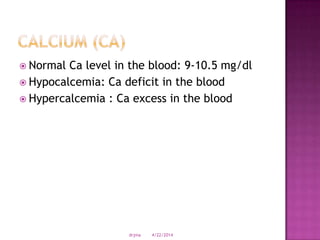
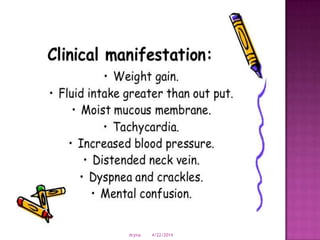
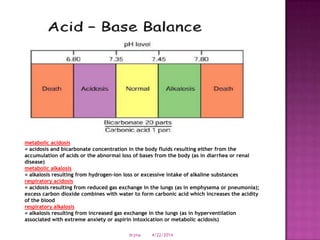
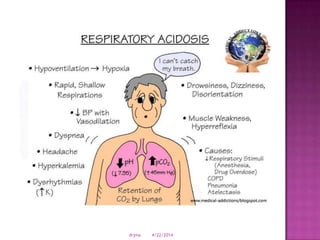
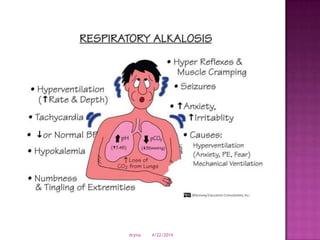
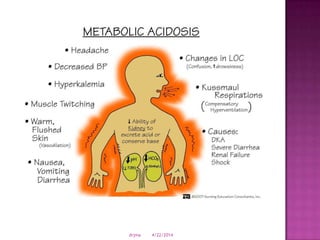
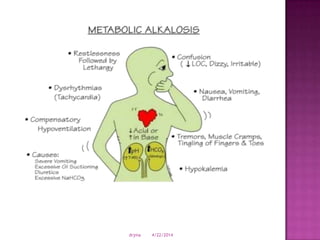
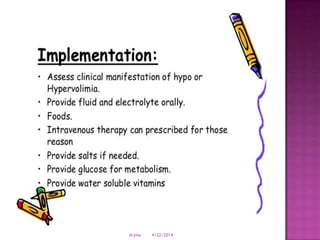
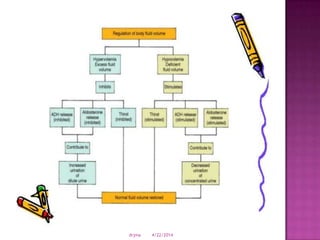
This document discusses body fluids and electrolyte balance. It begins by outlining learning objectives related to body fluids, electrolytes, and fluid and electrolyte imbalances. It then provides details on the composition and functions of body fluids, the fluid compartments of the body, key electrolytes like sodium, potassium and calcium, factors that influence fluid balance, common fluid and electrolyte imbalances, and nursing interventions.