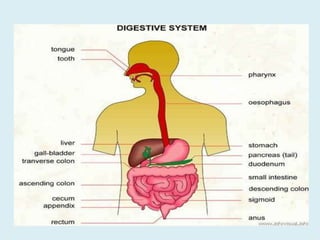
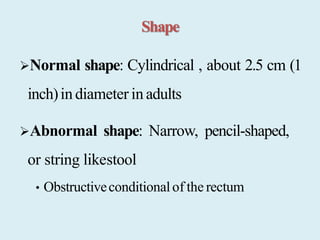
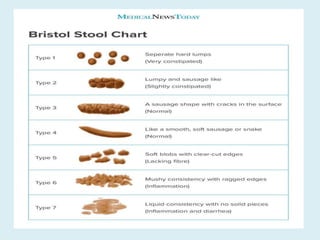
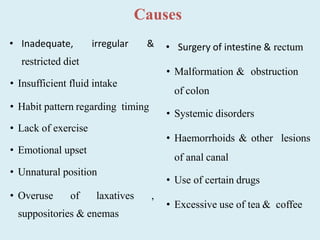
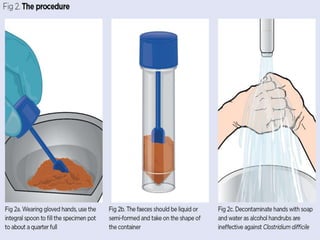
The document provides information on the physiology of bowel elimination or defecation. It discusses the normal process of defecation including the role of muscles in moving fecal material through the digestive tract. It describes factors that influence defecation frequency and the signals that stimulate the urge to defecate. The document also covers the composition of feces, normal and abnormal characteristics of feces, and factors that can affect bowel elimination such as diet, medications and medical conditions.