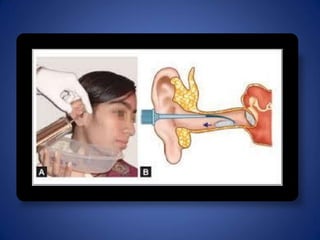
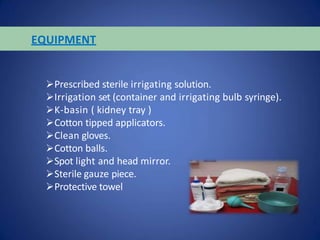
Ear irrigation is used to treat earwax impaction or foreign objects in the ear canal. It involves flushing the ear canal with sterile water or saline to remove debris. Contraindications include a perforated eardrum, ear infection, or foreign objects that may swell with moisture. The procedure positions the patient and inserts a bulb syringe filled with warm sterile solution into the ear canal while visualizing for debris removal. Complications can include ear infection, vertigo, or temporary or permanent hearing loss if not performed carefully.








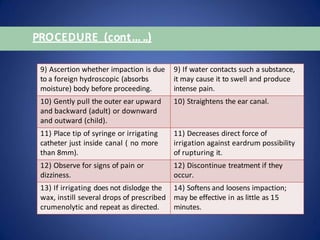
![PROCEDURE (cont… ..)
NURSING ACTION RATIONALE
5) Position protective towels. 5) Water often runs down neck onto
clothing.
PERFORMANCE PHASE
6) Use a cotton applicator to remove
any discharge on outer ear.
6) Prevents carrying discharge deeper
into canal.
7) Place basin close to the
patient’s
head and under the ear.
7) Provides a receptacle to receive
irrigating solution.
8) Test temperature of solution. It
should be comfortable to the inner ear
aspect of wrist area ( approximately
98.6°F [37°C] or body temperature.
8) Solution that are hot or cold are
most uncomfortable and may initiate a
feeling of dizziness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earirrigation-230627082232-d08beb42/85/ear-Irrigation-pptx-10-320.jpg)